|
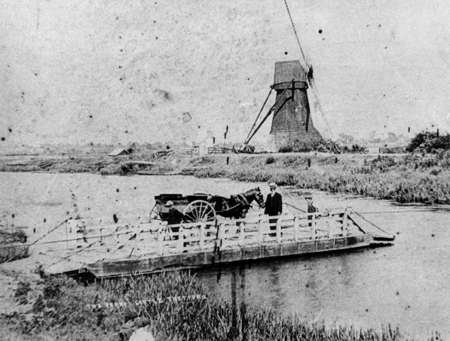
Little Thetford
Little Thetford is a small village in the civil parish of Thetford, south of Ely in Cambridgeshire, England, about by road from London. The village is built on a boulder clay island surrounded by flat fenland countryside, typical of settlements in this part of the East of England. During the Mesolithic era, the fenland basin was mostly dry and forested, although subject to salt and fresh water incursions. The marshes and meres of this fenland may therefore have been difficult to occupy, other than seasonally, but there is evidence of human settlement on the island since the late Neolithic Age; a Bronze Age causeway linked the village with the nearby Barway, to the south-east. An investigation, prior to a 1995 development in the village, discovered a farm and large tile-kiln of Romano-British origin; further investigations uncovered an earlier settlement of the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The Roman road Akeman Street passed through the north-west corner of the parish, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxing The Compass
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 'points' (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these rules: 8-wind compass rose * The four cardinal directions are north (N), east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes provide habitats for many kinds of invertebrates, fish, amphibians, waterfowl and aquatic mammals. This biological productivity means that marshes contain 0.1% of global sequestered terrestrial carbon. Moreover, they have an outsized influence on climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The female equivalent is abbess. Origins The title had its origin in the monasteries of Egypt and Syria, spread through the eastern Mediterranean, and soon became accepted generally in all languages as the designation of the head of a monastery. The word is derived from the Aramaic ' meaning "father" or ', meaning "my father" (it still has this meaning in contemporary Hebrew: אבא and Aramaic: ܐܒܐ) In the Septuagint, it was written as "abbas". At first it was employed as a respectful title for any monk, but it was soon restricted by canon law to certain priestly superiors. At times it was applied to various priests, e.g. at the court of the Frankish monarchy the ' ("of the palace"') and ' ("of the camp") were chaplains to the Merovingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea, with The Wash to the north-west. The county town is the city of Norwich. With an area of and a population of 859,400, Norfolk is a largely rural county with a population density of 401 per square mile (155 per km2). Of the county's population, 40% live in four major built up areas: Norwich (213,000), Great Yarmouth (63,000), King's Lynn (46,000) and Thetford (25,000). The Broads is a network of rivers and lakes in the east of the county, extending south into Suffolk. The area is protected by the Broads Authority and has similar status to a national park. History The area that was to become Norfolk was settled in pre-Roman times, (there were Palaeolithic settlers as early as 950,000 years ago) with camps along the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ælfwaru
Ælfwaru (died 27 February 1007) was an Anglo-Saxon noblewoman, who bequeathed her lands to churches such as Ely, and Ramsey. Chroniclers, writing in the 12th century, transcribed such bequests, from the original cyrographs. Ælfwaru's cyrograph has not survived. Ælfwaru's father, Æthelstan Mannessune, had two sons: Eadnoth, and Godric; and two daughters: Ælfwaru, and Ælfwyn. Lineage Her lineage is unknown. However, modern historians have constructed a plausible family tree. Ælfwaru is believed to be one of two daughters to Æthelstan Mannessune (d. 986), the other being Ælfwyn, abbess of Chatteris. If this is the case, Ælfwaru's brothers were St Eadnoth the martyr (d. 1016), first abbot of Ramsey, and Godric (d.1013).Brooks (ed.) p. 51 Death Ælfwaru is believed to have died on, or at least her obituary recorded for, 27 February.MS Cambridge, Trinity College O. 2.1 ''Liber Benefactorum Ecclesiae Ramesiensis'' records the year, 1007Ramsey Cartulary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman (a relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers became dominant in England, their language replaced the languages of Roman Britain: Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cratendune
Cratendune () is the name of the lost village reported in the ''Liber Eliensis'', the history of the abbey, then Ely Cathedral, compiled towards the end of the 12th century, as the 500th anniversary of the traditional founding date drew near. As no direction is indicated in ''Liber Eliensis'', a number of archaeological sites are therefore candidates for this lost village. History Reading from the ''Liber Eliensis'' MS folio 2, which is a 12th century Benedictine history of Ely written in Latin, Bentham describes Æthelberht of Kent, Chief of the Saxon Kings, founding a church at the insistence of Augustine (died 26 May 604). The church, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, was located about Bentham (1771) p. 11 says ''about a mile distant from the present city'' from what is now Ely Cathedral at a place called ''Cratendune''. The date mentioned for this founding was the year 607,The date is given in ''Chronicon Abbatum et Episcoporum Eliensum'', which depends in part on ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened within Britain, and the identity was not merely imported. Anglo-Saxon identity arose from interaction between incoming groups from several Germanic tribes, both amongst themselves, and with indigenous Britons. Many of the natives, over time, adopted Anglo-Saxon culture and language and were assimilated. The Anglo-Saxons established the concept, and the Kingdom, of England, and though the modern English language owes somewhat less than 26% of its words to their language, this includes the vast majority of words used in everyday speech. Historically, the Anglo-Saxon period denotes the period in Britain between about 450 and 1066, after their initial settlement and up until the Norman Conquest. Higham, Nicholas J., and Martin J. Ryan. ''The A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akeman Street (Cambridgeshire)
Akeman Street is the name given to a Roman road in eastern England that runs from Cambridgeshire to the north coast of Norfolk. It is approximately long and runs roughly north-northeast. Akeman Street joined Ermine Street near Wimpole Hall, then ran northeast to the settlement at Durolipons (now Cambridge), where it crossed a Roman road now known as the Via Devana. Within north Cambridge, the road followed the present-day Stretten Avenue, Carlton Way and Mere Way running northeast past Landbeach before joining the present A10 and on towards Ely and The Fens. It then reached Denver and the coast at Brancaster. The road was constructed on top of an earlier trackway some time in the 2nd Century CE, or later, and it has been speculated that it was part of the creation of an imperial estate under Hadrian. See also * Akeman Street * Roman roads in Britain Roman roads in Britannia were initially designed for military use, created by the Roman Army during the nearly fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Roads In Britain
Roman roads in Britannia were initially designed for military use, created by the Roman Army during the nearly four centuries (AD 43–410) that Britannia was a province of the Roman Empire. It is estimated that about of paved trunk roads (surfaced roads running between two towns or cities) were constructed and maintained throughout the province. Most of the known network was complete by 180. The primary function of the network was to allow rapid movement of troops and military supplies, but it subsequently provided vital infrastructure for commerce, trade and the transportation of goods. A considerable number of Roman roads remained in daily use as core trunk roads for centuries after the end of Roman rule in Britain in 410. Some routes are now part of the UK's national road network. Others have been lost or are of archeological and historical interest only. After the Romans departed, systematic construction of paved highways in the United Kingdom did not resume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barway
Barway is a hamlet in Cambridgeshire, England, about three miles south of Ely. It is on Soham Lode, which flows into the River Cam. The population is included in the civil parish of Soham Soham ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of East Cambridgeshire, in Cambridgeshire, England, just off the A142 between Ely and Newmarket. Its population was 10,860 at the 2011 census. History Archaeology The region between De .... External links Hamlets in Cambridgeshire Soham {{Cambridgeshire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Track in the Somerset Levels, England, which dates from the Neolithic age. Timber causeways may also be described as both boardwalks and bridges. Etymology When first used, the word ''causeway'' appeared in a form such as "causey way" making clear its derivation from the earlier form "causey". This word seems to have come from the same source by two different routes. It derives ultimately, from the Latin for heel, ''calx'', and most likely comes from the trampling technique to consolidate earthworks. Originally, the construction of a causeway utilised earth that had been trodden upon to compact and harden it as much as possible, one layer at a time, often by enslaved bodies or flocks of sheep. Today, this work is done by machines. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |