|
List Of AMD Ryzen Processors
The Advanced Micro Devices, AMD Ryzen family is an x86-64 microprocessor family from AMD, based on the Zen microarchitecture. The Ryzen lineup includes Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, Ryzen 7, Ryzen 9, and Ryzen Threadripper with up to 64 cores. All consumer Ryzens have an unlocked multiplier and all support Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) except earlier Zen/Zen+ based desktop Ryzen 3 and Zen/Zen+/Zen 2 (Lucienne excluded) based mobile Ryzen 3. Desktop processors Zen (microarchitecture), Zen based (1st generation) Summit Ridge and Whitehaven (1000 series CPUs) Whitehaven (1000 series HEDT CPUs) Raven Ridge (2000 series APUs) Zen+ based (2nd generation) Pinnacle Ridge (2000 series CPUs) Colfax (2000 series HEDT CPUs) Picasso (3000 series APUs) Zen 2 based (3rd generation) Matisse and Castle Peak (3000 series CPUs) Castle Peak (3000 series HEDT/workstation CPUs) Renoir (4000 series CPUs) Based on the Ryzen 4000G series APUs with the integrated GPU disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactured its own processors, the company later outsourced its manufacturing, a practice known as going fabless, after GlobalFoundries was spun off in 2009. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, graphics processors, and FPGAs for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. History First twelve years Advanced Micro Devices was formally incorporated by Jerry Sanders, along with seven of his colleagues from Fairchild Semiconductor, on May 1, 1969. Sanders, an electrical engineer who was the director of marketing at Fairchild, had, like many Fairchild executives, grown frustrated with the increasing lack of support, opportunity, and flexibility within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryzen
Ryzen ( ) is a brand of multi-core x86-64 microprocessors designed and marketed by AMD for desktop, mobile, server, and embedded platforms based on the Zen microarchitecture. It consists of central processing units (CPUs) marketed for mainstream, enthusiast, server, and workstation segments and accelerated processing units (APUs) marketed for mainstream and entry-level segments and embedded systems applications. AMD announced a new series of processors on December 13, 2016, named "Ryzen", and delivered them in Q1 2017, the first of several generations. The 1000 series featured up to eight cores and 16 threads, with a 52% instructions per cycle (IPC) increase over their prior CPU products. The second generation of Ryzen processors, the Ryzen 2000 series, released in April 2018, featured the Zen+ microarchitecture, a 12 nm process (GlobalFoundries); the aggregate performance increased 10% (of which approximately 3% was IPC, 6% was frequency); most importantly, Zen+ fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, first released in 1999. It introduced two new modes of operation, 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new 4-level paging mode. With 64-bit mode and the new paging mode, it supports vastly larger amounts of virtual memory and physical memory than was possible on its 32-bit predecessors, allowing programs to store larger amounts of data in memory. x86-64 also expands general-purpose registers to 64-bit, and expands the number of them from 8 (some of which had limited or fixed functionality, e.g. for stack management) to 16 (fully general), and provides numerous other enhancements. Floating-point arithmetic is supported via mandatory SSE2-like instructions, and x87/ MMX style registers are generally not used (but still available even in 64-bit mode); instead, a set of 16 vector registers, 128 bits each, is used. (Each register can store one or two double-preci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the cost of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen Microarchitecture
Zen is the codename for a family of computer processor microarchitectures from Advanced Micro Devices, AMD, first launched in February 2017 with the first generation of its Ryzen CPUs. It is used in Ryzen (desktop and mobile), Ryzen Threadripper (workstation/high end desktop), and Epyc (server). Comparison History First generation The first generation Zen was launched with the Ryzen 1000 series of CPUs (codenamed Summit Ridge) in February 2017. The first Zen-based preview system was demonstrated at Electronic Entertainment Expo 2016, E3 2016, and first substantially detailed at an event hosted a block away from the Intel Developer Forum 2016. The first Zen-based CPUs reached the market in early March 2017, and Zen-derived Epyc server processors (codenamed "Naples") launched in June 2017 and Zen-based AMD Accelerated Processing Unit, APUs (codenamed "Raven Ridge") arrived in November 2017. This first iteration of Zen utilized Global Foundries' 14 nm manufacturing pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneous Multithreading
Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) is a technique for improving the overall efficiency of superscalar CPUs with hardware multithreading. SMT permits multiple independent threads of execution to better use the resources provided by modern processor architectures. Details The term ''multithreading'' is ambiguous, because not only can multiple threads be executed simultaneously on one CPU core, but also multiple tasks (with different page tables, different task state segments, different protection rings, different I/O permissions, etc.). Although running on the same core, they are completely separated from each other. Multithreading is similar in concept to preemptive multitasking but is implemented at the thread level of execution in modern superscalar processors. Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) is one of the two main implementations of multithreading, the other form being temporal multithreading (also known as super-threading). In temporal multithreading, only one thread of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen (microarchitecture)
Zen is the codename for a family of computer processor microarchitectures from AMD, first launched in February 2017 with the first generation of its Ryzen CPUs. It is used in Ryzen (desktop and mobile), Ryzen Threadripper (workstation/high end desktop), and Epyc (server). Comparison History First generation The first generation Zen was launched with the Ryzen 1000 series of CPUs (codenamed Summit Ridge) in February 2017. The first Zen-based preview system was demonstrated at E3 2016, and first substantially detailed at an event hosted a block away from the Intel Developer Forum 2016. The first Zen-based CPUs reached the market in early March 2017, and Zen-derived Epyc server processors (codenamed "Naples") launched in June 2017 and Zen-based APUs (codenamed "Raven Ridge") arrived in November 2017. This first iteration of Zen utilized Global Foundries' 14 nm manufacturing process. First generation refresh Zen+ was first released in April 2018, powering the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen+
Zen+ is the codename for a computer processor microarchitecture by AMD. It is the successor to the first gen Zen microarchitecture, first released in April 2018, powering the second generation of Ryzen processors, known as Ryzen 2000 for mainstream desktop systems, Threadripper 2000 for high-end desktop setups and Ryzen 3000G (instead of 2000G) for accelerated processing units (APUs). Features Zen+ uses GlobalFoundries' 12 nm fabrication process, an optimization of the 14 nm process used for Zen, with only minor design rule changes. This means that the die sizes between Zen and Zen+ are identical as AMD chose to use the new smaller transistors to increase the amount of empty space, or "dark silicon", between the various features on the die. This was done to improve power efficiency & reduce thermal density to allow for higher clock speeds, rather than design an entirely new floorplan for a physically smaller die (which would have been significantly more work and thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
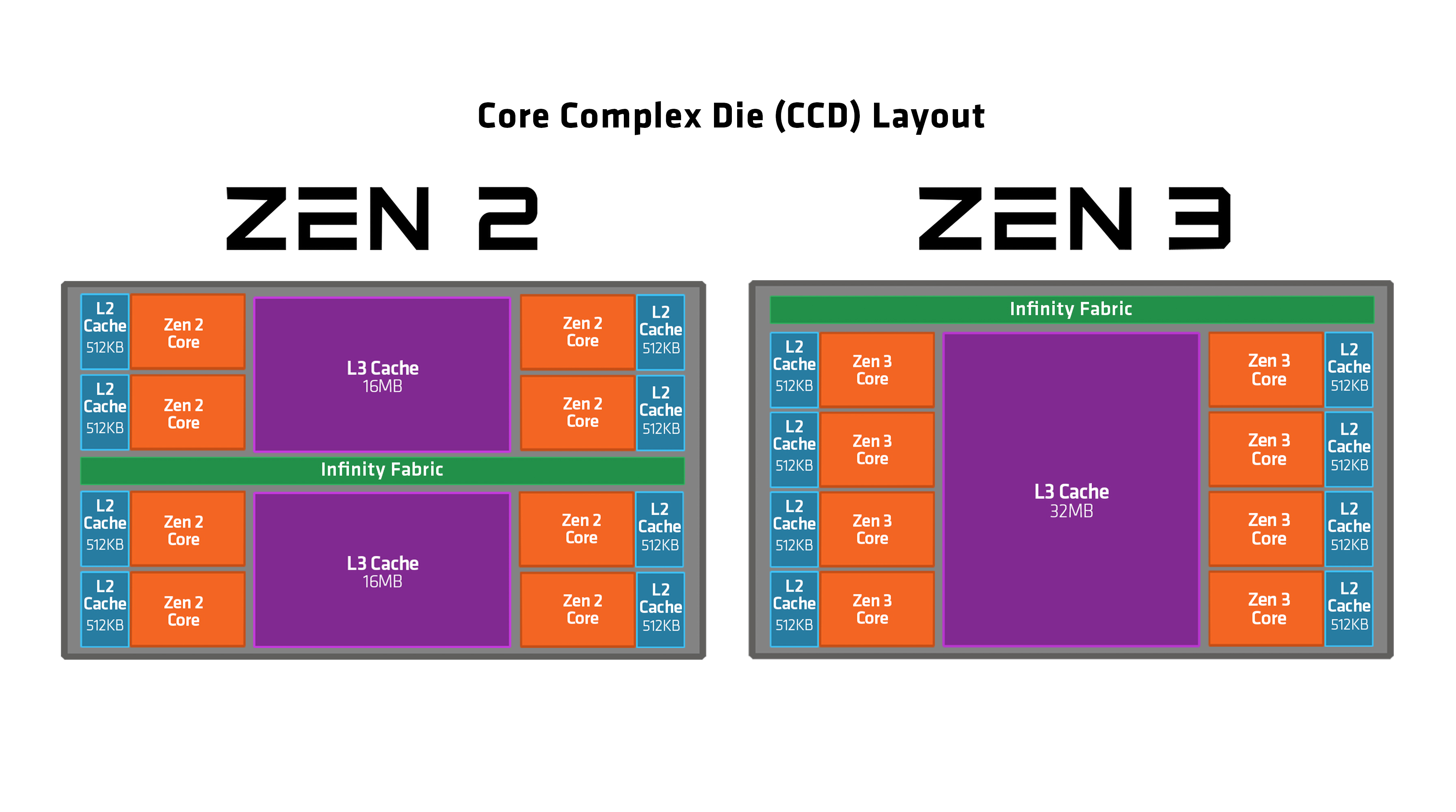
Zen 2
Zen 2 is a computer processor microarchitecture by AMD. It is the successor of AMD's Zen and Zen+ microarchitectures, and is fabricated on the 7 nanometer MOSFET node from TSMC. The microarchitecture powers the third generation of Ryzen processors, known as Ryzen 3000 for the mainstream desktop chips (codename "Matisse"), Ryzen 4000U/H (codename "Renoir") and Ryzen 5000U (codename "Lucienne") for mobile applications, as Threadripper 3000 for high-end desktop systems, and as Ryzen 4000G for accelerated processing units (APUs). The Ryzen 3000 series CPUs were released on 7 July 2019, while the Zen 2-based Epyc server CPUs (codename "Rome") were released on 7 August 2019. An additional chip, the Ryzen 9 3950X, was released in November 2019. At CES 2019, AMD showed a Ryzen third-generation engineering sample that contained one chiplet with eight cores and 16 threads. AMD CEO Lisa Su also said to expect more than eight cores in the final lineup. At Computex 2019, AMD revealed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated GPU
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. Modern GPUs are efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. Their parallel structure makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) for algorithms that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card or embedded on the motherboard. In some CPUs, they are embedded on the CPU die. In the 1970s, the term "GPU" originally stood for ''graphics processor unit'' and described a programmable processing unit independently working from the CPU and responsible for graphics manipulation and output. Later, in 1994, Sony used the term (now standing for ''graphics processing unit'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen 3
Zen 3 is the codename for a CPU microarchitecture by AMD, released on November 5, 2020. It is the successor to Zen 2 and uses TSMC's 7 nm process, 7 nm process for the chiplets and GlobalFoundries's 14 nm process, 14 nm process for the I/O die on the server chips and 12 nm for desktop chips. Zen 3 powers Ryzen 5000 mainstream desktop processors (codenamed "Vermeer") and Epyc server processors (codenamed "Milan"). Zen 3 is supported on motherboards with List of AMD chipsets#AM4 chipsets, 500 series chipsets; 400 series boards also saw support on select B450 / X470 motherboards with certain BIOSes. Zen 3 is expected to be the last microarchitecture before AMD switches to DDR5 memory and new sockets. According to AMD, Zen 3 has a 19% higher instructions per cycle (IPC) on average than Zen 2. On April 1, 2022, AMD released the new Ryzen 6000 series for the laptop, using an improved "Zen 3+" architecture, bringing RDNA 2 graphics integrated in a APU to the PC for the first time. On Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen 4
Zen 4 is the codename for a CPU microarchitecture by AMD, released on September 27, 2022. It is the successor to Zen 3 and uses TSMC's N5 process for CCDs. Zen 4 powers Ryzen 7000 mainstream desktop processors (codenamed "Raphael") and will be used in high-end mobile processors (codenamed "Dragon Range"), thin & light mobile processors (codenamed "Phoenix"), as well as Epyc 9004 server processors (codenamed "Genoa" and "Bergamo"). Features Like its predecessor, Zen 4 in its Desktop Ryzen variants features one or two Core Complex Dies (CCDs) built on TSMC's 5 nm process and one I/O die built on 6 nm. Previously, the I/O die on Zen 3 was built on GlobalFoundries' 14 nm process. Zen 4's I/O die includes integrated RDNA 2 graphics for the first time on any Zen architecture. Zen 4 marks the first utilization of the 5 nm process for x86-based desktop processors. On desktop and server platforms, Zen 4 has moved from DDR4 to DDR5 memory; DDR4 is not supported. Addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |