|
List Of Nabataean Kings ...
The Rulers of Nabataea, reigned over the Nabataean Kingdom (also rendered as ''Nabataea'', ''Nabatea'', or ''Nabathea''), inhabited by the Nabateans, located in present-day Jordan, southern Syria, southern Israel and north-western Saudi Arabia. The queens of the later Nabataean Kingdom figure side by side with their husbands as co-rulers on their coins. List See also *Lists of office-holders References {{Reflist Sources''Jewish Virtual Library''*Martha Ross, ''Rulers and Governments of the World – Vol1, Earliest Times to 1491''. London & New York: Bowker Publishing Company, 1978. Nabataean monarchs Nabatea Nabataeans Nabatea Nabatean The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Kingdom
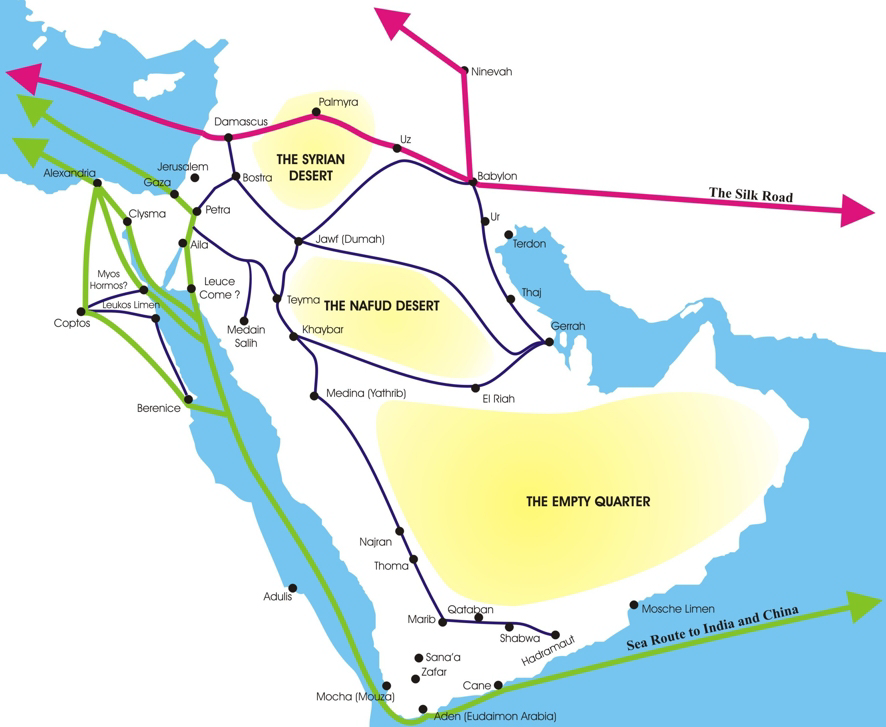
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Red Sea coast into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. Although the Nabataeans were initially embedded in Aramaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaqilath
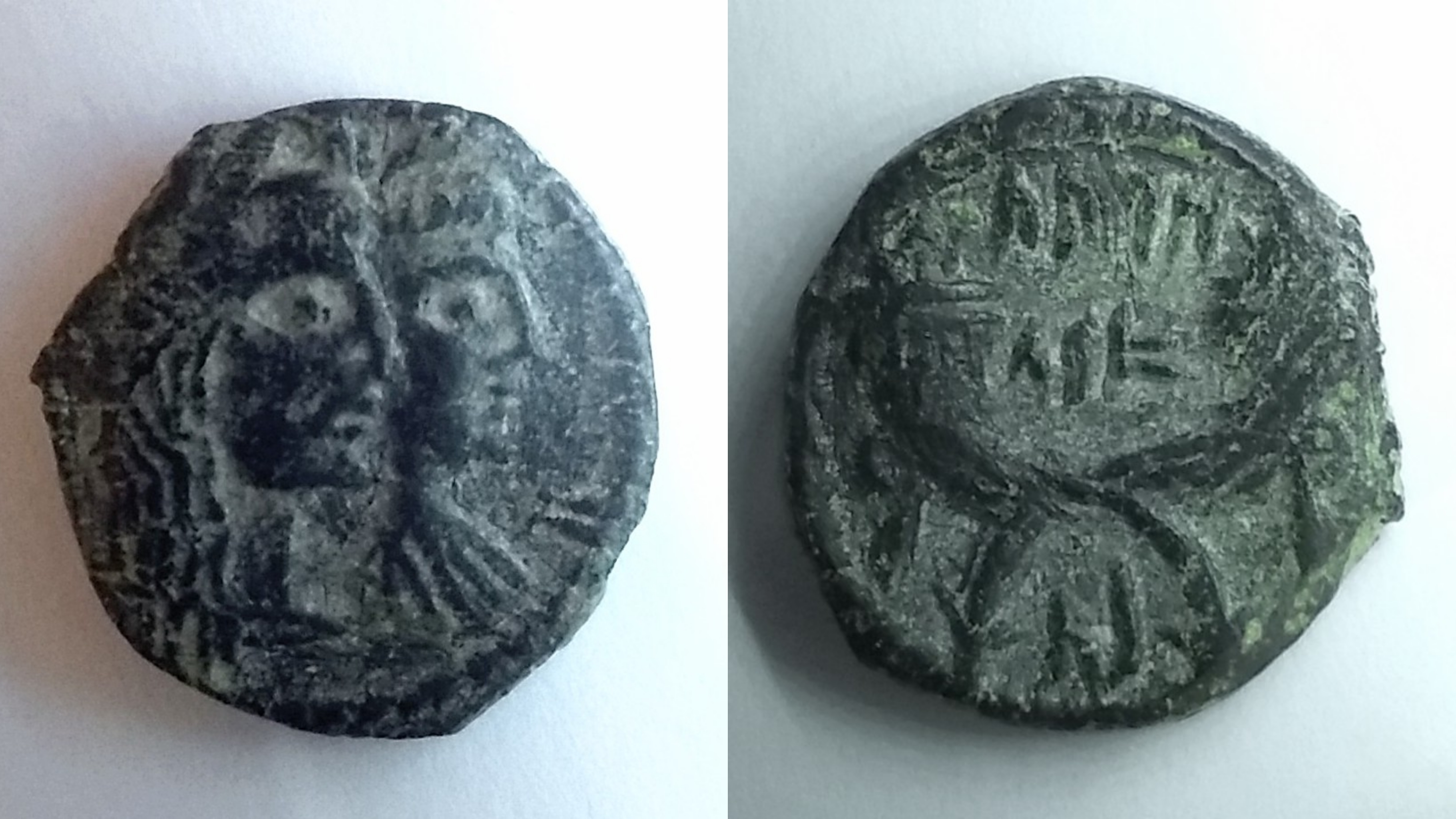
Shaqilath (Nabataean Aramaic: , ''ŠQYLT''; also spelled ''Shaqilat'', ''Shaqeela'', ''Shaqeelah'', ''Šagīlat'') was a queen of the Nabataeans. She was the second wife and co-ruler of Aretas IV of the Nabataeans in AD 16–40. She married King Aretas IV in 16 AD and had four children with him: Hagru or Hajir, Malik, Jameelah and Shaqilath II. Her role as queen and her proximity to the king is emphasized by her title "the Sister of the King". During the reign of King Aretas IV and Shaqilat, the trades expanded to distant areas in the ancient world and industry, commerce and civilization of the Nabataeans flourished. Copper and silver coins where she is depicted with her husband have been recovered and they offer expressive examples and models of the Nabataean civilization in terms of the culture of clothing. See also * List of rulers of Nabatea * Shaqilath II Shaqilath II (Nabataean Aramaic: , ''ŠQYLT''; fl. 70), was a queen of the Nabataeans. She was the daughter of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Asian Rulers
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Monarchs
List of monarchs may refer to: *List of current sovereign monarchs *List of current constituent monarchs *List of living former sovereign monarchs *List of monarchs by nickname *List of fictional monarchs *A king list, used as an early form of periodisation By current countries Note: The list includes both current monarchies and current countries that have abolished the monarchy. *Afghanistan *Albania *Andorra *Antigua and Barbuda *Armenia *Australia * Austria (and Austria-Hungary) *The Bahamas *Bahrain *Barbados *Belarus *Belize *Belgium *Benin *Bosnia *Bhutan *Brazil *Brunei *Bulgaria *Burundi *Cambodia *Canada *Central Africa *China *Croatia *Czechia *Denmark *Egypt *Estonia *Eswatini *Ethiopia *Fiji *Finland *France *The Gambia *Georgia *Ghana *Germany *Grenada *Greece *Guyana *Haiti *Hungary *Iceland *India *Iran *Iraq *Ireland *Israel *Italy *Jamaica *Japan *Jordan *Kenya *Korea *Kuwait *Laos *Lesotho *Libya *Liechtenstein *Lithuania *Luxembourg *Madagascar *Malawi *Malaysia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Monarchs
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Office-holders
These are lists of incumbents (individuals holding offices or positions), including heads of states or of subnational entities. A historical discipline, archontology, focuses on the study of past and current office holders. Incumbents may also be found in the countries' articles ( main article and " Politics of") and the list of national leaders, recent changes in 2020 in politics and government, and past leaders on State leaders by year and Colonial governors by year. Various articles group lists by title, function or topic: e.g. abdication, assassinated persons, cabinet (government), chancellor, ex-monarchs (20th century), head of government, head of state, lieutenant governor, mayor, military commanders, minister (and ministers by portfolio below), order of precedence, peerage, president, prime minister, Reichstag participants (1792), secretary of state. Heads of international organizations * President of the European Council * President of the European Commissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
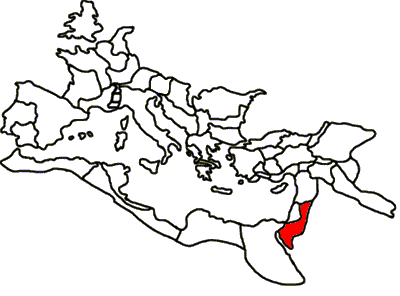
Arabia Petraea
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province ( la, Provincia Arabia; ar, العربية البترائية; grc, Ἐπαρχία Πετραίας Ἀραβίας) or simply Arabia, was a frontier province of the Roman Empire beginning in the 2nd century. It consisted of the former Nabataean Kingdom in Jordan, southern Levant, the Sinai Peninsula and northwestern Arabian Peninsula. Its capital was Petra. It was bordered on the north by Syria, on the west by Judaea (merged with Syria from AD 135) and Egypt, and on the south and east by the rest of Arabia, known as Arabia Deserta and Arabia Felix. The territory was annexed by Emperor Trajan, like many other eastern frontier provinces of the Roman Empire, but held onto, unlike Armenia, Mesopotamia and Assyria, well after Trajan's rule, its desert frontier being called the Limes Arabicus. It produced the Emperor Philippus, who was born around 204. As a frontier province, it included a desert populated by Arabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presided over one of the greatest military expansions in Roman history and led the empire to attain its greatest territorial extent by the time of his death. He is also known for his philanthropic rule, overseeing extensive public building programs and implementing social welfare policies, which earned him his enduring reputation as the second of the Five Good Emperors who presided over an era of peace within the Empire and prosperity in the Mediterranean world. Trajan was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in present-day Spain, a small Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in the province of Hispania Baetica. He came from a branch of the gens Ulpia, the ''Ulpi Traiani'', that originated in the Umbrian town of Tuder. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbel II Soter
Rabbel II Soter (Nabataean Aramaic: ''Rabʾel dī ʾaḥyēy wa-šēzīb ʿammeh'', "Rabbel, who gave life and deliverance to his people") was the last ruler of the Nabataean Kingdom, ruling from 70 to 106. After the death of his father, Malichus II, Rabbel still a child, ascended to the throne. His mother, Shaqilath II, assumed the regency of the Nabataean Kingdom, during the minority of her son Rabel II in 70-76 AD. His sister Gamilath became queen of the Nabataeans. Rabbel gave himself the Greek title "Soter",Taylor (2001), pp.73-74 meaning "Savior". He reigned with his first wife Queen Gamilath and his second wife Queen Hagaru. Gamilat was a queen in 76–102 CE and Hagru was a queen in 102–106. After his death in 106, the Roman emperor Trajan faced practically no resistance and conquered the kingdom on 22 March 106. It became the Roman province of Arabia Petraea, with Bosra becoming its provincial capital. See also * List of rulers of Nabatea The Rulers of Nabataea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaqilath II
Shaqilath II (Nabataean Aramaic: , ''ŠQYLT''; fl. 70), was a queen of the Nabataeans. She was the daughter of Aretas IV of the Nabataeans. She ruled jointly with her husband Malichus II in 40–70. After his death she was regent for her son Rabel II in 70–76 AD. Copper and silver coins where she is depicted with her husband, and coins of her with her son, have been recovered. Some of these coins are dated with regnal years to the left of the queen. See also * List of rulers of Nabatea * Shaqilath Shaqilath (Nabataean Aramaic: , ''ŠQYLT''; also spelled ''Shaqilat'', ''Shaqeela'', ''Shaqeelah'', ''Šagīlat'') was a queen of the Nabataeans. She was the second wife and co-ruler of Aretas IV of the Nabataeans in AD 16–40. She married Kin ... References in Power" last accessed January 10, 2007* Dated Coins of Antiquity Cohen 1st-century Nabataean monarchs 1st-century women rulers {{MEast-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malichus II
Malichus II (Nabataean Aramaic: ''Malīḵū'' or ''Malīḵūʾ'') was ruler of Nabatea from 40 to 70 AD. Malichus' reign is sometimes perceived as a period of declining Nabataean power, but this view depends in part on Nabataea having controlled Damascus in the period 34–40. The Romans had, however, diverted the routes of spice and perfume cargo shipments to Egypt. Rome was very powerful, so Malichus cooperated. In 66, a Jewish revolt occurred in Judaea. Malichus sent 5,000 cavalry and 1,000 infantry to help the Emperor Titus crush the rebellion. Malichus II died in AD 70,Jane Taylor: ''Petra And the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. I. B. Tauris 2001, , p. 73 () and was succeeded by his son, Rabbel II Soter, initially under the regency of his widowed queen Šagīlat II. See also *List of rulers of Nabatea The Rulers of Nabataea, reigned over the Nabataean Kingdom (also rendered as ''Nabataea'', ''Nabatea'', or ''Nabathea''), inhabited by the Nabateans, located in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuldu
Chuldu or Huldu (Nabataean Aramaic: ''Ḥūldū''; fl. 1st-century CE), was a Queen of the Nabataeans, spouse and co-ruler of Aretas IV in 9 BC–AD 16. She ruled jointly with her husband from 9 BCE until 16 CE. Copper and silver coins where she is depicted with her husband have been recovered. Little is known about the exact date and reason of the transition from Chuldu to Shaqilath, who appears on coins after an unexplained gap in 18 CE. Maurice Satre suggested previous gaps in the minting of coins could have been due to a period of capitulation to Ancient Rome. She has been presumed to be the mother of Malichus, Obodas and Rabbel, and of three daughters, Phasa'el (first wife of Herod Antipas), Shu'dat and Hagera. The latter also had a son, also called Aretas, grandson of Aretas IV. See also List of rulers of Nabatea The Rulers of Nabataea, reigned over the Nabataean Kingdom (also rendered as ''Nabataea'', ''Nabatea'', or ''Nabathea''), inhabited by the Nabateans, locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |