|
Lemuria In Popular Culture
Lemuria is the name of a mythological "lost land" which was purported to have been located in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is said in Tamil legend to have been civilised for over 20,000 years, with its population speaking Tamil. The concept of Lemuria has been rendered obsolete by modern understanding of plate tectonics and continental drift, which have disproven the past existence of a "lost continent". However, it persists in the literature of pseudoarchaeology and has been used as a location and inspiration in a wide range of novels, television shows, films and music. Speculative Authors "Lemuria" entered the lexicon of the occult through the works of Helena Blavatsky, a co-founder of the Theosophical Society, who claimed that the Mahatmas had shown her an ancient, pre-Atlantean '' Book of Dzyan''. Lemuria is mentioned in one of the 1882 Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett. According to L. Sprague de Camp, Blavatsky's concept of Lemuria was influenced by other contemporane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumari Kandam Map
Kumari may refer to: Places * Kumari, Nepal, a town in central Nepal * Kumari (Afyon), a city in Turkey * Kumari (Kutahya), a town in Turkey * Kumari (island), an island in Estonia Religion * Kumari (goddess), in Hinduism * Kaumari, one of the Matrikas, a group of Hindu goddesses * Devi Kanya Kumari, the virgin goddess, South India Other uses * Kumari, the female form of the South Asian title and name Kumar * ''Kumari'' (1952 film), a 1952 Tamil-language film * ''Kumari'' (1977 film), a 1977 Nepali film * ''Kumari'' (2022 film), a 2022 Malayalam-language film * Kumari, an Andorian battle cruiser in the Star Trek universe * Kumari Bank Limited, a commercial bank of Nepal People * Kumari (actress) (1921–2008), Indian film actress * Kumari Kamala (born 1934), Indian classical dancer * Kumari Thankam (?–2011), Malayalam film actress during the 1950s * Deepika Kumari (born 1994), Indian archer * Eerik Kumari (1912–1984), Estonian naturalist * Vinod Kumari, Indian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult
In modern English, ''cult'' is usually a pejorative term for a social group that is defined by its unusual religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals, or its common interest in a particular personality, object, or goal. This sense of the term is controversial and weakly defined—having divergent definitions both in popular culture and academia—and has also been an ongoing source of contention among scholars across several fields of study. Richardson, James T. 1993. "Definitions of Cult: From Sociological-Technical to Popular-Negative." ''Review of Religious Research'' 34(4):348–56. . . An older sense of the word involves a set of religious devotional practices that are conventional within their culture, related to a particular figure, and often associated with a particular place. References to the "cult" of a particular Catholic saint, or the imperial cult of ancient Rome, for example, use this sense of the word. While the literal and original sense of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Webster Leadbeater
Charles Webster Leadbeater (; 16 February 1854 – 1 March 1934) was a member of the Theosophical Society, Co-Freemasonry, author on occult subjects and co-initiator with J. I. Wedgwood of the Liberal Catholic Church. Originally a priest of the Church of England, his interest in spiritualism caused him to end his affiliation with Anglicanism in favour of the Theosophical Society, where he became an associate of Annie Besant. He became a high-ranking officer of the Society and remained one of its leading members until his death in 1934, writing over 60 books and pamphlets and maintaining regular speaking engagements. Early life Leadbeater was born in Stockport, Cheshire, in 1854. His father, Charles, was born in Lincoln and his mother Emma was born in Liverpool. He was an only child. By 1861, the family had relocated to London, where his father was a railway contractor's clerk. In 1862, when Leadbeater was eight years old, his father died from tuberculosis. Four years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Scott-Elliot
William Scott-Elliot (sometimes incorrectly spelled Scott-Elliott) (1849–1919) was a theosophist who elaborated Helena Blavatsky's concept of root races in several publications, most notably ''The Story of Atlantis'' (1896) and ''The Lost Lemuria'' (1904), later combined in 1925 into a single volume called ''The Story of Atlantis and the Lost Lemuria''. In 1893 he married Matilda (Maude) Louise Travers (1859-1929), daughter of Dr Robert Boyle Travers F.R.C.S., of Farsid Lodge, Rostellan, County Cork, Ireland. Theosophical writings Scott-Elliot was an East India Merchant and amateur anthropologist. An early member of the London Lodge of the Theosophical society, in 1893 he wrote ''The Evolution of Humanity'', issued as part of the Transactions of the London Lodge (issue 17). Scott-Elliot came into contact with theosophist Charles Webster Leadbeater who said he received knowledge about ancient Atlantis and Lemuria from the Theosophical Masters by "astral clairvoyance." Leadbeater t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperborea
In Greek mythology, the Hyperboreans ( grc, Ὑπερβόρε(ι)οι, ; la, Hyperborei) were a mythical people who lived in the far northern part of the known world. Their name appears to derive from the Greek , "beyond Boreas" (the God of the North Wind), although some scholars prefer a derivation from ("to carry over"). Despite their location in an otherwise frigid part of the world, the Hyperboreans were believed to inhabit a sunny, temperate, and divinely-blessed land. In many versions of the story, they lived north of the Riphean Mountains, which shielded them from the effects of the cold North Wind. The oldest myths portray them as the favorites of Apollo, and some ancient Greek writers regarded the Hyperboreans as the mythical founders of Apollo's shrines at Delos and Delphi. Later writers disagreed on the existence and location of the Hyperboreans, with some regarding them as purely mythological, and others connecting them to real-world peoples and places in no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes. Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the female or male. For example, the great majority of tunicata, tunicates, pulmonate molluscs, opisthobranch, earthworms, and slugs are hermaphrodites. Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species and to a lesser degree in other vertebrates. Most plants are also hermaphrodites. Animal species having different sexes, male and female, are called Gonochorism, gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphrodite. There are also species where hermaphrodites exist alongside males (called androdioecy) or alongside females (called gynodioecy), or all three exist in the same species ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Race
Root races are stages in human evolution in the esoteric cosmology of theosophist Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, as described in her book ''The Secret Doctrine'' (1888). These races existed mainly on now-lost continents. Blavatsky's model was developed by later theosophists, most notably William Scott-Elliot in ''The Story of Atlantis'' (1896) and ''The Lost Lemuria'' (1904). Annie Besant further developed the model in ''Man: Whence, How and Whither'' (1913). Both Besant and Scott-Elliot relied on information from Charles Webster Leadbeater obtained by "astral clairvoyance". Further elaboration was provided by Rudolf Steiner in ''Atlantis and Lemuria'' (1904). Rudolf Steiner, and subsequent theosophist authors, have called the time periods associated with these races Epochs (Steiner felt that the term "race" was not adequate anymore for modern humanity). Sources According to historian James Webb, the occult concept of succeeding prehistoric races, as later adopted by Blavatsky, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
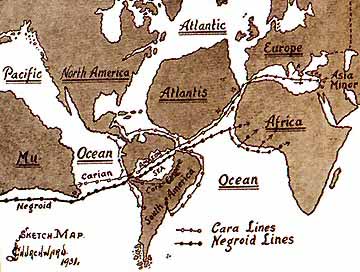
Mu (mythical Lost Continent)
Mu is a mythical lost continent introduced by Augustus Le Plongeon (1825–1908), who identified the "Land of Mu" with Atlantis. The name was subsequently identified with the hypothetical land of Lemuria by James Churchward (1851–1936), who asserted that it was located in the Pacific Ocean before its destruction. The place of Mu in both pseudoscience and fantasy fiction is discussed in detail in ''Lost Continents'' (1954, 1970) by L. Sprague de Camp. Geologists dismiss the existence of Mu and the lost continent of Atlantis as physically impossible, as a continent can neither sink nor be destroyed in the short period of time asserted in legends and folklore and literature about these places. Mu's existence is considered to have no factual basis. History of the concept Augustus Le Plongeon The mythical idea of the "Land of Mu" first appeared in the works of the British-American antiquarian Augustus Le Plongeon (1825–1908), after his investigations of the Maya ruins in Yucatán. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Churchward
James Churchward (27 February 1851 – 4 January 1936) was a British occult writer, inventor, engineer, and fisherman. Churchward is most notable for proposing the existence of a lost continent, called " Mu," in the Pacific Ocean. His writings on Mu are considered to be pseudoscience. Gardner, Martin. (1957). ''Fads and Fallacies in the Name of Science''. Dover Publications. p. 170. Fagan, Brian M. (1996). ''The Oxford Companion to Archaeology''. Oxford University Press. p. 582. Life Churchward was born in Bridestow, Okehampton, Devon at Stone House to Henry and Matilda (née Gould) Churchward. James had four brothers and four sisters. In November 1854, his father Henry died and the family moved in with Matilda's parents in the hamlet of Kigbear, near Okehampton. Census records indicate the family moved to London when James was 18, after his maternal grandfather George Gould died. His younger brother Albert Churchward (1852–1925) became a Masonic author. Churchward went out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthroposophy
Anthroposophy is a spiritualist movement founded in the early 20th century by the esotericist Rudolf Steiner that postulates the existence of an objective, intellectually comprehensible spiritual world, accessible to human experience. Followers of anthroposophy aim to engage in spiritual discovery through a mode of thought independent of sensory experience. While much of anthroposophy is pseudoscientific, proponents claim to present their ideas in a manner that is verifiable by rational discourse and say that they seek precision and clarity comparable to that obtained by scientists investigating the physical world. Anthroposophy has its roots in German idealism, mystical philosophies, and pseudoscience including racist pseudoscience. Steiner chose the term ''anthroposophy'' (from Greek , 'human', and '' sophia'', 'wisdom') to emphasize his philosophy's humanistic orientation. He defined it as "a scientific exploration of the spiritual world", Others have variously called it a "ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
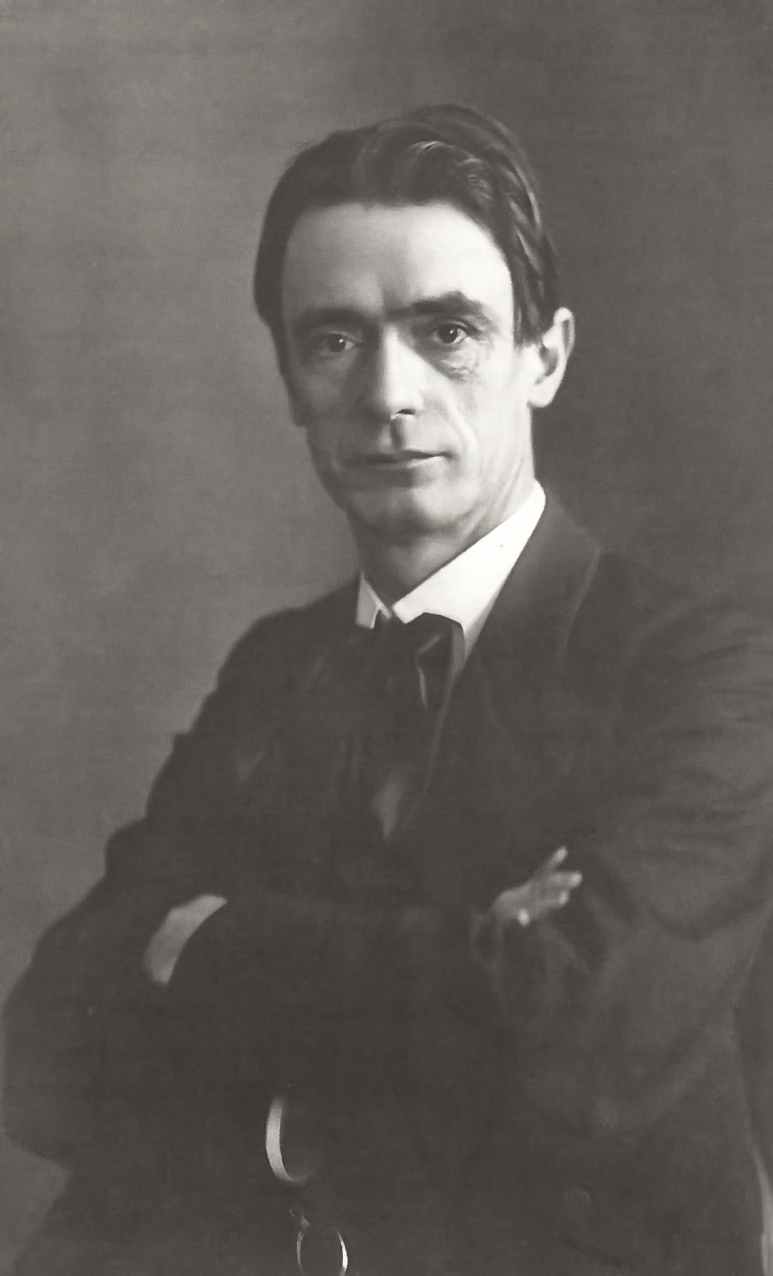
Rudolf Steiner
Rudolf Joseph Lorenz Steiner (27 or 25 February 1861 – 30 March 1925) was an Austrian occultist, social reformer, architect, esotericist, and claimed clairvoyant. Steiner gained initial recognition at the end of the nineteenth century as a literary critic and published works including ''The Philosophy of Freedom''. At the beginning of the twentieth century he founded an esoteric spiritual movement, anthroposophy, with roots in German idealist philosophy and theosophy. Many of his ideas are pseudoscientific. He was also prone to pseudohistory. In the first, more philosophically oriented phase of this movement, Steiner attempted to find a synthesis between science and spirituality. His philosophical work of these years, which he termed "spiritual science", sought to apply what he saw as the clarity of thinking characteristic of Western philosophy to spiritual questions, differentiating this approach from what he considered to be vaguer approaches to mysticism. In a second pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |