|
Lopévi
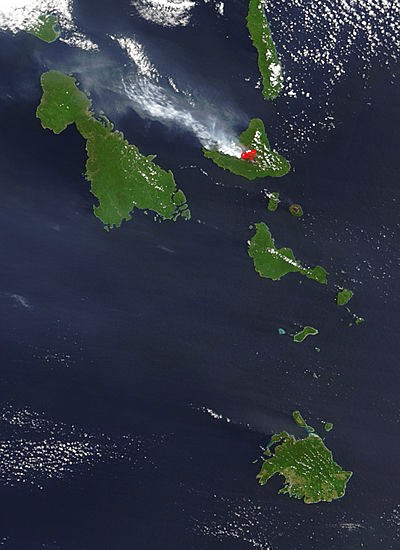
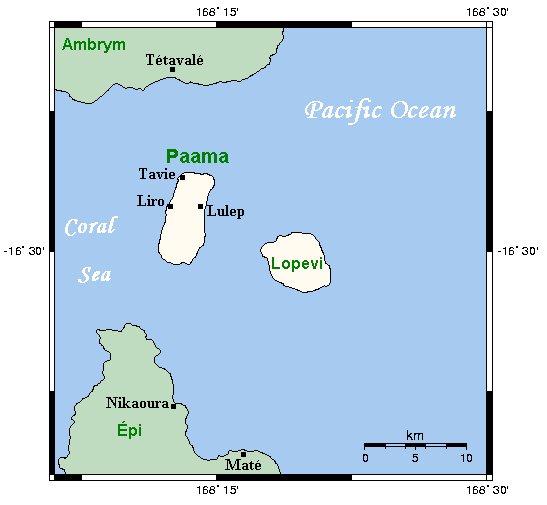
Lopevi (or Lopévi) is an uninhabited island in Malampa Province, Vanuatu. It lies to the southeast of Ambrym and east of Paama. Geography Lopevi consists of the 7-km-wide cone of the active stratovolcano by the same name. It reaches a peak of 1413 m above sea level, the tallest point in central Vanuatu. It has erupted at least 22 times since 1862. The island was formerly inhabited, but in 1960 the population moved to nearby Paama or Epi (island), Epi because of the recurrent danger. Lopevi is on the New Hebrides Plate, where it lies above the subduction, subducted Australian Plate to the west. Because there are no earthquakes between 50 and 200 km below the Earth's surface, it is thought that the subducted plate has fractured, and does not appear between these depths. References External links John Seach site, with photographs Uninhabited islands of Vanuatu Malampa Province Volcanoes of Vanuatu Holocene stratovolcanoes Active volcanoes {{Vanuatu-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epi (island)
Epi (or Épi, Api; formerly known as Tasiko or Volcano Island) is an island in Shefa Province, Vanuatu, at the north end of the Shepherd Islands. The island is long northwest–southeast, and wide, with an area of . Its shoreline measures 130 km. In 1986 it had a population of 3,035 but in 2009 it had increased to 5,200. Geology and Geography The island is of volcanic origin, and its highest point, Mount Pomare, which reaches a height of 833 m above sea level, is a quaternary volcano. It lies 13 km from the more prominent Lopévi volcano. To the east is the largely underwater East Epi volcano. The neighboring islets are Tefala, Namuka, and Lamen. On the northwest edge of the island is the sandy beach Lamen Bay, and the nearby small island of Lamen (pop. 500). The bay has some coral reefs which are the habitat of the dugong. On the west coast is Cape Forland. In the southeast is Valesdir. In the northeast is Drummond Bay, with the Nikaura Marine Prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji. Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island, Espíritu Santo, in 1606. Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it . In the 1880s, France and the United Kingdom claimed parts of the archipelago, and in 1906, they agreed on a framework for jointly managing the archipelago as the New Hebrides through an Anglo-French condominium. An independence movement arose in the 1970s, and the Republic of Vanuatu was fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malampa Province
Malampa is one of the six provinces of Vanuatu, located in the center of the country. It consists of three main islands: Malakula, Ambrym and Paama, and takes its name from the first syllable of their names. It includes a number of other islands – the small islands of Uripiv, Norsup, Rano, Wala, Atchin and Vao off the coast of Malakula, and the volcanic island of Lopevi (currently uninhabited). Also included are the Maskelynes Islands and some more small islands along the south coast of Malakula. Population It has a population of 36,722 (2009 census) - Government of Vanuatu people and an area of 2,779 km2. Its capital is |
Ambrym
Ambrym is a volcanic island in Malampa Province in the archipelago of Vanuatu. Volcanic activity on the island includes lava lakes in two craters near the summit. Etymology Ambrym (also known as ''Ambrin'', ''"ham rim"'' in the Ranon language) was allegedly named by Captain Cook, who is said to have anchored off there in 1774. In fact, his expedition never touched Ambrym. Geography Located near the center of the Vanuatuan archipelago, Ambrym is roughly triangular in shape, about wide. With of surface area, it is the fifth largest island in the country. The summit at the centre of the island is dominated by a desert-like caldera, which covers an area of . With the exception of human settlements, the rest of the island is covered by a dense jungle. Important Bird Area The western part of the island, comprising 17,605 ha of forest, together with gardens around habitation, has been recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paama
Paama (Paama language: VoumCrowley, Terry. (1982). ''The Paamese Language of Vanuatu. Pacific Linguistics, Series B – No. 87''. Canberra: ANU Printing Services.) is a small island in Malampa Province, Vanuatu. The island is about 8 km from north to south and only 5 km or so at its widest point. The island is dominated by hills, rising to a height of around 550 m in the north. Paama lies a short distance south of Ambrym, a little further east of Malakula, about 7 km west of the large active volcano Lopevi (Ulvae, in the vernacular (see Crowley 1982), and a short distance north of the island of Epi (island), Epi. During daylight, all of Paama's neighbouring islands are clearly visible from various locations on the island. Indeed, on a clear night the red glow of Ambrym's twin volcanos can be seen clearly from the black sand beach at Liro. The now uninhabited island of Lopevi dominates the view east from the village of Lulep, on the northeast coast of the is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hebrides Plate
The New Hebrides Plate, sometimes called the Neo-Hebridean Plate, is a minor tectonic plate located in the Pacific Ocean, near the island country of Vanuatu. The plate is bounded on the southwest by the Indo-Australian Plate which is subducting below it. The New Hebrides Trench is seismically active, producing See also * List of earthquakes in Vanuatu Earthquakes in Vanuatu are frequent and are sometimes accompanied by tsunami, though these events are not often destructive. The archipelago, which was formerly known as New Hebrides, lies atop a complex and active plate boundary in the southwester ... References Citations * {{DEFAULTSORT:New Hebrides Plate Tectonic plates Geology of the Pacific Ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Plate
The Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately when India broke away and began moving north. Australia and Antarctica began rifting and completely separated roughly . The Australian plate later fused with the adjacent Indian Plate beneath the Indian Ocean to form a single Indo-Australian Plate. However, recent studies suggest that the two plates have once again split apart and have been separate plates for at least 3 million years and likely longer. The Australian Plate includes the continent of Australia, including Tasmania, as well as portions of New Guinea, New Zealand and the Indian Ocean basin. Scope The continental crust of this plate covers the whole of Australia, the Gulf of Carpentaria, southern New Guinea, the Arafura Sea, the Coral Sea. The continental crust also includes northwestern N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uninhabited Islands Of Vanuatu
The list of uninhabited regions includes a number of places around the globe. The list changes year over year as human beings migrate into formerly uninhabited regions, or migrate out of formerly inhabited regions. List As a group, the list of uninhabited places are called the "nonecumene". This is a special geography term which means the uninhabited area of the world. * Virtually all of the Ocean *Virtually all of Antarctica *Most of The Arctic *Most of Greenland *Most of The Sahara * Antipodes Islands * Ashmore and Cartier Islands * Bajo Nuevo Bank * Baker Island * Ball's Pyramid * Balleny Islands * Big Major Cay * Bouvet Island * Much of the interior of Brazil * Caroline Island * Clipperton Island * The semi-arid regions and deserts of Australia * Devon Island * Much of Eastern Oregon * Elephant Island * Elobey Chico * Ernst Thälmann Island * Much of Fiordland, New Zealand * Goa Island * Gough Island * Hans Island * Harmil * Hashima Island * Hatutu * Heard Island and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Vanuatu
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |