|
Low Cocklaw
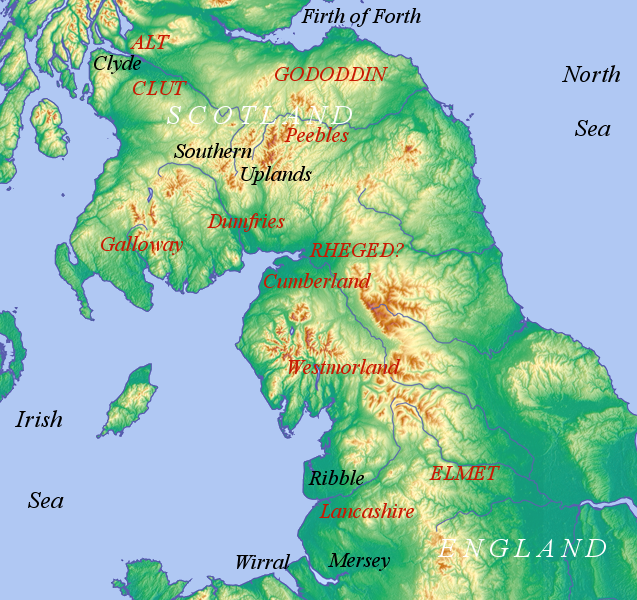
Low Cocklaw is a small hamlet about west of Berwick-upon-Tweed, England. Until the early 1980s it was a working farm but is now entirely residential. It is surrounded by rolling farmland which is dominated by cereal growing. Etymology Allen Mawer rather tentatively identified the early place-name Creklawe~Crokelawe attested in 1296 with Cocklaw. If so, the initial ''cr''- points to a Cumbric origin: Cumbric ''crug'' 'hill', to which was later added Old English Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ... ''hlǣw'' 'hill'. But if this identification is incorrect, ''Cocklaw'' on its own would more obviously be an entirely Old English word, combining ''cocc'' 'cock' and ''hlǣw'' 'hill'.Bethany Fox, 'The P-Celtic Place-Names of North-East England and South-East Scotland', T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berwick-upon-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed (), sometimes known as Berwick-on-Tweed or simply Berwick, is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, and the northernmost town in England. The 2011 United Kingdom census recorded Berwick's population as 12,043. The town is at the mouth of the River Tweed on the east coast, south east of Edinburgh, north of Newcastle upon Tyne, and north of London. Uniquely for England, the town is slightly further north than Denmark's capital Copenhagen and the southern tip of Sweden further east of the North Sea, which Berwick borders. Berwick was founded as an Anglo-Saxon settlement in the Kingdom of Northumbria, which was annexed by England in the 10th century. A civil parish and town council were formed in 2008 comprising the communities of Berwick, Spittal and Tweedmouth. It is the northernmost civil parish in England. The area was for more than 400 years central to historic border wars between the Kingdoms of Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey. It is bordered by land on three sides; by the Scottish Borders region to the north, County Durham and Tyne and Wear to the south, and Cumbria to the west. The fourth side is the North Sea, with a stretch of coastline to the east. A predominantly rural county with a landscape of moorland and farmland, a large area is part of Northumberland National Park. The area has been the site of a number of historic battles with Scotland. Name The name of Northumberland is recorded as ''norð hẏmbra land'' in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, meaning "the land north of the Humber". The name of the kingdom of ''Northumbria'' derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the people south of the Humber Estuary. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berwick-upon-Tweed (UK Parliament Constituency)
Berwick-upon-Tweed () is a parliamentary constituency in Northumberland represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2015 by Anne-Marie Trevelyan, a Conservative. It was a parliamentary borough in the county of Northumberland of the House of Commons of England from 1512 to 1706, then of the House of Commons of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1885. It returned two Members of Parliament (MPs), elected by the bloc vote system. It has been a county constituency since 1885, electing one MP under the first-past-the-post system. Profile The constituency of Berwick-upon-Tweed is in the county of Northumberland. It includes as its northernmost point the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed and stretches south to include the towns of Alnwick and Amble — the Northumberland coast forms its long eastern boundary. Its length is roughly 50 miles (80 km) and its area is 2,310 square kilometres. Predominantly r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlet (place)
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. Its size relative to a Parish (administrative division), parish can depend on the administration and region. A hamlet may be considered to be a smaller settlement or subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. The word and concept of a hamlet has roots in the Anglo-Norman settlement of England, where the old French ' came to apply to small human settlements. Etymology The word comes from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ', corresponding to Old French ', the diminutive of Old French ' meaning a little village. This, in turn, is a diminutive of Old French ', possibly borrowed from (West Germanic languages, West Germanic) Franconian languages. Compare with modern French ', Dutch language, Dutch ', Frisian languages, Frisian ', German ', Old English ' and Modern English ''home''. By country Afghanistan In Afghanistan, the counterpart of the hamlet is the Qila, qala (Dari language, Dari: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen Mawer
Sir Allen Mawer (8 May 1879 − 22 July 1942) was an English philologist. A notable researcher of Viking activity in the British Isles, Mawer is best known as the founder of the English Place-Name Society, and as Provost (education), Provost of University College London from 1929 to 1942. Early life Allen Mawer was born at Bow, London, on 8 May 1879. He was born the second child and eldest son of five children, to George Henry Mawer of South Hackney and Clara Isabella Allen. His father was a commercial traveller in fancy trimmings and secretary of the Country Towns' Mission. Mawer's parents were of strong religious feeling who valued education. Through them, he acquired an abiding love for literature and history, and early knowledge of Ancient Greek, Greek and Latin. Education Mawer entered Coopers' Company and Coborn School, Coopers' Company Grammar School at the age of ten, where he won a scholarship at the end of his first term. In 1897 he sat as an external candidate for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the semi-independent Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British House Of Commons
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 members known as members of Parliament (MPs). MPs are elected to represent constituencies by the first-past-the-post system and hold their seats until Parliament is dissolved. The House of Commons of England started to evolve in the 13th and 14th centuries. In 1707 it became the House of Commons of Great Britain after the political union with Scotland, and from 1800 it also became the House of Commons for Ireland after the political union of Great Britain and Ireland. In 1922, the body became the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland after the independence of the Irish Free State. Under the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949, the Lords' power to reject legislation was reduced to a delaying power. The gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Northumberland (UK Parliament Constituency)
North Northumberland (formally the "Northern Division of Northumberland") was a county constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was represented by two Members of Parliament (MPs), elected by the bloc vote system. The area was created by the Great Reform Act of 1832 by the splitting of Northumberland constituency into Northern and Southern divisions. It was abolished by the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885, when Northumberland was divided into four single member divisions: Berwick-upon-Tweed, Hexham, Tyneside and Wansbeck. Boundaries 1832–1885: The Wards of Bamborough, Coquetdale, Glendale and Morpeth, and the Berwick Bounds. Members of Parliament *''Constituency created'' ( 1832) Elections Elections in the 1830s Grey was appointed as Secretary at War, requiring a by-election. Elections in the 1840s Elections in the 1850s Percy was appointed a Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Northumberland
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |