|
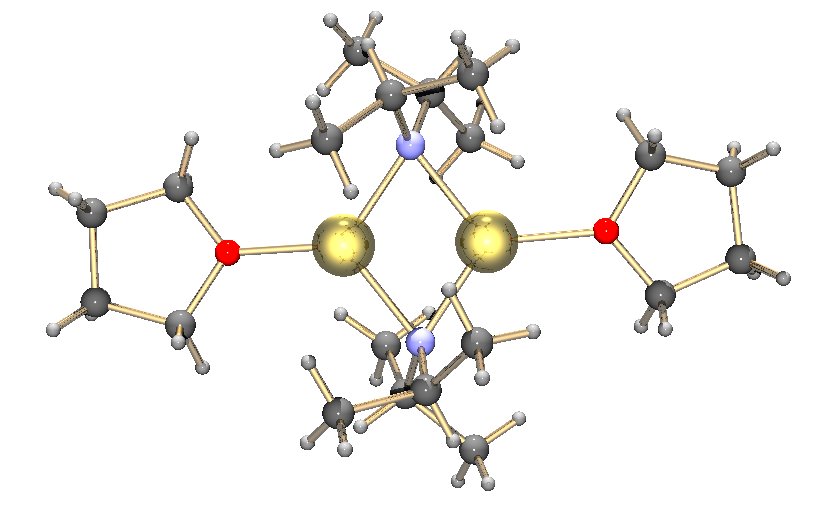
Lithium Tetramethylpiperidide
Lithium tetramethylpiperidide (often abbreviated LiTMP or LTMP) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula . It is used as a non-nucleophilic base, being comparable to LiHMDS in terms of steric hindrance. Synthesis It is synthesised by the deprotonation of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine with ''n''-butyllithium at −78 °C. Recent reports show that this reaction can also be performed 0 °C. The compound is stable in a THF/ethylbenzene solvent mixture and is commercially available as such. Structure Like many lithium reagents it has a tendency to aggregate, forming a tetramer in the solid state. See also *Lithium diisopropylamide *Lithium amide Lithium amide or lithium azanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure. Lithium amide can be made by treating lithium metal with liquid ammonia: : Other lithium amides The co ... References {{Lithium compounds Lithium compounds Non-nucleophilic bases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetramer
A tetramer () ('' tetra-'', "four" + '' -mer'', "parts") is an oligomer formed from four monomers or subunits. The associated property is called ''tetramery''. An example from inorganic chemistry is titanium methoxide with the empirical formula Ti(OCH3)4, which is tetrameric in solid state and has the molecular formula Ti4(OCH3)16. An example from organic chemistry is kobophenol A, a substance that is formed by combining four molecules of resveratrol. In biochemistry, it similarly refers to a biomolecule formed of four units, that are the same (homotetramer), i.e. as in Concanavalin A or different (heterotetramer), i.e. as in hemoglobin. Hemoglobin has 4 similar sub-units while immunoglobulins have 2 very different sub-units. The different sub-units may have each their own activity, such as binding biotin in avidin tetramers, or have a common biological property, such as the allosteric binding of oxygen in hemoglobin. See also * Cluster chemistry; atomic and molecular cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-nucleophilic Bases
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is a sterically hindered organic base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical non-nucleophilic bases are bulky, such that protons can attach to the basic center but alkylation and complexation is inhibited. Non-nucleophilic bases A variety of amines and nitrogen heterocycles are useful bases of moderate strength (pKa of conjugate acid * ''N'',''N''-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA, also called Hünig's Base), p * 1,8-Diazabicycloundec-7-ene (DBU) - useful for E2 elimination reactions, pKa = 13.5 * 1,5-Diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-5-ene (DBN) - comparable to DBU * 2,6-Di-tert-butylpyridine, a weak non-nucleophilic base pKa = 3.58 * Phosphazene bases, such as t-Bu-P4''Activation in anionic polymerization: Why phosphazene bases are very exciting promoters'' S. Boileau, N. Illy Prog. Polym. Sci., 2011, 36, 1132-1151, {{doi, 10. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Compounds
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Amide
Lithium amide or lithium azanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure. Lithium amide can be made by treating lithium metal with liquid ammonia: : Other lithium amides The conjugate bases of amines are known as amides. Thus, a ''lithium amide'' may also refer to any compound in the class of the lithium salt of an amine. These compounds have the general form , with the chemical lithium amide itself as the parent structure. Common lithium amides include lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), lithium tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP), and lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS). They are produced by the reaction of Li metal with the appropriate amine: : Lithium amides are very reactive compounds. Specifically, they are strong bases. Examples Lithium tetramethylpiperidide has been crystallised as a tetramer. On the other hand, the lithium derivative of bis(1-phenylethyl)amine crystallises as a trimer: It is also possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide (commonly abbreviated LDA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula . It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature. It is a colorless solid, but is usually generated and observed only in solution. It was first prepared by Hamell and Levine in 1950 along with several other hindered lithium diorganylamides to effect the deprotonation of esters at the α position without attack of the carbonyl group. Preparation and structure LDA is commonly formed by treating a cooled (0 to −78 °C) mixture of tetrahydrofuran and diisopropylamine with ''n''-butyllithium. When dissociated, the diisopropylamide anion can become protonated to form diisopropylamine. Diisopropylamine has a p''K''a value of 36. Therefore, its conjugate base is suitable for the deprotonation of compounds with greater acidity, importantly, such weakly acidic compounds (carbon acids) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Tetramethylpiperide Tetramer
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira ( ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, Scopus, EBSCO databases, ProQuest databases, Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed, and the Science Citation Index Expanded. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 16.383. Editors-in-chief The following people are or have been editor-in-chief: * 1879–1880 – Hermann Endemann * 1880–1881 – Gideon E. Moore * 1881–1882 – Hermann End ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylbenzene
Ethylbenzene is an organic compound with the formula . It is a highly flammable, colorless liquid with an odor similar to that of gasoline. This monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is important in the petrochemical industry as an reaction intermediate in the production of styrene, the precursor to polystyrene, a common plastic material. In 2012, more than 99% of ethylbenzene produced was consumed in the production of styrene. Occurrence and applications Ethylbenzene occurs naturally in coal tar and petroleum. The dominant application of ethylbenzene is its role as an intermediate in the production of polystyrene. Catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene gives hydrogen and styrene: : → C6H5CH=CH2 + As of May 2012, more than 99% of all the ethylbenzene produced is used for this purpose. Ethylbenzene hydroperoxide, a reagent and radical initiator, is produced by autoxidation of ethylbenzene: :C6H5CH2CH3 + O2 → C6H5CH(O2H)CH3 Niche uses Ethylbenzene is added to gasoline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Butyllithium
''n''-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated ''n''-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly employed as a strong base (superbase) in the synthesis of organic compounds as in the pharmaceutical industry. Butyllithium is commercially available as solutions (15%, 25%, 1.5 M, 2 M, 2.5 M, 10 M, etc.) in alkanes such as pentane, hexanes, and heptanes. Solutions in diethyl ether and THF can be prepared, but are not stable enough for storage. Annual worldwide production and consumption of butyllithium and other organolithium compounds is estimated at 2000 to 3000 tonnes. Although butyllithium is colorless, ''n''-butyllithium is usually encountered as a pale yellow solution in alkanes. Such solutions are stable indefinitely if properly stored,. but in practice, they degrade upon aging. Fine white precipitate (li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |