|
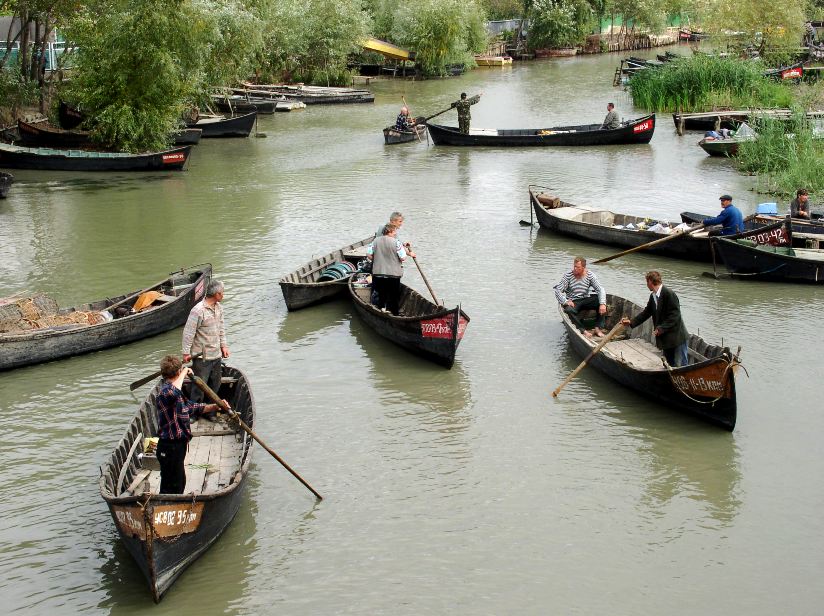
Lipovens
, flag = Flag of the Lipovans.png , flag_caption = Flag of the Lipovans , image = Evstafiev-lipovane-slava-cherkeza.jpg , caption = Lipovans during a ceremony in front of the Lipovan church in the Romanian village of Slava Cercheză in 2004 , population = , region1 = , pop1 = 23,487 , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 700–800 , ref4 = , religions = Old Believers (Eastern Orthodox Christianity) , languages = Russian, Romanian, Ukrainian, Bulgarian , related = Russians , footnotes = The Lipovans or Lippovans (russian: Липовáне; ro, Lipoveni; uk, Липовани; bg, Липованци) are ethnic Russian Old Believers living in Romania, Ukraine, Moldova and Bulgaria who settled in the Principality of Moldavia, in the east of the Principality of Wallachia (Muntenia), and in the regions of Dobruja and Budjak during the 17th and 18th centuries. According to the 2011 Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slava Cercheză
Slava Cercheză (russian: Черкезская Слава) is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania. Its name means the Cherkess ( Circassian) Slava, in reference to the Dobrujan Circassian community that used to inhabit the village before the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878). Besides the titular village, the commune also includes the village of ''Slava Rusă'' (russian: Русская Слава, ''Russian Slava''). Situated near the site of ancient Libida, the commune is home to an important Russian-speaking Lipovan community (79.9% of the population) dating from the late 17th or early 18th century. The Uspenia monastery in the village of Slava Rusă is the seat of the Orthodox Old Rite Eparchy of Slava, founded in the 19th century, with authority over most of Dobruja. The Vovidenia convent A convent is a community of monks, nuns, religious brothers or, sisters or priests. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community. The word is parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
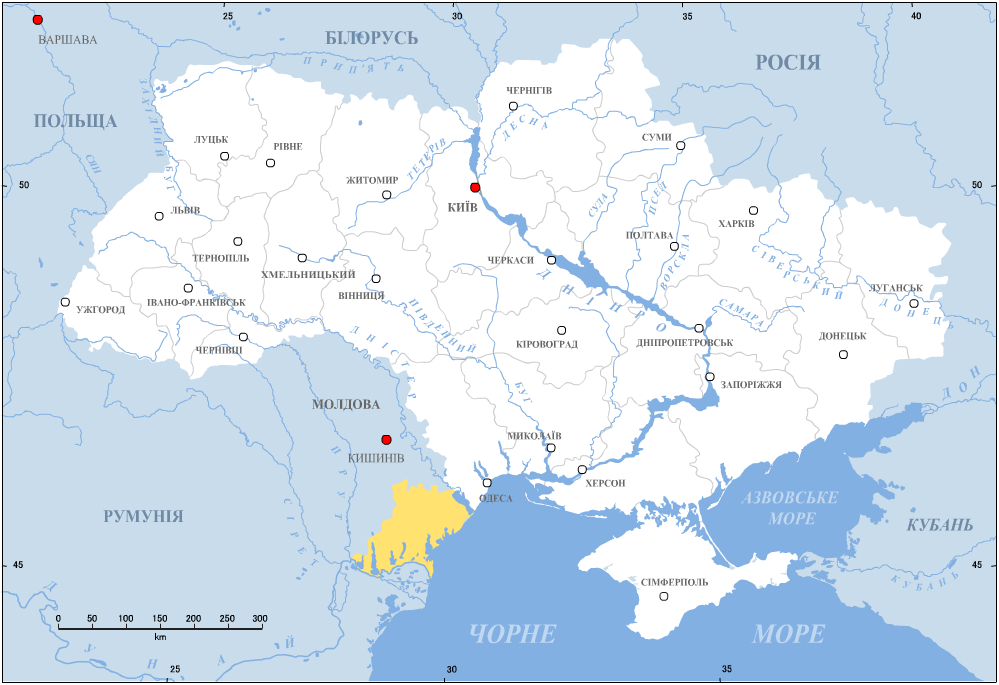
Budjak
Budjak or Budzhak (Bulgarian and Ukrainian: Буджак; ro, Bugeac; Gagauz and Turkish: ''Bucak''), historically part of Bessarabia until 1812, is a historical region in Ukraine and Moldova. Lying along the Black Sea between the Danube and Dniester rivers, this sparsely populated multi-ethnic 600,000-people region of is located in the southern part of historical Bessarabia. Nowadays, the larger part of the region is included in Ukraine's Odesa Oblast, while the rest is included in the southern districts of Moldova. The region is bordered to the north by the rest of Moldova, to the west and south by Romania, and to the east by the Black Sea and the rest of Ukraine. Name and geography Historically, Budjak was the southeastern steppe region of Moldavia. Bordered by the northern Trajan's Wall at its north end, by the Danube river and Black Sea to its south, by Tigheci Hills (just east of the Prut River) to the west, and Dniester River to the east, it was known as ''histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissenters
A dissenter (from the Latin ''dissentire'', "to disagree") is one who dissents (disagrees) in matters of opinion, belief, etc. Usage in Christianity Dissent from the Anglican church In the social and religious history of England and Wales, and, by extension, Ireland, however, it refers particularly to a member of a religious body who has, for one reason or another, separated from the established church or any other kind of Protestant who refuses to recognise the supremacy of the established church in areas where the established church is or was Anglican.. Originally, the term included English and Welsh Roman Catholics whom the original draft of the Nonconformist Relief Act 1779 styled " Protesting Catholic Dissenters". In practice, however, it designates Protestant Dissenters referred to in sec. ii. of the Act of Toleration of 1689 (see English Dissenters). The term recusant, in contrast, came to refer to Roman Catholics rather than Protestant dissenters. Dissent from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikita Pustosvyat
Nikita Pustosvyat (russian: Никита Пустосвят, real name Nikita Konstantinovich Dobrynin (Никита Константинович Добрынин)) (? – June 11, 1683) was one of the leaders of the Russian Old Believers during Raskol. Life The year of his birth is unknown. He was dubbed ''Pustosvyat'' ("hollow saint") by adherents of Patriarch Nikon. Nikita was a priest in Suzdal and participated in editing of church books under Patriarch Joseph. In 1659, Nikita arrived to Moscow and lodged a complaint about Stefan, Archbishop of Suzdal, accusing him of digression from Orthodoxy. When Stefan was acquitted, Nikita denounced him to Tsar Aleksey Mikhaylovich. The church council of 1666–1667 found him guilty and expelled him from the priesthood. The supporters of the old faith played an important role in the Moscow uprising of 1682, and the Old Believers gained support among the ''streltsy , image = 01 106 Book illustrations of Historical description of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more familiar one. The form or the meaning of an archaic, foreign, or otherwise unfamiliar word is reinterpreted as resembling more familiar words or morphemes. The term ''folk etymology'' is a loan translation from German language, German ''Volksetymologie'', coined by Ernst Förstemann in 1852. Folk etymology is a Productivity (linguistics), productive process in historical linguistics, language change, and social relation, social interaction. Reanalysis of a word's history or original form can affect its spelling, pronunciation, or meaning. This is frequently seen in relation to loanwords or words that have become archaic or obsolete. Examples of words created or changed through folk etymology include the English dialectal form wikt:sparrowgrass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Fields
The Wild Fields ( uk, Дике Поле, translit=Dyke Pole, russian: Дикое Поле, translit=Dikoye Polye, pl, Dzikie pola, lt, Dykra, la, Loca deserta or , also translated as "the wilderness") is a historical term used in the Polish–Lithuanian documents of the 16th to 18th centuries to refer to the Pontic steppe in the territory of present-day Eastern and Southern Ukraine and Western Russia, north of the Black Sea and Azov Sea. According to Ukrainian historian Vitaliy Shcherbak the term appeared sometime in the 15th century for territory between the Dniester and mid-Volga when colonization of the region by Zaporozhian Cossacks started.Shcherbak, V. Wild Field (ДИКЕ ПОЛЕ)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. 2004 Shcherbak notes that the term's contemporaries, such as Michalo Lituanus, Blaise de Vigenère, and Józef Wereszczyński,Sas, P. Duchy of the Zaporizhian Host, the project of Józef Wereszczyński (КНЯЗІВСТВО ВІЙСЬКО ЗАПОРОЗ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilia
''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperateness, temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Britain and Ireland they are commonly called lime trees, although they are not related to the citrus Lime (fruit), lime. The genus occurs in Europe and eastern North America, but the greatest species diversity is found in Asia. Under the Cronquist system, Cronquist classification system, this genus was placed in the family Tiliaceae, but genetic research summarised by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group has resulted in the incorporation of this genus, and of most of the previous family, into the Malvaceae. ''Tilia'' species are mostly large, deciduous trees, reaching typically tall, with oblique-cordate (heart-shaped) leaves across. As with elms, the exact number of species is uncertain, as many of the species can Hybrid (biology), hybridise readily, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aydemir
Aydemir ( bg, Айдемир, also ''Aidemir'', ''Ajdemir'') is a village in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Silistra Municipality, Silistra Province. Aydemir has 5711 inhabitants in 2016, down from 9095 short after the fall of communism in 1992. It is the second most populous village in Bulgaria: the village of Lozen took the lead as its population grew up to 6252 people while Aydemir lost many inhabitants in the same period. Aydemir lies at , 31 m above sea level. The village is located in the valley of the Danube, 3 km south of the river and 8 km west of Silistra, on the road from Silistra to Rousse. The mayor is Rumen Angelov. Aydemir is divided into three parts: the centre, the quarter of Delenkite and the quarter of Tataritsa, which was founded in 1674 by Old Believer Nekrasov Cossacks (''see Russians in Bulgaria'') at a location prior to that inhabited by Tatars. Tataritsa is now one of the only two Lipovan villages in Bulgaria, the other being Kazashko. The villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazashko
Kazashko (Bulgarian: Казашко) is a village in north-eastern Bulgaria. It is located in the municipality of Varna, Varna Province. As of March 2015 the village has a population of 349. It is one of the only two Lipovan , flag = Flag of the Lipovans.png , flag_caption = Flag of the Lipovans , image = Evstafiev-lipovane-slava-cherkeza.jpg , caption = Lipovans during a ceremony in front of the Lipovan church in the Romanian village of Slava Cercheză in 200 ... villages in Bulgaria, the other being Tataritsa. References Villages in Varna Province {{Varna-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brăila
Brăila (, also , ) is a city in Muntenia, eastern Romania, a port on the Danube and the capital of Brăila County. The ''Sud-Est'' Regional Development Agency is located in Brăila. According to the 2011 Romanian census there were 180,302 people living within the city of Brăila, making it the 11th most populous city in Romania. The current mayor of Brăila is . History Origins Before 14th century, a small village existed in the place of today's Brăila, probably inhabited by fishermen and small merchants.Rădvan, p.248 The village fell to the Mongols during the 1241 Mongol invasion of Europe and it was under direct control of the rulers of Argeș in mid-14th century. A settlement called ''Drinago'' was found in several 14th century Catalan and Castillian portolan charts ( Angelino de Dalorto, 1325/1330 and Angelino Dulcert, 1339), as well as in the ''Book of Knowledge of All Kingdoms''. This may have been an erroneous transcription of ''Brillago'', a name which was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iași
Iași ( , , ; also known by other alternative names), also referred to mostly historically as Jassy ( , ), is the second largest city in Romania and the seat of Iași County. Located in the historical region of Moldavia, it has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Romanian social, cultural, academic and artistic life. The city was the capital of the Principality of Moldavia from 1564 to 1859, then of the United Principalities from 1859 to 1862, and the capital of Romania from 1916 to 1918. Known as the Cultural Capital of Romania, Iași is a symbol of Romanian history. Historian Nicolae Iorga stated that "there should be no Romanian who does not know of it". Still referred to as "The Moldavian Capital", Iași is the main economic and business centre of Romania's Moldavian region. In December 2018, Iași was officially declared the Historical Capital of Romania. At the 2011 census, the city-proper had a population of 290,422 (making it the fourth most populous in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constanța County
Constanța () is a county ( județ) of Romania on the border with Bulgaria, in the Dobruja region. Its capital city is also named Constanța. Demographics In 2011, it had a population of 684,082 and the population density was 96/km2. The degree of urbanization is much higher (about 75%) than the Romanian average. In recent years the population trend is: The majority of the population are Romanians. There are important communities of Turks and Tatars, remnants of the time of Ottoman rule. Currently the region is the centre of the Muslim minority in Romania. A great number of Aromanians have migrated to Dobruja in the last century, and they consider themselves a cultural minority rather than an ethnic minority. There are also Romani. Geography *Călărași County and Ialomița County are to the west. *Tulcea County and Brăila County are to the north. *Bulgaria (Dobrich Province and Silistra Province) are to the south. Economy The predominant industries in the county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |