|
Lake Ojibway
Lake Ojibway was a prehistoric lake in what is now northern Ontario and Quebec in Canada. Ojibway was the last of the great proglacial lakes of the last ice age. Comparable in size to Lake Agassiz (to which it was likely linked), and north of the Great Lakes, it was at its greatest extent c. 8,500 years BP. The former lakebed forms the modern Clay Belt, an area of fertile land. Lake Ojibway was relatively short-lived. The lake drained in what must have been a catastrophic and dramatic manner around 8,200 years BP. One hypothesis is that a weakening ice dam separating it from Hudson Bay broke, as the lake was roughly above sea level. A comparable mechanism produced the Missoula floods that created the channeled scablands of the Columbia River basin. A recent analysis states it has not been conclusively determined whether the lake drained by a breach of the ice dam, by water spilling over the glacier, or by a flood under the glacier. It is also not conclusively known whether t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Agassiz
Lake Agassiz was a large glacial lake in central North America. Fed by glacial meltwater at the end of the last glacial period, its area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined. First postulated in 1823 by William H. Keating, it was named by Warren Upham in 1879 after Louis Agassiz, when Upham recognized that the lake was formed by glacial action. Geological progression During the last ice age, northern North America was covered by an ice sheet, which alternately advanced and retreated with variations in the climate. This continental ice sheet formed during the period now known as the Wisconsin glaciation, and covered much of central North America between 30,000 and 10,000 years ago. As the ice sheet disintegrated, its meltwaters created an immense proglacial lake. Around 13,000 years ago, this lake came to cover much of what are now southeastern Manitoba, northwestern Ontario, northern Minnesota, eastern North Dakota, and Saskatchewan. At its greatest exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlement and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midcontinent Rift System
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North American craton, began to split apart during the Mesoproterozoic era of the Precambrian, about 1.1 billion years ago. The rift failed, leaving behind thick layers of igneous rock that are exposed in its northern reaches, but buried beneath later sedimentary formations along most of its western and eastern arms. Those arms meet at Lake Superior, which is contained within the rift valley. The lake's north shore in Ontario and Minnesota defines the northern arc of the rift. From the lake, the rift's eastern arm trends south to central lower Michigan, and possibly into Indiana, Ohio, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Alabama. The western arm runs from Lake Superior southwest through portions of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, and Nebraska to northeastern Kansas, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Maumee
Lake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 17,500 calendar years, or 14,000 Radiocarbon Years Before Present (RCYBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey. Origin As the ice sheet retreated at the end of the last ice age, it left meltwater in a previously existing low-lying area that was the valley of an eastward-flowing river known as the Erigan River that probably emptied into the Atlantic Ocean following the route of today's Saint Lawrence River. Some geologists think that the Erigan could have been a downstream segment of the preglacial Teays River system. The glaciers destroyed or disturbed most of the preglacial drainage patterns and enlarged and deepened the Erigan basin. Lake Maumee is the first of a series of glacial lakes which occupied the Erie basin. It was prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Chicago
Lake Chicago was a prehistoric proglacial lake that is the ancestor of what is now known as Lake Michigan, one of North America's five Great Lakes. Fed by retreating glaciers, it drained south through the Chicago Outlet River. Origin The city of Chicago lies in a broad plain that, hundreds of millions of years ago, was a great interior basin covered by warm, shallow seas. These seas covered portions of North America from the Arctic Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. Evidence of these seas is found in the fossils of coral, such as those unearthed in Illinois quarries at Stony Island Avenue, Thornton Quarry, and McCook, Illinois, or at 18th Street and Damen Avenue in Chicago. Evidence may also be found in the fossils in the Niagara limestone bedrock found throughout the Chicago area and extending all the way to Niagara, New York. Much later, the polar ice cap crept four times down across the continent, covering the region with ice to a depth of a mile (1500 m) or more. As the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Algonquin
Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing. The lake varied in size, but it was at its biggest during the post-glacial period and gradually shrunk to the current Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. About 7,000 years ago, the lake was replaced by Lake Chippewa and Lake Stanley as the glaciers retreated and 3,000 years later by the current Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Superior. Physiography About 11,000 years before present, the Laurentian Glacier had retreated northward, forming a boundary across the northern edges of Lake Superior and Lake Huron. The water level was at above sea level, creating a single body of water in the three basins of Lake Michigan, Lake Huron and Lake Superior.Bulletin 4, The Glacial Lakes around Michigan; William R. Farrand, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champlain Sea
The Champlain Sea (french: Mer de Champlain) was a prehistoric inlet of the Atlantic Ocean into the North American continent, created by the retreating ice sheets during the closure of the last glacial period. The inlet once included lands in what are now the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario, as well as parts of the American states of New York and Vermont. Origins The mass of ice from the continental ice sheets had depressed the rock beneath it over millennia. At the end of the last glacial period, while the rock was still depressed, the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa River valleys, as well as modern Lake Champlain, at that time the Lake Vermont, were below sea level and flooded with rising worldwide sea levels, once the ice no longer prevented the ocean from flowing into the region. As the land gradually rose again, in the process known as isostatic rebound, the sea coast gradually retreated to its current location. The sea lasted from about 13,000 years ago to ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
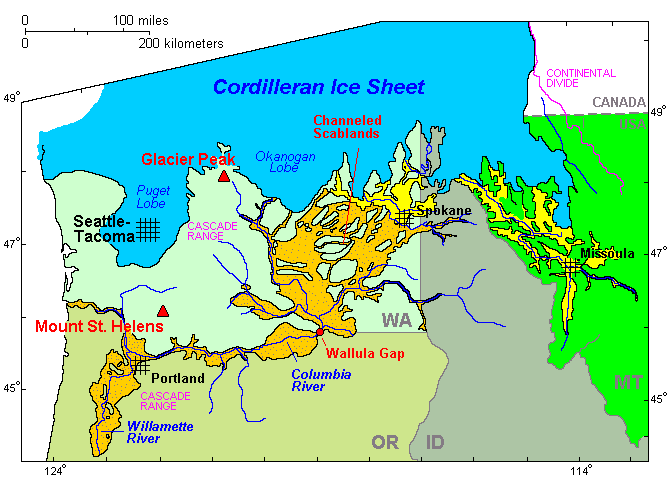
Lake Missoula
Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. The lake measured about and contained about of water, half the volume of Lake Michigan. The ''Glacial Lake Missoula National Natural Landmark'' is located about 110 kilometres (68 mi) northwest of Missoula, Montana, at the north end of the Camas Prairie Valley, just east of Montana Highway 382 and Macfarlane Ranch. It was designated as a National Natural Landmark in 1966 because it contains the great ripples (often measuring high and long) that served as a strong supporting element for J Harlen Bretz's contention that Washington State's Channeled Scablands were formed by repeated cataclysmic floods over only about 2,000 years, rather than through the millions of years of erosion that had been previously assumed. The lake was the result of an ice dam on the Clark Fork caused by the southern encroachment of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Lake Outburst Flood
A glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) is a type of outburst flood caused by the failure of a dam containing a glacial lake. An event similar to a GLOF, where a body of water contained by a glacier melts or overflows the glacier, is called a jökulhlaup. The dam can consist of glacier ice or a terminal moraine. Failure can happen due to erosion, a buildup of water pressure, an avalanche of rock or heavy snow, an earthquake or cryoseism, volcanic eruptions under the ice, or massive displacement of water in a glacial lake when a large portion of an adjacent glacier collapses into it. Increasing glacial melting because of climate change, alongside other environmental effects of climate change (i.e permafrost melting) mean that regions with glaciers are likely to see increased flooding risks from GLOFs. This is especially true in the Himalayas where geologies are more active. Definition A glacial lake outburst flood is a type of outburst flood occurring when water dammed by a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrrell Sea
The Tyrrell Sea, named after Canada, Canadian geologist Joseph Tyrrell, is another name for prehistoric Hudson Bay, namely as it existed during the retreat of the Laurentide Ice Sheet. Roughly 8,000 years before present, BP, the Laurentide Ice Sheet thinned and split into two lobes, one centred over Quebec-Labrador, the other over District of Keewatin, Keewatin. This drained Glacial Lake Ojibway, a massive proglacial lake south of the ice sheet, leading to the formation of the early Tyrrell Sea. The weight of the ice had isostasy, isostatically depressed the surface as much as 270-280 metres, m below its current level, making the Tyrrell Sea much larger than modern Hudson Bay. Indeed, in some places the shoreline was 100 to 250 km farther inland than at present."Geomorphology From Spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Cooling
Global cooling was a conjecture, especially during the 1970s, of imminent cooling of the Earth culminating in a period of extensive glaciation, due to the cooling effects of aerosols or orbital forcing. Some press reports in the 1970s speculated about continued cooling; these did not accurately reflect the scientific literature of the time, which was generally more concerned with warming from an enhanced greenhouse effect. In the mid 1970s, the limited temperature series available suggested that the temperature had decreased for several decades up to then. As longer time series of higher quality became available, it became clear that global temperature showed significant increases overall. Introduction: general awareness and concern By the 1970s, scientists were becoming increasingly aware that estimates of global temperatures showed cooling since 1945, as well as the possibility of large scale warming due to emissions of greenhouse gases. In the scientific papers which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |