|
Leithaprodersdorf
Leithaprodersdorf, also (Leitha-Prodersdorf; hr, Lajtaproderštof, hu, Lajtapordány, Lajtha-Pordány) is an Austrian town located in the Eisenstadt-Umgebung district of the state of Burgenland. The town is located on Burgenland's northern border with Lower Austria, near the state capital of Eisenstadt. History Although the first historical mention of Leithaprodersdorf was in 1232, there is evidence of habitation in the area which predates the historical mention by several hundred years, dating back to the time of the Roman Empire. Previous archaeological expeditions have noted that the area around Leithaprodersdorf was heavily settled in ancient Roman times. Ancient archaeological finds in the area include two large estates and a watchtower. Additionally, the estates' graveyards have also been discovered, with some graves and even a few grave stones still intact. The names on the extant gravestones are Celtic-Roman in nature and are thought to date from between the 1st and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisenstadt-Umgebung
The Bezirk Eisenstadt-Umgebung ( hr, Kotar Željezno-okolica) is an administrative district (''Bezirk'') in the federal state of Burgenland, Austria. The area of the district is 455.5 km², with a population of 44,257 (2022), and a population density of 98 persons per km². The administrative center of the district is Eisenstadt ( hr, Željezno), itself a Statutory city (Austria), statutory city outside of the district. Administrative divisions The district consists of the below municipalities and towns: * Breitenbrunn, Austria, Breitenbrunn (1,907) * Donnerskirchen (1,745) * Großhöflein (1,940) * Hornstein, Austria, Hornstein (2,769) * Klingenbach (1,167) * Leithaprodersdorf (1,159) * Loretto, Austria, Loretto (463) * Mörbisch am See (2,322) * Müllendorf (1,326) * Neufeld an der Leitha (3,187) * Oggau am Neusiedler See (1,807) * Oslip (1,279) * Purbach am Neusiedlersee (2,701) * Sankt Margarethen im Burgenland (2,711) * Schützen am Gebirge (1,400) * Siegendorf (2,959) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wulkaprodersdorf
Wulkaprodersdorf ( hr, Vulkaprodrštof, hu, Vulkapordány, Vulka-Pordány) is a town in the district of Eisenstadt-Umgebung in the Austrian state of Burgenland. Population See also * Wulka * Leithaprodersdorf Leithaprodersdorf, also (Leitha-Prodersdorf; hr, Lajtaproderštof, hu, Lajtapordány, Lajtha-Pordány) is an Austrian town located in the Eisenstadt-Umgebung district of the state of Burgenland. The town is located on Burgenland's northern borde ... References Cities and towns in Eisenstadt-Umgebung District {{Burgenland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seibersdorf
Seibersdorf is an Austrian market town with 1,283 residents in the District of Baden in Lower Austria. Geography Seibersdorf lies in the industrial belt of Lower Austria. The municipality has an area of 20.2 km², 9.36 percent of which is forested. Seibersdorf contains the following districts: Deutsch-Brodersdorf, Seibersdorf. History In antiquity, the area was part of the Roman province of Pannonia. Located in the Austrian heartland, Lower Austria played a key part in much of Austrian history. Population Infrastructure Seibersdorf is best known as the site of Austrian Research Centers, now called the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT). The International Atomic Energy Agency also operates laboratories within the same premises. See also * Leithaprodersdorf Leithaprodersdorf, also (Leitha-Prodersdorf; hr, Lajtaproderštof, hu, Lajtapordány, Lajtha-Pordány) is an Austrian town located in the Eisenstadt-Umgebung district of the state of Burgenland. The town is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leitha
The Leitha (; or , formerly ; Czech and sk, Litava) is a river in Austria and Hungary, a right tributary of the Danube. It is long ( including its source river Schwarza). Its basin area is . Etymology The ''Lithaha'' River in the Carolingian Avar March was first mentioned in an 833 deed issued by Louis the German, son of the Carolingian emperor Louis the Pious and ruler over the stem duchy of Bavaria. The Old High German name ''lît'' probably referred to a Pannonian ( Illyrian) denotation for "mud", as maintained in the former Hungarian name ''Sár'' (cf. ''mocsár:'' swamp). Course The Leitha rises in Lower Austria at the confluence of its two headstreams, the Schwarza, discharging the Schneeberg, Rax and Schneealpe ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps, and the Pitten. Between Ebenfurth and Leithaprodersdorf, and between Bruck an der Leitha and Gattendorf, the Leitha forms part of the border between the Austrian states of Lower Austria and Burgenland. East of Nickels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Stone
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually Rock (geology), stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christianity, Christian, Judaism, Jewish, and Islam, Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, date of birth, and date of death inscribed on it, along with a personal message, or prayer, but may contain pieces of funerary art, especially details in stone relief. In many parts of Europe, insetting a photograph of the deceased in a frame is very common. Use The stele (plural stele, stelae), as it is called in an archaeological context, is one of the oldest forms of funerary art. Originally, a tombstone was the stone lid of a stone coffin, or the coffin itself, and a gravestone was the stone slab that was laid over a grave (burial), grave. Now, all three terms are also used for markers placed at the head of the grave. Some graves in the 18th century also contained footstones to demarcat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities And Towns In Eisenstadt-Umgebung District
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and Urban density, densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, Public utilities, utilities, land use, Manufacturing, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wulka
The Wulka () is a river of Burgenland, Austria. Its basin area is . The river springs near Forchtenstein and the border to Lower Austria. It flows through Trausdorf an der Wulka and discharges near Donnerskirchen into Lake Neusiedl, in former times a runoff-free lake, but nowadays drained by an artificial channel, the , into the Danube. An article in the Journal of Hydrology stated that "Waste water treatment Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environme ... plants contributed up to 68% of monthly flow of River Wulka into the lake." See also * Rosalia Mountains References {{Authority control Rivers of Austria Rivers of Burgenland Tourist attractions in Burgenland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
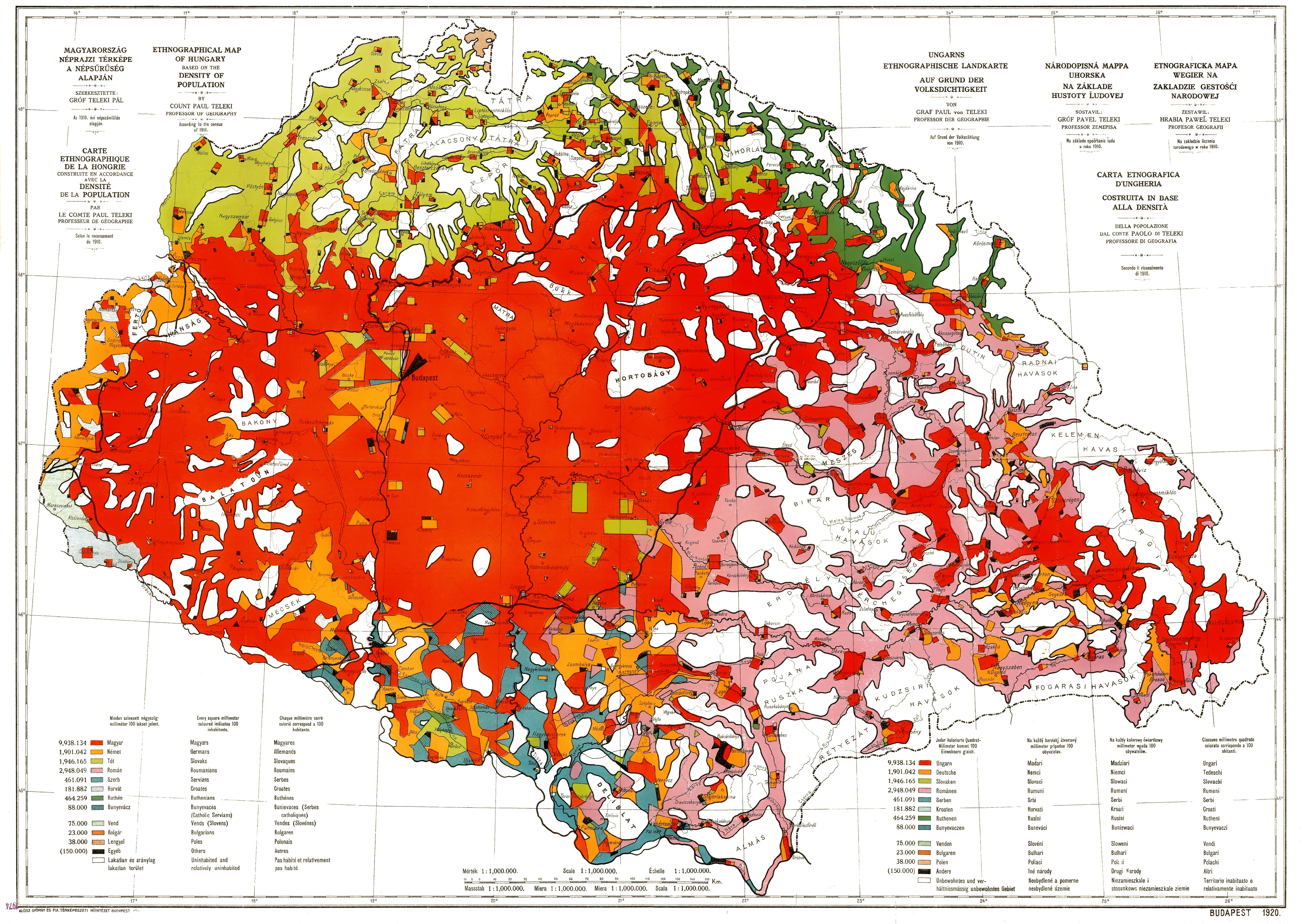
Magyarization
Magyarization ( , also ''Hungarization'', ''Hungarianization''; hu, magyarosítás), after "Magyar"—the Hungarian autonym—was an assimilation or acculturation process by which non-Hungarian nationals living in Austro-Hungarian Transleithania adopted the Hungarian national identity and language in the period between the Compromise of 1867 and Austria-Hungary's dissolution in 1918. Magyarization occurred both voluntarily and as a result of social pressure, and was mandated in certain respects by specific government policies. Before the World War I, only three European countries declared ethnic minority rights, and enacted minority-protecting laws: the first was Hungary (1849 and 1868), the second was Austria (1867), and the third was Belgium (1898). In contrast, the legal systems of other pre-WW1 era European countries did not allow the use of European minority languages in primary schools, in cultural institutions, in offices of public administration and at the legal courts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike (construction)
A levee (), dike ( American English), dyke ( Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlines. The purpose of a levee is to keep the course of rivers from changing and to protect against flooding of the area adjoining the river or coast. Levees can be naturally occurring ridge structures that form next to the bank of a river, or be an artificially constructed fill or wall that regulates water levels. Ancient civilizations in the Indus Valley, ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and China all built levees. Today, levees can be found around the world, and failures of levees due to erosion or other causes can be major disasters. Etymology Speakers of American English (notably in the Midwest and Deep South) use the word ''levee'', from the French word (from the feminine past participle of the French verb , 'to raise'). It ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentric
In geometry, two or more objects are said to be concentric, coaxal, or coaxial when they share the same center or axis. Circles, regular polygons and regular polyhedra, and spheres may be concentric to one another (sharing the same center point), as may cylinders (sharing the same central axis). Geometric properties In the Euclidean plane, two circles that are concentric necessarily have different radii from each other.. However, circles in three-dimensional space may be concentric, and have the same radius as each other, but nevertheless be different circles. For example, two different meridians of a terrestrial globe are concentric with each other and with the globe of the earth (approximated as a sphere). More generally, every two great circles on a sphere are concentric with each other and with the sphere. By Euler's theorem in geometry on the distance between the circumcenter and incenter of a triangle, two concentric circles (with that distance being zero) are the cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |