|
Loch Ness Monster Surface
In mathematics, the Loch Ness monster is a surface with infinite genus but only one end. It appeared named this way already in a 1981 article by . The surface can be constructed by starting with a plane (which can be thought of as the surface of Loch Ness) and adding an infinite number of handles (which can be thought of as loops of the Loch Ness monster). See also * Cantor tree surface In dynamical systems, the Cantor tree is an infinite-genus surface homeomorphic to a sphere with a Cantor set removed. The blooming Cantor tree is a Cantor tree with an infinite number of handles added in such a way that every end is a limit of ha ... * Jacob's ladder surface References * * * *{{Citation , last1=Arredondo , first1=John A. , last2=Ramírez-Maluendas , first2= Camilo, title=On the Infinite Loch Ness monster , url=http://cmuc.karlin.mff.cuni.cz/cmuc1704/abs/arredo.htm , doi=10.14712/1213-7243.2015.227 , year=2017 , journal= Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Ness Monster Surface
In mathematics, the Loch Ness monster is a surface with infinite genus but only one end. It appeared named this way already in a 1981 article by . The surface can be constructed by starting with a plane (which can be thought of as the surface of Loch Ness) and adding an infinite number of handles (which can be thought of as loops of the Loch Ness monster). See also * Cantor tree surface In dynamical systems, the Cantor tree is an infinite-genus surface homeomorphic to a sphere with a Cantor set removed. The blooming Cantor tree is a Cantor tree with an infinite number of handles added in such a way that every end is a limit of ha ... * Jacob's ladder surface References * * * *{{Citation , last1=Arredondo , first1=John A. , last2=Ramírez-Maluendas , first2= Camilo, title=On the Infinite Loch Ness monster , url=http://cmuc.karlin.mff.cuni.cz/cmuc1704/abs/arredo.htm , doi=10.14712/1213-7243.2015.227 , year=2017 , journal= Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a neighborhood that is homeomorphic to an open subset of n-dimensional Euclidean space. One-dimensional manifolds include lines and circles, but not lemniscates. Two-dimensional manifolds are also called surfaces. Examples include the plane, the sphere, and the torus, and also the Klein bottle and real projective plane. The concept of a manifold is central to many parts of geometry and modern mathematical physics because it allows complicated structures to be described in terms of well-understood topological properties of simpler spaces. Manifolds naturally arise as solution sets of systems of equations and as graphs of functions. The concept has applications in computer-graphics given the need to associate pictures with coordinates (e.g. CT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus (mathematics)
In mathematics, genus (plural genera) has a few different, but closely related, meanings. Intuitively, the genus is the number of "holes" of a surface. A sphere has genus 0, while a torus has genus 1. Topology Orientable surfaces The genus of a connected, orientable surface is an integer representing the maximum number of cuttings along non-intersecting closed simple curves without rendering the resultant manifold disconnected. It is equal to the number of handles on it. Alternatively, it can be defined in terms of the Euler characteristic ''χ'', via the relationship ''χ'' = 2 − 2''g'' for closed surfaces, where ''g'' is the genus. For surfaces with ''b'' boundary components, the equation reads ''χ'' = 2 − 2''g'' − ''b''. In layman's terms, it's the number of "holes" an object has ("holes" interpreted in the sense of doughnut holes; a hollow sphere would be considered as having zero holes in this sense). A torus has 1 such h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End (topology)
In topology, a branch of mathematics, the ends of a topological space are, roughly speaking, the connected components of the "ideal boundary" of the space. That is, each end represents a topologically distinct way to move to infinity within the space. Adding a point at each end yields a compactification of the original space, known as the end compactification. The notion of an end of a topological space was introduced by . Definition Let ''X'' be a topological space, and suppose that :K_1 \subseteq K_2 \subseteq K_3 \subseteq \cdots is an ascending sequence of compact subsets of ''X'' whose interiors cover ''X''. Then ''X'' has one end for every sequence :U_1 \supseteq U_2 \supseteq U_3 \supseteq \cdots, where each ''U''''n'' is a connected component of ''X'' \ ''K''''n''. The number of ends does not depend on the specific sequence of compact sets; there is a natural bijection between the sets of ends associated with any two such sequences. Using this definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Ness
Loch Ness (; gd, Loch Nis ) is a large freshwater loch in the Scottish Highlands extending for approximately southwest of Inverness. It takes its name from the River Ness, which flows from the northern end. Loch Ness is best known for claimed sightings of the cryptozoological Loch Ness Monster, also known affectionately as "Nessie" ( gd, Niseag). It is one of a series of interconnected, murky bodies of water in Scotland; its water visibility is exceptionally low due to a high peat content in the surrounding soil. The southern end connects to Loch Oich by the River Oich and a section of the Caledonian Canal. The northern end connects to Loch Dochfour via the River Ness, which then ultimately leads to the North Sea via the Moray Firth. Loch Ness is the second-largest Scottish loch by surface area after Loch Lomond at , but due to its great depth it is the largest by volume in the British Isles. Its deepest point is , making it the second deepest loch in Scotland after Loch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Ness Monster
The Loch Ness Monster ( gd, Uilebheist Loch Nis), affectionately known as Nessie, is a creature in Scottish folklore that is said to inhabit Loch Ness in the Scottish Highlands. It is often described as large, long-necked, and with one or more humps protruding from the water. Popular interest and belief in the creature has varied since it was brought to worldwide attention in 1933. Evidence of its existence is anecdotal, with a number of disputed photographs and sonar readings. The scientific community explains alleged sightings of the Loch Ness Monster as hoaxes, wishful thinking, and the misidentification of mundane objects. The pseudoscience and subculture of cryptozoology has placed particular emphasis on the creature. Origin of the name In August 1933, the ''Courier'' published the account of George Spicer's alleged sighting. Public interest skyrocketed, with countless letters being sent in detailing different sightingsR. Binns ''The Loch Ness Mystery Solved'' pp 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantor Tree Surface
In dynamical systems, the Cantor tree is an infinite-genus surface homeomorphic to a sphere with a Cantor set removed. The blooming Cantor tree is a Cantor tree with an infinite number of handles added in such a way that every end is a limit of handles. See also *Jacob's ladder surface *Loch Ness monster surface In mathematics, the Loch Ness monster is a surface with infinite genus but only one end. It appeared named this way already in a 1981 article by . The surface can be constructed by starting with a plane (which can be thought of as the surface ... References * *{{Citation , last1=Walczak , first1=Paweł , title=Dynamics of foliations, groups and pseudogroups , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Tl4WkcHzhIAC , publisher=Birkhäuser Verlag , series=Instytut Matematyczny Polskiej Akademii Nauk. Monografie Matematyczne (New Series) athematics Institute of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Mathematical Monographs (New Series), isbn=978-3-7643-7091-6 , mr=20563 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
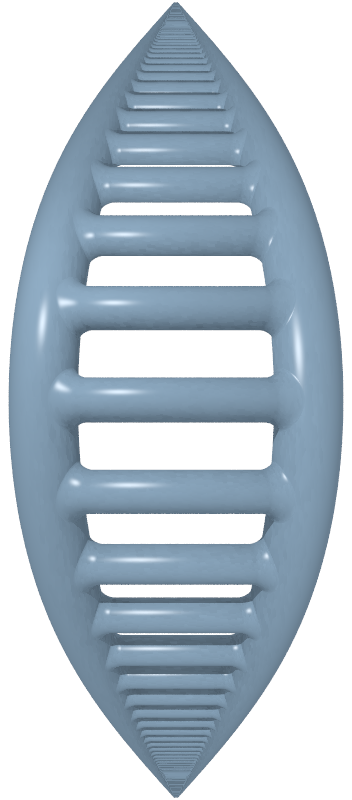
Jacob's Ladder Surface
In mathematics, Jacob's ladder is a surface with infinite genus and two ends. It was named after Jacob's ladder by Étienne , because the surface can be constructed as the boundary of a ladder that is infinitely long in both directions. See also *Cantor tree surface In dynamical systems, the Cantor tree is an infinite-genus surface homeomorphic to a sphere with a Cantor set removed. The blooming Cantor tree is a Cantor tree with an infinite number of handles added in such a way that every end is a limit of ha ... * Loch Ness monster surface References * * Surfaces {{Topology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology (journal)
''Topology'' was a peer-reviewed mathematical journal covering topology and geometry. It was established in 1962 and was published by Elsevier. The last issue of ''Topology'' appeared in 2009. Pricing dispute On 10 August 2006, after months of unsuccessful negotiations with Elsevier about the price policy of library subscriptions, the entire editorial board of the journal handed in their resignation, effective 31 December 2006. Subsequently, two more issues appeared in 2007 with papers that had been accepted before the resignation of the editors. In early January the former editors instructed Elsevier to remove their names from the website of the journal, but Elsevier refused to comply, justifying their decision by saying that the editorial board should remain on the journal until all of the papers accepted during its tenure had been published. In 2007 the former editors of ''Topology'' announced the launch of the ''Journal of Topology'', published by Oxford University Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Mathematics
The ''Annals of Mathematics'' is a mathematical journal published every two months by Princeton University and the Institute for Advanced Study. History The journal was established as ''The Analyst'' in 1874 and with Joel E. Hendricks as the founding editor-in-chief. It was "intended to afford a medium for the presentation and analysis of any and all questions of interest or importance in pure and applied Mathematics, embracing especially all new and interesting discoveries in theoretical and practical astronomy, mechanical philosophy, and engineering". It was published in Des Moines, Iowa, and was the earliest American mathematics journal to be published continuously for more than a year or two. This incarnation of the journal ceased publication after its tenth year, in 1883, giving as an explanation Hendricks' declining health, but Hendricks made arrangements to have it taken over by new management, and it was continued from March 1884 as the ''Annals of Mathematics''. The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |