Lake Chicago on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lake Chicago was a prehistoric

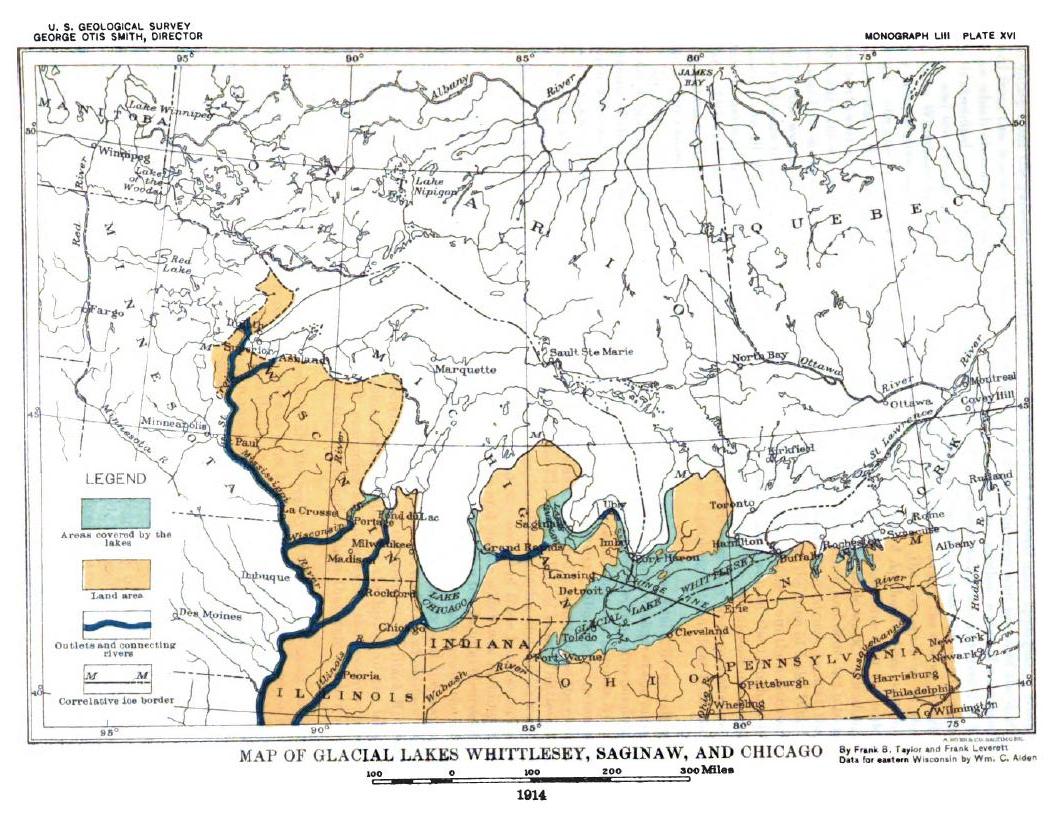 The ice continued northward forming the next phase of Lake Chicago. The lake level remained at 640' above sea level, but the ice margin was a third of the way north, opening a channel across
The ice continued northward forming the next phase of Lake Chicago. The lake level remained at 640' above sea level, but the ice margin was a third of the way north, opening a channel across  When the ice retreated northward enough to open the
When the ice retreated northward enough to open the
Oak Park - Ancient Lake Chicago & Continental Divide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chicago, Lake Former lakes of the United States Geology of Illinois Geology of Indiana Geological history of the Great Lakes Proglacial lakes Lake Michigan Glacial lakes of the United States Geography of Chicago
proglacial lake
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around the ...
that is the ancestor of what is now known as Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
, one of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
's five Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. Fed by retreating glaciers, it drained south through the Chicago Outlet River.
Origin
The city ofChicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
lies in a broad plain that, hundreds of millions of years ago, was a great interior basin covered by warm, shallow seas. These seas covered portions of North America from the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
. Evidence of these seas is found in the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s of coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
, such as those unearthed in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
quarries
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their environ ...
at Stony Island Avenue
Stony Island Avenue is a major street on South Side of the city of Chicago, designated 1600 East in Chicago's street numbering system. It runs from 56th Street south to the Calumet River. Stony Island Avenue continues sporadically south of the Ca ...
, Thornton Quarry
Thornton Quarry is one of the largest construction aggregate, aggregate quarry, quarries in the world, located in Thornton, Illinois just south of Chicago. The quarry is 1.5 miles (2.5 km) long, 0.5 miles (1 km) wide, and 450 feet (137 ...
, and McCook, Illinois
McCook is a village in Cook County, Illinois, United States, and is an industrial suburb of Chicago. As of the 2020 census, the village population was 249, which is the lowest population of all municipalities in the county.
History
McCook was na ...
, or at 18th Street and Damen Avenue in Chicago. Evidence may also be found in the fossils in the Niagara limestone bedrock found throughout the Chicago area and extending all the way to Niagara, New York
Niagara is a town in Niagara County, New York, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town had a total population of 8,378. The town is named after the famous waterfall Niagara Falls.
The Town of Niagara is the neighbor to the City of Niaga ...
.
Much later, the polar ice cap
A polar ice cap or polar cap is a high-latitude region of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite that is covered in ice.
There are no requirements with respect to size or composition for a body of ice to be termed a polar ice cap, nor a ...
crept four times down across the continent, covering the region with ice to a depth of a mile (1500 m) or more. As the climate changed, the ice melted, the last great ice flow (the Wisconsin Glacier
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
period, which covered much of northern half of North America) retreated, and an outlet for the melting water developed through the Sag River and the Des Plaines River
The Des Plaines River () is a river that flows southward for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed May 13, 2011 through southern Wisconsin and northern Illinois''American Her ...
Valley around Mt. Forest, in the area known as the Palos. The Kankakee Torrent
The Kankakee Torrent was a catastrophic flood that occurred about 19,000 calibrated years agoCurry, B.B., Hajic, E.R., Clark, J.A., Befus, K.M., Carrell, J.E. and Brown, S.E., 2014. "The Kankakee Torrent and other large meltwater flooding ev ...
poured through those valleys, eventually leaving behind the prehistoric Lake Chicago, the ancestor of Lake Michigan.
Chronology
13,000 to 11,000 years before present The earliest formation of Lake Chicago occurred when the Michigan Lobe of the glacier retreated northward into the basin of modernLake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
, ca 13,000 years ago.Bulletin 4, The GLACIAL LAKES around Michigan; William R. Farrand, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan; 1988 The edge of the retreating glacier formed moraines
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
, the Park Moraine
A park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are green spaces set aside for recreation inside towns and cities. N ...
in present-day Illinois and the Lake Borders Moraine
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
in Indiana and Michigan.The Illinois Ice Lobe; Frank Leverett; U.S. Geological Survey, Monograph, #38; Government Printing Office; Washington, D.C.; 1899, Plates 14, 16, 53
Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, draining the Lake Saginaw
Lake Saginaw occupied the basin of Saginaw Bay. There were two periods when it was an independent lake, not associated with a larger body of water in the Huron basin. The first Lake Saginaw was a contemporary of the last stages of Lake Maumee. ...
and Lake Whittlesey
Lake Whittlesey was a proglacial lake that was an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 years ago. As the Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin Glacier retreated at the end of the last ice age, it left melt-water in a previously-existing ...
proglacial lakes
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around the ...
in the Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrology, Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the , Strait ...
and Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
basins.
Mohawk River
The Mohawk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 river in the U.S. state of New York. It is the largest tributary of the Hudson River. The Mohawk f ...
valley, the waters in the Lake Huron and Lake Erie basin diverted from the Michigan outlet, leaving Lake Chicago as a headwaters lake. Continued northward migration of the glacier set the stage for the next major proglacial lakes in the Lake Michigan basin as Lake Algonquin
Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing ...
and then Nipissing Great Lakes
Nipissing Great Lakes was a prehistoric proglacial lake. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Georgian Bay and Lake Michigan. It formed about 7,500 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the L ...
.
Size
Extending somewhat further south, west and east than Lake Michigan, Lake Chicago extended west to present dayLa Grange, Illinois
''(the barn)''
, nickname =
, motto = ''Tradition & Pride – Moving Forward''
, anthem = ''My La Grange'' by Jimmy Dunne
, image_map = File:Cook County Illinois Incorporated and Unincorporated areas La Grange Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 26 ...
and south beyond Homewood and Lansing, Illinois
Lansing is a village in Cook County, Illinois, United States. Lansing is a south suburb of Chicago. The population was 29,076 at the 2020 census.
Geography
Lansing is located at (41.565785, -87.545791). It is south of the Chicago city limits a ...
, completely covering what is now Northwest Indiana
Northwest Indiana, nicknamed The Region after the Calumet Region, comprises Lake, Porter, LaPorte, Newton and Jasper counties in Indiana. This region neighbors Lake Michigan and is part of the Chicago metropolitan area. According to the 2020 Ce ...
, including the cities of Hammond and Gary, Indiana
Gary is a city in Lake County, Indiana, United States. The city has been historically dominated by major industrial activity and is home to U.S. Steel's Gary Works, the largest steel mill complex in North America. Gary is located along the ...
.
As the Wisconsin Glacier
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
continued to retreat, it created new outlets for the water in Lake Chicago, including Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Falls, ...
, and the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
. As these outlets were developed, a partial lake capture
In geology, lake capture is the process of capture (see Stream capture) of the waters collected in a lake by a neighbor river basin.
The occurrence of a lake capture is mainly controlled by the water balance at the lake's basin and the changes in ...
occurred and the water level in Lake Chicago began to drop in three observable stages of 15 to 20 feet (5–6 m) each. Eventually even the outlet to the southwest dried up, and the Des Plaines River overflowed into the basin that became Lake Michigan.
Outlet and beaches
As the Michigan Lobe of the Labradorean Ice Cap retreated northward, the area of Lake Chicago increased.Publication 9. Geological Series 7; Surface Geology and Agricultural Conditions of the Southern Peninsula of Michigan; Frank Leverett with a Chapter on Climate by C. F. Schneider; Michigan Geological and Biological Survey Lansing Michigan; 1911 Lake Chicago’s initial outlet was to the southwest through theDes Plaines River
The Des Plaines River () is a river that flows southward for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed May 13, 2011 through southern Wisconsin and northern Illinois''American Her ...
valley, thence down the Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the D ...
to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
. The highest beach is the Glenwood Shoreline
The Glenwood Shoreline is an ancient shoreline of the precursor to Lake Michigan, Lake Chicago. It is named after the town of Glenwood, Illinois. The shoreline was formed when the lake was higher during the last ice age, while ice blocked the Stra ...
, which is to above the level of Lake Michigan. There are two additional beaches formed when the Des Plaines outlet was abandoned for other outlets to the north and east: the Calumet Shoreline The Calumet Shoreline is an ancient shoreline of Lake Michigan located in the Lake Michigan Basin. It can be clearly seen as a sand ridge along Ridge Road south of Chicago. Closer to the lake from the Calumet Shoreline, there are the Tolleston sho ...
, about to above the current lake, and the Tolleston Beach to above Lake Michigan. The name Lake Chicago is used for the lake when it drains through the Des Plaines outlet. The Calumet and Tolleston Beach lake is Lake Algonquin
Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing ...
.
The outlet channel is more than wide and cuts through glacial deposits. Near the head of the channel, rock layers have been cut through. It is probable that the distinct beaches from Lake Chicago are the result of these rock layers giving way rapidly, dropping the lake level from higher to lower levels. After each stage, the next barrier remained solid, holding the lake stable and creating distinct beaches. If the outlet were formed by a steady erosion of the barrier, it would have been less likely that the well-defined beaches would have been created.
Along the eastern shore of Lake Michigan, the beaches of Lake Chicago have been destroyed by erosion, except the highest beach, much of which has also been destroyed. The best remaining segments are along the southern tip of Lake Michigan in Indiana.
Lake bed deposits
Lake Chicago covered only a narrow strip of land on the south and east side of modern Lake Michigan. FromHolland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
northward across the Lake Chicago, the lake bed extends 10 to 25 miles (16 to 40 km) inland. The widest expanse is almost entirely fine sand. There is more sand than clay in a narrow strip along the shore. The clayey portions have till at only a few inches depth. The offshore winds along the east shore of Lake Michigan have created sand dunes, burying the older glacial beaches and lake beds.
Today
Vast amounts of sand in spits,dunes
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, fl ...
and beach lines—particularly at the southern tip of Lake Michigan—were left behind by each of the three stages of lake level drop. Today, evidence of these vast sand deposits is still clearly visible. Northern Indiana, for example, contains the Indiana Dunes
Indiana Dunes National Park is a United States national park located in northwestern Indiana managed by the National Park Service. It was authorized by Congress in 1966 as the Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore and was redesignated as the nation ...
, and many of the Chicago area's trails and roads follow some of these ancient beach lines or ridges in the sand spits.
For example, Ridge Road from Homewood, Illinois, through Thornton and Lansing, Illinois
Lansing is a village in Cook County, Illinois, United States. Lansing is a south suburb of Chicago. The population was 29,076 at the 2020 census.
Geography
Lansing is located at (41.565785, -87.545791). It is south of the Chicago city limits a ...
, and then crossing the state border into Munster and Highland, Indiana, is one; Michigan City Road through Riverdale, Dolton, and Calumet City, Illinois, is another; LaGrange Road is another; Riverside Drive in Riverside; Ridgeland Avenue in Oak Park, or Grosse Point Road, Carpenter Road, and Ridge Avenue (The Rosehill Spit) in the Rogers Park/West Ridge neighborhood of Chicago, north of Devon Avenue and continuing north through Evanston, Illinois, are some others. Blue Island, Illinois
Blue Island is a city in Cook County, Illinois, located approximately south of Chicago's Loop. Blue Island is adjacent to the city of Chicago and shares its northern boundary with that city's Morgan Park neighborhood. The population was 22,558 ...
, and Stony Island were, literally, islands left behind as Lake Chicago's water level fell.
See also
References
External links
*Bretz, J.H. 1939. Geology of the Chicago Region, Part 1 - General. Illinois State Geological Survey, Bulletin 65. 118 pages. *Killey, Myrna M. 1998. Illinois' Ice Age Legacy. Illinois State Geological Survey GeoScience Education Series 14. 66 pages. *Willman, W.B. 1971. Summary of the Geology of the Chicago Area. Illinois State Geological Survey, Urbana, IL. Circular 460. 77 pages.Oak Park - Ancient Lake Chicago & Continental Divide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chicago, Lake Former lakes of the United States Geology of Illinois Geology of Indiana Geological history of the Great Lakes Proglacial lakes Lake Michigan Glacial lakes of the United States Geography of Chicago