|
Louis Émile Javal
Louis Émile Javal (May 5, 1839 – January 20, 1907) was a French ophthalmologist born in Paris. Javal is remembered for his studies of physiological optics and his work involving a disorder known as strabismus. Early life He was born in Paris to Léopold Javal (1804-1872) and Auguste Javal (née von Lämel; 1817-1893). Academic background Originally trained as a civil engineer, he switched to the medical profession, receiving his degree from the University of Paris in 1868. Following graduation, he traveled to Berlin, where he studied under Albrecht von Graefe (1828-1870). During the Franco-Prussian War he served as a medical officer. In 1878 he opened an ophthalmological laboratory at the Sorbonne and was its director until 1900. Like his father politically active, he represented the district of Yonne in the French Parliament from 1884 to 1889. Contributions in ophthalmology With his student Hjalmar August Schiøtz (1850-1927), he constructed an early keratom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often occurs at birth and can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear; however, it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular curvature of the cornea and protective reaction changes in the lens of the eye, called lens astigmatism, that has the same mechanism as spasm of accomodation. Diagnosis is by an eye examination called autorefractor keratometry (objective, allows to see lens and cornea components of astigmatism) and subjective refraction, but subjective methods are almost always inaccurate, if lens astigmatism is not fully removed first with a week of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazare Weiller
Lazare Weiller (20 July 1858 – 12 August 1928) was a French engineer, industrialist and politician. He was born in Alsace and received a technical education in England and in his cousin's copper factory in Angoulême. He was very interested in the physical sciences, particularly the use of electricity to transmit sound and images. He proposed a system for scanning, transmitting and displaying images that was the basis for experiments by various television pioneers. He sponsored early aviation experiments by the Wright brothers. He founded several companies including a telephone wire manufacturer, a taximeter manufacturer, the first Parisian cab company to use automobiles, an aircraft company and a wireless telegraphy company. He was a deputy during World War I (1914–18) and then a senator until his death. Life Lazare Weiller was born in Sélestat, Bas-Rhin, on 20 July 1858. His parents were Leopold Weiller (born 1807) and Reine Ducasse/Duckes (born 1819). He came from a Jewis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The most common cause is infection by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Reform
A reform movement or reformism is a type of social movement that aims to bring a social or also a political system closer to the community's ideal. A reform movement is distinguished from more radical social movements such as revolutionary movements which reject those old ideals, in that the ideas are often grounded in liberalism, although they may be rooted in socialist (specifically, social democratic) or religious concepts. Some rely on personal transformation; others rely on small collectives, such as Mahatma Gandhi's spinning wheel and the self-sustaining village economy, as a mode of social change. Reactionary movements, which can arise against any of these, attempt to put things back the way they were before any successes the new reform movement(s) enjoyed, or to prevent any such successes. United Kingdom After two decades of intensely conservative rule, the logjam broke in the late 1820s with the repeal of obsolete restrictions on Nonconformists, followed by the dram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
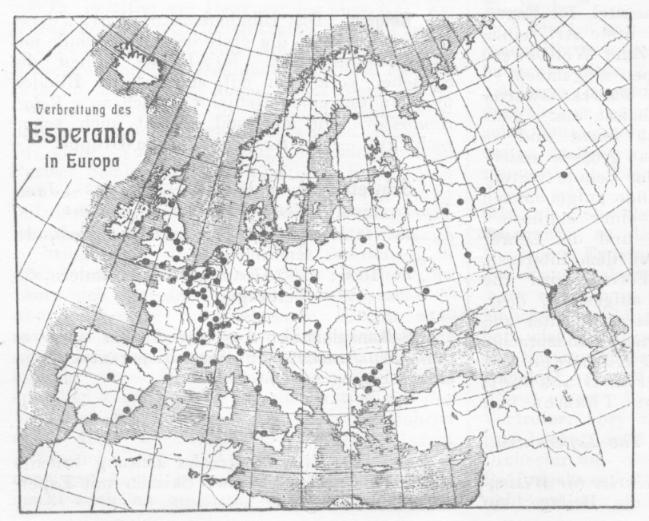
Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwik Łazarz Zamenhof
L. L. Zamenhof (15 December 185914 April 1917) was an ophthalmologist who lived for most of his life in Warsaw. He is best known as the creator of Esperanto, the most widely used constructed international auxiliary language. Zamenhof first developed the Esperanto language in 1873 while still in school. He grew up fascinated by the idea of a world without war and believed that this could happen with the help of a new international auxiliary language. The language would be a tool to gather people together through neutral, fair, equitable communication. He successfully formed a community that continues today despite the World Wars of the 20th century, attempts to reform the language, and more modern IALs (the only other language like it at the time was Volapük). Additionally, Esperanto has developed like other languages: through the interaction and creativity of its users. In light of his achievements, and his support of intercultural dialogue, UNESCO selected Zamenhof as one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment– visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks including reading and walking. Low vision is a functional definition of visual impairment that is chronic, uncorrectable with treatment or correctable lenses, and impacts daily living. As such low vision can be used as a disability metric and varies based on an individual's experience, environmental demands, accommodations, and access to services. The American Academy of Ophthalmology defines visual impairment as the best-corrected visual acuity of less than 20/40 in the better eye, and the World Health Organization defines it as a presenting acuity of less than 6/12 in the better eye. The term blindness is used for complete or nearly complete vision loss. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromia
Heterochromia is a variation in coloration. The term is most often used to describe color differences of the iris, but can also be applied to color variation of hair or skin. Heterochromia is determined by the production, delivery, and concentration of melanin (a pigment). It may be inherited, or caused by genetic mosaicism, chimerism, disease, or injury. It occurs in humans and certain breeds of domesticated animals. Heterochromia of the eye is called heterochromia iridum or heterochromia iridis. It can be complete or sectoral. In complete heterochromia, one iris is a different color from the other. In sectoral heterochromia, part of one iris is a different color from its remainder. In central heterochromia, there is a ring around the pupil or possibly spikes of different colors radiating from the pupil. Though multiple causes have been posited, the scientific consensus is that a lack of genetic diversity is the primary reason behind heterochromia, at least in domestic anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naked-eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnifying, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microscope, or eye protection. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lenses is still considered "naked". In astronomy, the naked eye may be used to observe celestial events and objects visible without equipment, such as conjunctions, passing comets, meteor showers, and the brightest asteroids, including 4 Vesta. Sky lore and various tests demonstrate an impressive variety of phenomena visible to the unaided eye. Basic properties Some basic properties of the human eye are: *Quick autofocus from distances of 25 cm (young people) to 50 cm (most people 50 years and older) to infinity. *Angular resolution: about 1 arcminute, approximately 0.017° or 0.0003 radians, which corresponds to 0.3 m at a 1 km distance. *Field of view (FOV): simultaneous visual perception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixation (visual)
Fixation or visual fixation is the maintaining of the gaze on a single location. An animal can exhibit visual fixation if it possess a fovea in the anatomy of their eye. The fovea is typically located at the center of the retina and is the point of clearest vision. The species in which fixational eye movement has been verified thus far include humans, primates, cats, rabbits, turtles, salamanders, and owls. Regular eye movement alternates between saccades and visual fixations, the notable exception being in smooth pursuit, controlled by a different neural substrate that appears to have developed for hunting prey. The term "fixation" can either be used to refer to the point in time and space of focus or the act of fixating. Fixation, in the act of fixating, is the point between any two saccades, during which the eyes are relatively stationary and virtually all visual input occurs. In the absence of retinal jitter, a laboratory condition known as retinal stabilization, perceptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)