|
List Of Telephony Terminology
This is a List of telephony terminology and acronyms which relate to telephony networks. A *Advanced Intelligent Network, (AIN), see also IN or Intelligent Network * Automatic number announcement circuit (ANAC) *Automated Attendant *ACD - Automatic call distributor * Articulation score B *Blue box - a device that was used to bypass the normal long-distance call switching tones typically used to obtain free calls. C *Call originator - (or ''calling party'', ''caller'' or ''A-party'') a person or device that initiates a telephone call by dialling a telephone number. *Call waiting - a system that notifies a caller of another incoming telephone call by sounding a sound in the earpiece. *Called party - (or ''callee'' or ''B-party'') * Caller *Calling party *Conference call (multi-party call) * COCOT D *Dial peer *Dial tone *Distribution frame * Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) E *Emergency telephone number *End instrument *Engset calculation *Erlang unit F *Fax - (contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Intelligent Network
The Intelligent Network (IN) is the standard network architecture specified in the ITU-T Q.1200 series recommendations. It is intended for fixed as well as mobile telecom networks. It allows operators to differentiate themselves by providing value-added services in addition to the standard telecom services such as PSTN, ISDN on fixed networks, and GSM services on mobile phones or other mobile devices. The intelligence is provided by network nodes on the service layer, distinct from the switching layer of the core network, as opposed to solutions based on intelligence in the core switches or equipment. The IN nodes are typically owned by telecommunications service providers such as a telephone company or mobile phone operator. IN is supported by the Signaling System #7 (SS7) protocol between network switching centers and other network nodes owned by network operators. Examples of IN services * Televoting * Call screening * Local number portability * Toll-free calls/Freephone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
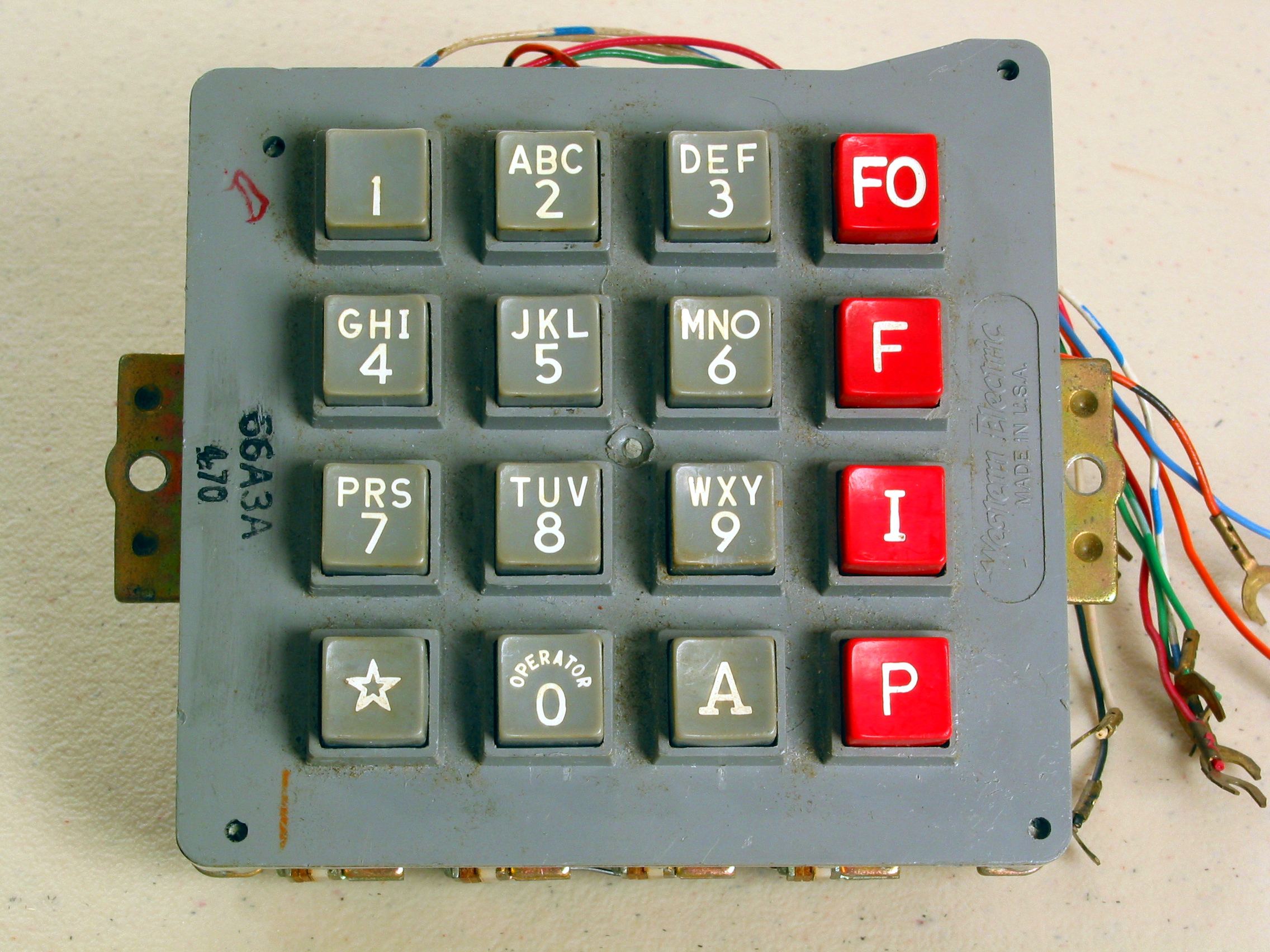
Dual-tone Multi-frequency Signaling
Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as ''MF4''. The Touch-Tone system using a telephone keypad gradually replaced the use of rotary dial and has become the industry standard for landline and mobile service. Other multi-frequency systems are used for internal signaling within the telephone network. Multifrequency signaling Before the development of DTMF, telephone numbers were dialed by users with a loop-disconnect (LD) signaling, more commonly known as pulse dialing (dial pulse, DP) in the United States. It functions by int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Network Interface Device
An Intelligent Network Interface Device, more commonly known as an "INID", is a system that provides triple play media services to customer homes. The system provides digital subscriber line access, advanced TV, and voice over internet protocol (VoIP) phone services to subscribed customers. The term may refer either to a standalone external residential gateway or to a system of multiple components that together provide RG functions. Models include the 2Wire HomePortal INID and the Entone Crescendo INID. AT&T's U-verse brand of services employs the 2Wire INID as an alternative residential gateway. Unlike the traditional Network Interface Device (NID) that it replaces, an INID includes an outdoor unit that mounts to the side of the subscriber's home in a hardened, weather-resistant enclosure that is easily accessible by carrier technicians; it also can include an indoor unit and a battery backup. By transferring intelligent gateway functions and all service and network terminations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inside Plant
In telecommunication, the term inside plant has the following meanings: *All the cabling and equipment installed in a telecommunications facility, including the main distribution frame (MDF) and all the equipment extending inward therefrom, such as PABX or central office equipment, MDF heat coil protectors, and grounding systems. *In radio and radar systems, all communications-electronics (C-E) equipment that is installed in buildings. Around the turn of the 21st century, DSLAMs became an important part of telephone company inside plant. Inside plant will also have distribution frames and other equipment including passive optical network (name depends on the Service Provider). Power A typical power system for a switching office in an inside plant consists of the elements listed below: *AC power system **AC input switch gear **Standby AC plant (where appropriate) **AC distribution system (essential and non-essential loads) **AC backup systems for uninterruptible loads and protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface Functionality
In telephony, interface functionality is the characteristic of interfaces that allows operators to support transmission, switching, and signaling functions identical to those used in the enhanced services provided by the carrier. As part of its comparably efficient interconnection (CEI) offering, the carrier must make available standardized telephone networking hardware and software Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ... interfaces that are able to support transmission, switching, and signaling functions identical to those used in the enhanced services provided by the carrier. References Telephony {{telephony-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, tunnels, water supply, sewerage, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications (including Internet access, Internet connectivity and Broadband, broadband access). In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing Commodity, commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal quality of life, living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment. Especially in light of the massive societal transformations needed to Climate change mitigation, mitigate and Climate change adaptation, adapt to climate change, contemporary infrastructure conversations frequently focus on sustainable development and gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunt Group
In telephony, line hunting (or hunt group) is the method of distributing phone calls from a single telephone number to a group of several phone lines. Specifically, it refers to the process or algorithm used to select which line will receive the call. Hunt groups are supported by some PBX phone systems. Also, some phone companies will provide this feature for a small fee (see also: Centrex). In the tariffs of some telephone companies, one may obtain hunting for free, but forward on busy is a charged service. Multi-line hunting ''Multiline hunting'' (sometimes MLH, ''line hunting'' or MHG, ''multiline hunting group'') is a feature that allows multiple telephone lines going into a business to act as a single group, called a ''hunt group''. This type of fallback is a somewhat more complex form of call forwarding. If the line called is busy, the call goes to the next available line. Only if no lines in the group are open does the calling party get a busy signal. Linear hunting I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howler Tone
The off-hook tone (also off-hook warning, howling tone, or howler tone) is a telephony signal for alerting a user that the telephone has been left off-hook without use for an extended period, effectively disabling the telephone line. North America The off-hook tone in exchanges of the North American Numbering Plan consists of a superposition of tones with the frequencies 1400 Hz, 2060 Hz, 2450 Hz, and 2600 hertz, played at a cadence of on and off. Section 17.2.8 ''Receiver-Off-Hook (ROH) Tone'' The signal is applied to the local loop by the switching system for |
Help Desk
A help desk is a department or person that provides assistance and information usually for electronic or computer problems. In the mid-1990s, research by Iain Middleton of Robert Gordon University studied the value of an organization's help desks. It found that value was derived not only from a reactive response to user issues, but also from the help desk's unique position of communicating daily with numerous customers or employees. Information gained in areas such as technical problems, user preferences, and satisfaction can be valuable for the planning and development work of other information technology units. Large help desks have a person or team responsible for managing the incoming requests, called "issues"; they are commonly called queue managers or queue supervisors. The queue manager is responsible for the issue queues, which can be set up in various ways depending on the help desk size or structure. Typically, large help desks have several teams that are experienced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handoff
In cellular telecommunications, handover, or handoff, is the process of transferring an ongoing call or data session from one channel connected to the core network to another channel. In satellite communications it is the process of transferring satellite control responsibility from one earth station to another without loss or interruption of service. Terminology American English uses the term ''handoff'', and this is most commonly used within some American organizations such as 3GPP2 and in American originated technologies such as CDMA2000. In British English the term ''handover'' is more common, and is used within international and European organisations such as ITU-T, IETF, ETSI and 3GPP, and standardised within European originated standards such as GSM and UMTS. The term handover is more common in academic research publications and literature, while handoff is slightly more common within the IEEE and ANSI organisations. Purpose In telecommunications there may be differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Frame
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra * Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erlang Unit
The erlang (symbol E) is a dimensionless unit that is used in telephony as a measure of offered load or carried load on service-providing elements such as telephone circuits or telephone switching equipment. A single cord circuit has the capacity to be used for 60 minutes in one hour. Full utilization of that capacity, 60 minutes of traffic, constitutes 1 erlang. Carried traffic in erlangs is the average number of concurrent calls measured over a given period (often one hour), while offered traffic is the traffic that would be carried if all call-attempts succeeded. How much offered traffic is carried in practice will depend on what happens to unanswered calls when all servers are busy. The CCITT named the international unit of telephone traffic the erlang in 1946 in honor of Agner Krarup Erlang. In Erlang's analysis of efficient telephone line usage he derived the formulae for two important cases, Erlang-B and Erlang-C, which became foundational results in teletraffic engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |