|
List Of Drinks
Drinks are liquids that can be consumed. In addition to basic needs, drinks form part of the culture of human society. In a commercial setting, drinks, other than water, may be termed beverages. Alcoholic Alcoholic drink – An alcoholic drink is a drink containing ethanol, commonly known as alcohol, although in chemistry the definition of an alcohol includes many other compounds. Alcoholic drinks, such as wine, beer, and liquor have been part of human culture and development for 8,000 years. Many brands of alcoholic drinks are produced worldwide. * Comparison of alcopops * List of alcoholic drinks Beer Beer – beer is produced by the saccharification of starch and fermentation of the resulting sugar. The starch and saccharification enzymes are often derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat.Barth, Roger. ''The Chemistry of Beer: The Science in the Suds'', Wiley 2013: . Most beer is also flavoured with hops, which add bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Milk And Lemon Teas - Chilli Cafe
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. In the Solar System, ice is abundant and occurs naturally from as close to the Sun as Mercury to as far away as the Oort cloud objects. Beyond the Solar System, it occurs as interstellar ice. It is abundant on Earth's surfaceparticularly in the polar regions and above the snow lineand, as a common form of precipitation and deposition, plays a key role in Earth's water cycle and climate. It falls as snowflakes and hail or occurs as frost, icicles or ice spikes and aggregates from snow as glaciers and ice sheets. Ice exhibits at least eighteen phases ( packing geometries), depending on temperature and pressure. When water is cooled rapidly (quenching), up to three types of amorphous ice can form depending on its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Beer Styles
Beer style is a term used to differentiate and categorize beers by various factors, including appearance, flavour, ingredients, production method, history, or origin. The term ''beer style'' and the structuring of world beers into defined categories is largely based on work done by writer Michael James Jackson in his 1977 book ''The World Guide To Beer''. Fred Eckhardt furthered Jackson's work, publishing ''The Essentials of Beer Style'' in 1989. There is no universally agreed list of beer styles, as different countries and organisations have different sets of criteria. Organisers of beer competitions such as the Campaign for Real Ale's (CAMRA) Champion Beer of Britain, the Beer Judge Certification Program (BJCP) local homebrewing competitions, the Brewers Association's World Beer Cup, and the Brewing Industry International Awards have categories in which beers are judged. The categories are varied and include processes or ingredients not usually regarded as defining beer sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer And Breweries By Region
This is a list of articles and categories dealing with beer and breweries by region: the breweries and beers in various regions. Beer is the world's most widely consumed alcoholic drink, and is the third-most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is thought by some to be the oldest fermented drink. A brewery is a dedicated building for the making of beer, though beer can be made at home, and has been for much of beer's history. A company that makes beer is called either a brewery or a brewing company. The diversity of size in breweries is matched by the diversity of processes, degrees of automation, and kinds of beer produced in breweries. A brewery is typically divided into distinct sections, with each section reserved for one part of the brewing process. List Africa Botswana * Kgalagadi Breweries Limited Cape Verde Egypt Ethiopia Kenya Morocco Nigeria South Africa Tanzania Asia Armenia Beer has been brewed by Armenians since ancient times. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer, at home by a homebrewer, or communally. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archaeological evidence suggests that emerging civilizations, including ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, brewed beer. Since the nineteenth century the brewing industry has been part of most western economies. The basic ingredients of beer are water and a fermentable starch source such as malted barley. Most beer is fermented with a brewer's yeast and flavoured with hops. Less widely used starch sources include millet, sorghum and cassava. Secondary sources (adjuncts), such as maize (corn), rice, or sugar, may also be used, sometimes to reduce cost, or to add a feature, such as adding wheat to aid in retaining the foamy head of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In general, preservation is implemented in two modes, chemical and physical. Chemical preservation entails adding chemical compounds to the product. Physical preservation entails processes such as refrigeration or drying.Erich Lück and Gert-Wolfhard von Rymon Lipinski "Foods, 3. Food Additives" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Preservative food additives reduce the risk of foodborne infections, decrease microbial spoilage, and preserve fresh attributes and nutritional quality. Some physical techniques for food preservation include dehydration, UV-C radiation, freeze-drying, and refrigeration. Chemical preservation and physical preservation techniques ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bittering Agent
A bittering agent is a flavoring agent added to a food or beverage to impart a bitter taste, possibly in addition to other effects. While many substances are bitter to a greater or lesser degree, a few substances are used specifically for their bitterness, especially to balance other flavors, such as sweetness. Notable beverage examples include caffeine, found naturally in tea and coffee and added to many soft drinks, hops in beer, and quinine in tonic water. Food examples include bitter melon, which may be mixed into a stir fry or soup for its bitter flavor. Potent bittering agents may also be added to dangerous products as aversive agents to make them foul tasting, so as to prevent accidental poisoning. Examples including anti-freeze, household cleaning products and pesticides such as slug pellets. In general dangerous products with bright colours, which may be appealing to children, often contain agents such as denatonium. However, the efficacy of using bittering agents for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant '' Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to which, in addition to bitterness, they impart floral, fruity, or citrus flavours and aromas. Hops are also used for various purposes in other beverages and herbal medicine. The hops plants have separate female and male plants, and only female plants are used for commercial production. The hop plant is a vigorous, climbing, herbaceous perennial, usually trained to grow up strings in a field called a hopfield, hop garden (in the South of England), or hop yard (in the West Country and United States) when grown commercially. Many different varieties of hops are grown by farmers around the world, with different types used for particular styles of beer. The first documented use of hops in beer is from the 9th century, though Hildegard of Binge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
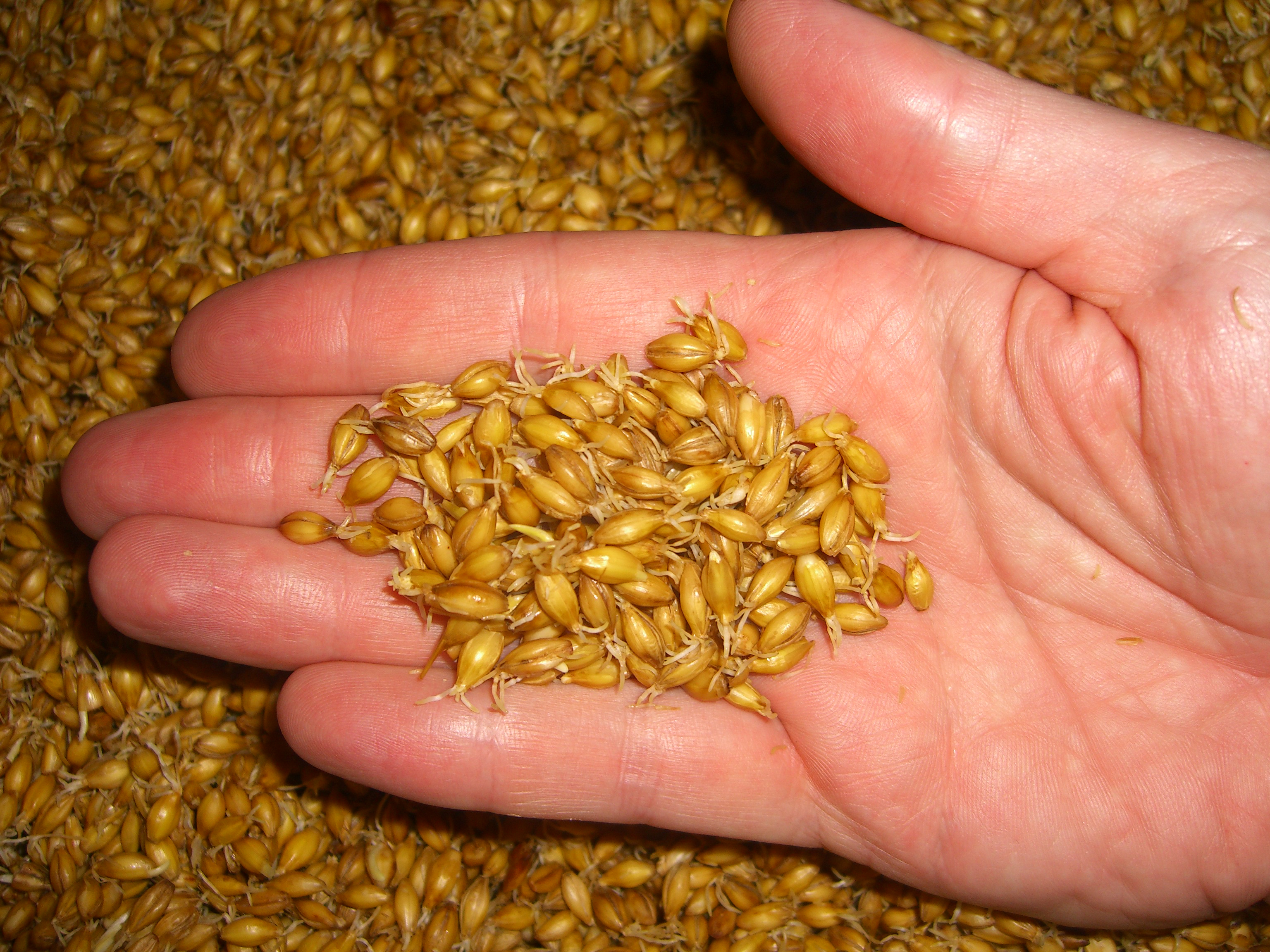
Malt
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air. Malted grain is used to make beer, whisky, malted milk, malt vinegar, confections such as Maltesers and Whoppers, flavored drinks such as Horlicks, Ovaltine, and Milo, and some baked goods, such as malt loaf, bagels, and Rich Tea biscuits. Malted grain that has been ground into a coarse meal is known as "sweet meal". Malting grain develops the enzymes (α-amylase, β-amylase) required for modifying the grains' starches into various types of sugar, including monosaccharide glucose, disaccharide maltose, trisaccharide maltotriose, and higher sugars called maltodextrines. It also develops other enzymes, such as proteases, that break down the proteins in the grain into forms that can be used by yeast. The point at which the malting process is stopped affects the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation (food)
In food processing, fermentation is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohol or organic acids using microorganisms—yeasts or bacteria—under anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions. Fermentation usually implies that the action of microorganisms is desired. The science of fermentation is known as zymology or zymurgy. The term "fermentation" sometimes refers specifically to the chemical conversion of sugars into ethanol, producing alcoholic drinks such as wine, beer, and cider. However, similar processes take place in the leavening of bread (CO2 produced by yeast activity), and in the preservation of sour foods with the production of lactic acid, such as in sauerkraut and yogurt. Other widely consumed fermented foods include vinegar, olives, and cheese. More localised foods prepared by fermentation may also be based on beans, grain, vegetables, fruit, honey, dairy products, and fish. History and prehistory Natural fermentation precedes human history. Since ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars produced from processed s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)