|
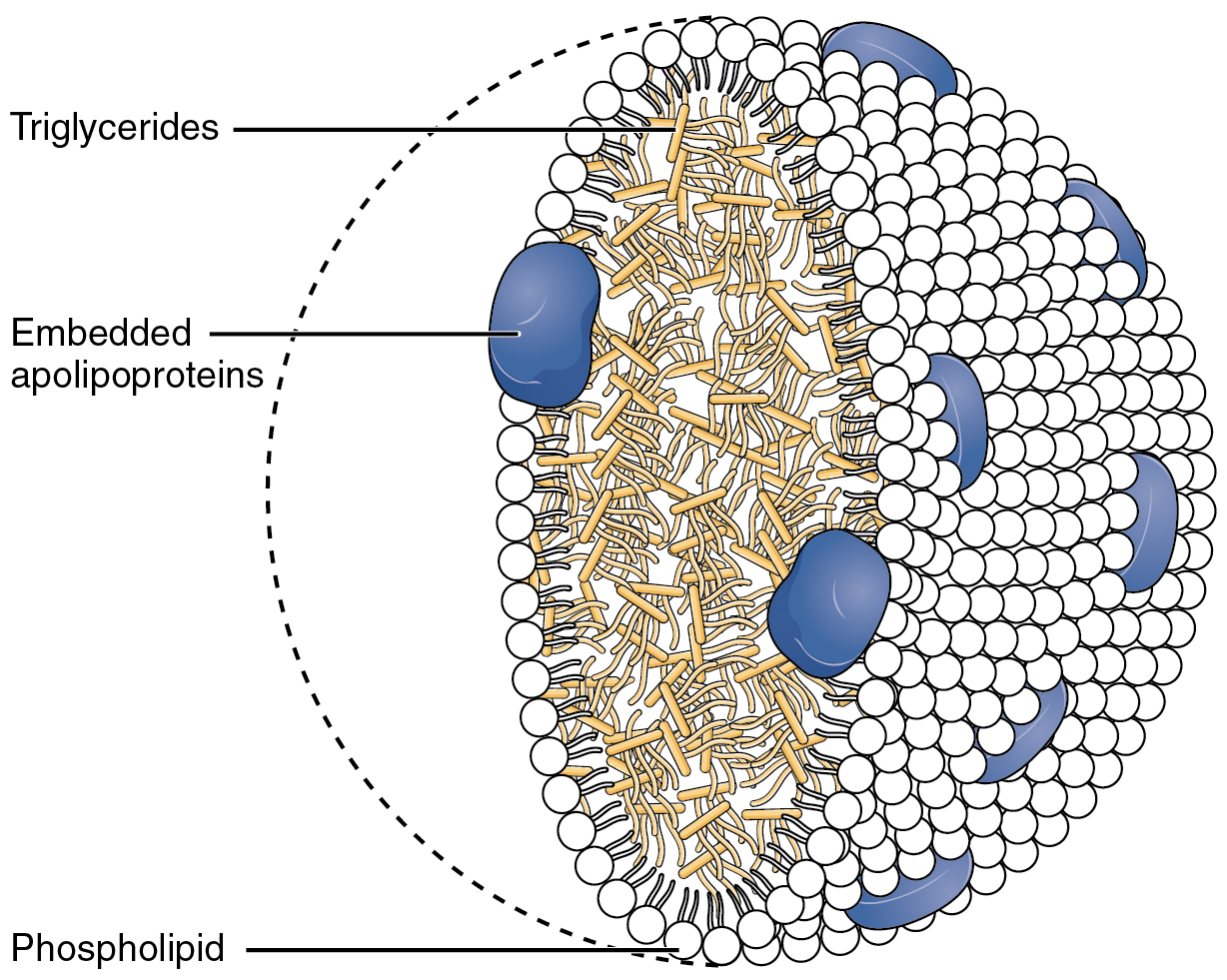
Lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, surrounded by a phospholipid outer shell, with the hydrophilic portions oriented outward toward the surrounding water and lipophilic portions oriented inward toward the lipid center. A special kind of protein, called apolipoprotein, is embedded in the outer shell, both stabilising the complex and giving it a functional identity that determines its role. Many enzymes, transporters, structural proteins, antigens, adhesins, and toxins are lipoproteins. Examples include plasma lipoprotein particles ( HDL, LDL, IDL, VLDL and chylomicrons). Subgroups of these plasma particles are primary drivers or modulators of atherosclerosis. Scope Transmembrane lipoproteins Some transmembrane proteolipids, especially those found in bacteria, are referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-density Lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density naming convention), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries. Overview Lipoproteins transfer lipids (fats) around the body in the extracellular fluid, making fats available to body cells for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins, typically 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by a single apolipoprotein B for LDL and the larger particles). A single LDL particle is about 220–275 angstroms in diameter, typically transporting 3,000 to 6,000 fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules) and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. The lipids carried include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides, amounts of each are variable. Increasing concentrations of HDL particles are associated with decreasing accumulation of atherosclerosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very-low-density Lipoprotein
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. VLDL is assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL is converted in the bloodstream to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). VLDL particles have a diameter of 30–80 nm. VLDL transports endogenous products, whereas chylomicrons transport exogenous (dietary) products. In the early 2010s both the lipid composition and protein composition of this lipoprotein were characterised in great detail. Function Very-low-density lipoproteins transport endogenous triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and cholesteryl esters. It functions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheroma, atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems, depending on which Artery, arteries are affected. The exact cause is not known and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory markers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, family history, genetic, and an unhealthy diet. Atheroma, Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. The narrowing of Artery, arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the body. Diagnosis is based upon a physical exam, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolipid
A proteolipid is a protein covalently linked to lipid molecules, which can be fatty acids, isoprenoids or sterols. The process of such a linkage is known as protein lipidation, and falls into the wider category of acylation and post-translational modification. Proteolipids are abundant in brain tissue, and are also present in many other animal and plant tissues. They are proteins covalenently bound to fatty acid chains, often granting them an interface for interacting with biological membranes. They are not to be confused with lipoproteins, a kind of spherical assembly made up of many molecules of lipids and some apolipoproteins. Structure Depending on the type of fatty acid attached to the protein, a proteolipid can often contain myristoyl, palmitoyl, or prenyl groups. These groups each serve different functions and have different preferences as to which amino acid residue they attach to. The processes are respectively named myristoylation (usually at N-terminal Gly), palm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate-density Lipoprotein
Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs) belong to the lipoprotein particle family and are formed from the degradation of very low-density lipoproteins as well as high-density lipoproteins. IDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. Each native IDL particle consists of protein that encircles various lipids, enabling, as a water-soluble particle, these lipids to travel in the aqueous blood environment as part of the fat transport system within the body. Their size is, in general, 25 to 35 nm in diameter, and they contain primarily a range of triglycerides and cholesterol esters. They are cleared from the plasma into the liver by receptor-mediated endocytosis, or further degraded by hepatic lipase to form LDL particles. Although one might intuitively assume that "intermediate-density" refers to a density between that of high-density and low- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. ULDLs are one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (sorted by density) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. A protein specific to chylomicrons is ApoB48. There is an inverse relationship in the density and size of lipoprotein particles: fats have a lower density than water or smaller protein molecules, and the larger particles have a higher ratio of internal fat molecules with respect to the outer emulsifying protein molecules in the shell. ULDLs, if in the region of 1,000 nm or more, are the only lipoprotein partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apolipoprotein
Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids (oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins) to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. However, because of their detergent-like (amphipathic) properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules (such as phospholipids) can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids (i.e., blood, lymph). In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. They also serve as enzyme cofactors for specific enzymes involved in the metabolism of lipoproteins. Apolipoproteins are also exploited by hepatitis C virus (HCV) to enable virus entry, assembly, and trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. ULDLs are one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (sorted by density) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. A protein specific to chylomicrons is ApoB48. There is an inverse relationship in the density and size of lipoprotein particles: fats have a lower density than water or smaller protein molecules, and the larger particles have a higher ratio of internal fat molecules with respect to the outer emulsifying protein molecules in the shell. ULDLs, if in the region of 1,000 nm or more, are the only lipoprotein partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |