|
Loch Hourn
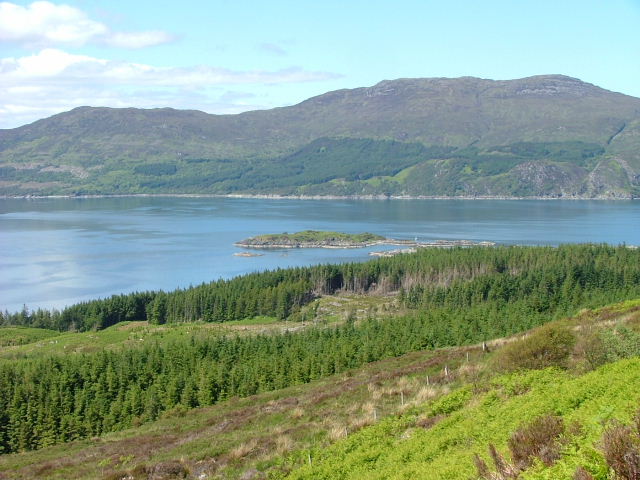
Loch Hourn ( gd, Loch Shubhairne) is a sea loch which separates the peninsulas of Glenelg to the north and Knoydart to the south, on the west coast of Scotland. Geography Loch Hourn runs inland from the Sound of Sleat, opposite the island of Skye, for 22 km (c. 14 miles) to the head of the loch at Kinloch Hourn. At the entrance, its confluence with the Sound of Sleat, it is 5 km (3 miles) wide, becoming less than 2 km wide for much of its length, with successive narrows in the upper reaches and reducing to a 300-metre-wide basin at the head. Sometimes described as the most fjord-like of the sea lochs of northwest Scotland, it is steep-sided, with Beinn Sgritheall to the north and Ladhar Bheinn rising from the southern shore. The sea floor has been shaped by glaciation into five progressively deeper basins with relatively shallow sills; combined with the narrow and sheltered aspect of the loch and the high local rainfall, these result in an unusually wide variation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenelg, Highland
Glenelg ( gd, Glinn Eilg, also ''Gleann Eilg'' is a scattered community area and civil parish in the Lochalsh area of Highland in western Scotland. Despite the local government reorganisation the area is considered by many still to be in Inverness-shire, the boundary with Ross-shire (where the post town of Kyle of Lochalsh is situated) being at the top of Mam Ratagan ("Ratagan Gap" or "pass") the single-track road entry into Glenelg. The main village is called Kirkton of Glenelg and commonly referred to as "Glenelg". There is a smaller hamlet less than to the south by the jetty and skirting Glenelg Bay known as Quarry. There are several other clusters of houses scattered over Glenelg including up Glen Beag and Glen More and on the road leading to the ferry at Kyle Rhea. The parish covers a large area including Knoydart, North Morar and the ferry port of Mallaig. At the 2001 census it had a population of 1,507. The smaller "settlement zone" around Kirkton had a population of 28 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knoydart
Knoydart (Scottish Gaelic: ''Cnòideart'') is a peninsula in Lochaber, Highland, on the west coast of Scotland. Knoydart is sandwiched between Lochs Nevis and Hourn — often translated as "Loch Heaven" (from the Gaelic ''Loch Néimh'') and "Loch Hell" (Gaelic: ''Loch Iutharn'') respectively, although the somewhat poetic nature of these derivations is disputed. Forming the northern part of what is traditionally known as ''na Garbh-Chrìochan'' or "the Rough Bounds", because of its harsh terrain and remoteness, Knoydart is also referred to as "Britain's last wilderness". It is only accessible by boat, or by a 16-mile (26 km) walk through rough country, and the seven miles (11 km) of tarred road are not connected to the UK road system. Knoydart is designated as one of the forty national scenic areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure their protection from inappropriate development. The designated area covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Of Sleat
The Sound of Sleat is a narrow sea channel off the western coast of Scotland. It divides the Sleat peninsula on the south-east side of the Isle of Skye from Morar, Knoydart and Glenelg on the Scottish mainland. The Sound extends in a south-south west direction for from Loch Alsh. It is widest () at the south-west entrance and narrows to just at Kyle Rhea, a narrow channel which connects the Sound through to Loch Alsh. The name is inherited from the peninsula to the north of the Sound, which derives its name from its Scottish Gaelic form ''Sléibhte'' (or ''Slèite''), which in turn comes from Old Norse ''sléttr'' meaning smooth or even. On the mainland side of the Sound are the entrances to Loch Nevis and Loch Hourn. The largest settlement on the mainland side is Mallaig which sits at the entrance to the Sound. On the Skye side of the Sound sit Knock Castle, a former stronghold of the MacDonalds, and the village of Armadale. The Sound is traversed on a regular basis in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
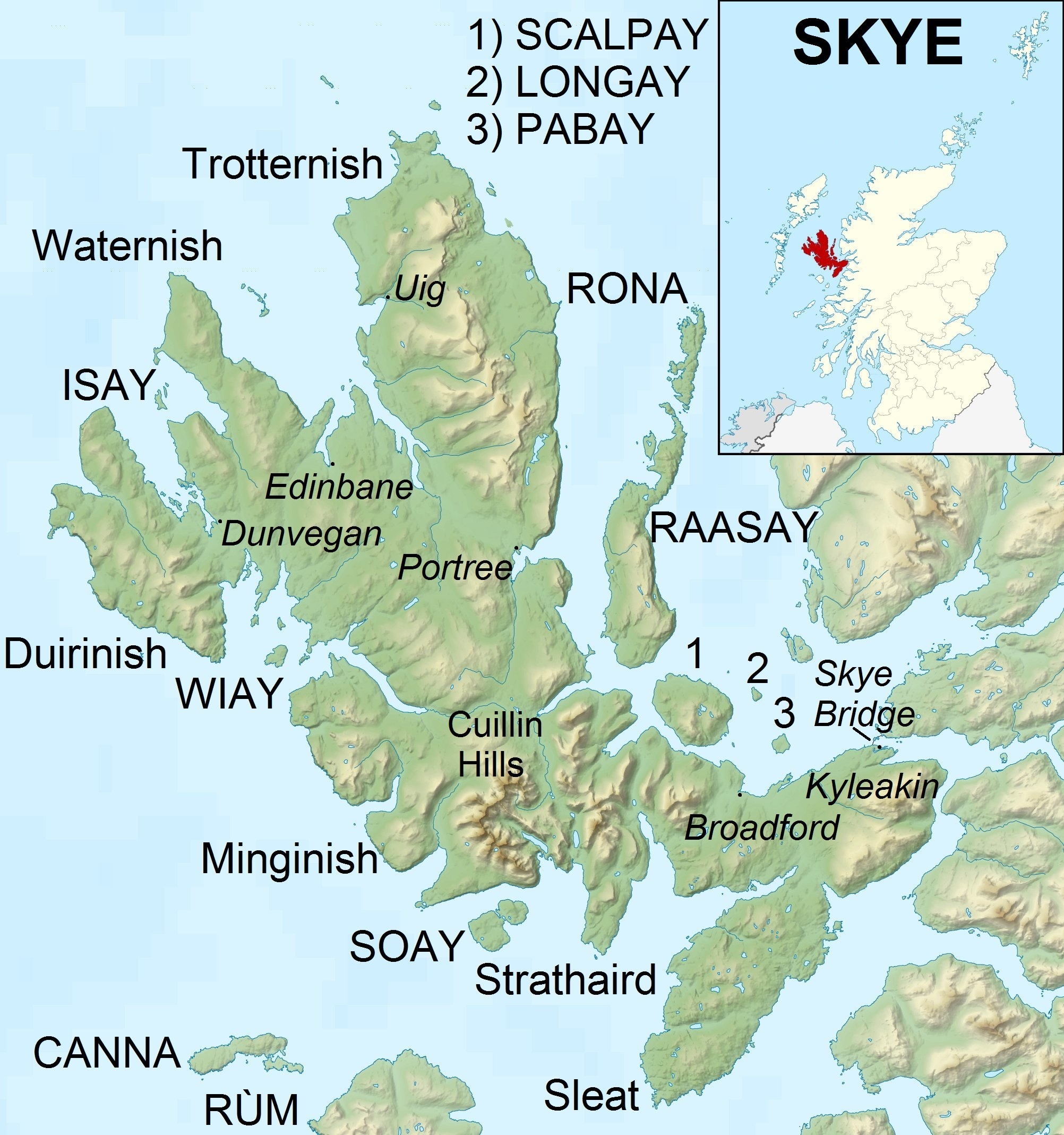
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazetteer For Scotland
The ''Gazetteer for Scotland'' is a gazetteer covering the geography, history and people of Scotland. It was conceived in 1995 by Bruce Gittings of the University of Edinburgh and David Munro of the Royal Scottish Geographical Society, and contains 25,870 entries as of July 2019. It claims to be "the largest dedicated Scottish resource created for the web". The Gazetteer for Scotland provides a carefully researched and editorially validated resource widely used by students, researchers, tourists and family historians with interests in Scotland. Following on from a strong Scottish tradition of geographical publishing, the ''Gazetteer for Scotland'' is the first comprehensive gazetteer to be produced for the country since Francis Groome's ''Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland'' (1882-6) (the text of which is incorporated into relevant entries). The aim is not to produce a travel guide, of which there are many, but to write a substantive and thoroughly edited description of the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinloch Hourn
Kinloch Hourn is a small settlement at the end of Loch Hourn, in the West Highlands of Scotland. The name comes from the Gaelic, Ceann Loch Shubhairne, for "the head of Loch Hourn". Kinloch Hourn is at the end of of single-track road, which runs west from a junction with the A87 beside Loch Garry. From Kinloch Hourn, a path continues along the south side of the loch to Barrisdale. The path then climbs over Màm Barrisdale, before dropping down to the village of Inverie in Knoydart. This route once had a number of townships along it, and may have been used as a coffin road. This is also used as a walking route into the mountains of Knoydart, including Ladhar Bheinn and Luinne Bheinn. To the north of Loch Hourn is the route of an old drove road A drovers' road, drove ''roador droveway is a route for droving livestock on foot from one place to another, such as to market or between summer and winter pasture (see transhumance). Many drovers' roads were ancient routes of unkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); or where two streams meet to become the source of a river of a new name (such as the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers at Pittsburgh, forming the Ohio); or where two separated channels of a river (forming a river island) rejoin at the downstream end. Scientific study of confluences Confluences are studied in a variety of sciences. Hydrology studies the characteristic flow patterns of confluences and how they give rise to patterns of erosion, bars, and scour pools. The water flows and their consequences are often studied with mathematical models. Confluences are relevant to the distribution of living organisms (i.e., ecology) as well; "the general pattern ownstream of confluencesof increasing stream flow and decreasing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch
''Loch'' () is the Scottish Gaelic, Scots language, Scots and Irish language, Irish word for a lake or sea inlet. It is Cognate, cognate with the Manx language, Manx lough, Cornish language, Cornish logh, and one of the Welsh language, Welsh words for lake, llwch. In English English and Hiberno-English, the Anglicisation, anglicised spelling lough is commonly found in place names; in Lowland Scots and Scottish English, the spelling "loch" is always used. Many loughs are connected to stories of lake-bursts, signifying their mythical origin. Sea-inlet lochs are often called sea lochs or sea loughs. Some such bodies of water could also be called firths, fjords, estuary, estuaries, straits or bays. Background This name for a body of water is Insular Celtic languages, Insular CelticThe current form has currency in the following languages: Scottish Gaelic, Irish language, Irish, Manx language, Manx, and has been borrowed into Scots language, Lowland Scots, Scottish English, Iri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beinn Sgritheall
Beinn Sgritheall or Beinn an Sgrithill (), also anglicized Ben Sgriol, is the highest mountain on the Glenelg peninsula in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. It is a Munro with a height of . The main approach is via Arnisdale on the shores of Loch Hourn or via Gleann Beag to the north, with its well-known brochs. The view from the summit was described by Sir Hugh Munro, a founder member of the Scottish Mountaineering Club, as "perhaps the most beautiful I have seen in Scotland".Brown, ''Hamish's Mountain Walk'', p. 224 Classification Mountains in the British Isles are classified according to height. At Beinn Sgritheall is a Munro, being a Scottish mountain over . It is also classified as a Marilyn given its prominence of . It is the highest mountain on the Glenelg peninsula, an area of largely uninhabited land bounded by Loch Alsh and Loch Duich to the north and by Loch Hourn to the west and south. Geography and geology Beinn Sgritheall consists of a narrow, curved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladhar Bheinn
Ladhar Bheinn is the highest mountain in the Knoydart region of the Highlands of Scotland. It is the most westerly Munro on the Scottish mainland. The mountain may be climbed from Barrisdale to the northeast or Inverie to the south. From Barrisdale the mountain may be climbed as part of circuit of Coire Dhorrcaill; this route involves a certain amount of scrambling Scrambling is a mountaineering term for ascending steep terrain using one's hands to assist in holds and balance.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. It is also used to describe terrain that falls between hiking and rock climbing (as a “scrambl ..., particularly on the section immediately north of the subsidiary summit of Stob a Chearcaill. References This listgives information about map, grid ref and neighbours Munros Marilyns of Scotland Mountains and hills of the Northwest Highlands One-thousanders of the British Isles {{Highland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |