|
Global Cooling
Global cooling was a conjecture, especially during the 1970s, of imminent cooling of the Earth culminating in a period of extensive glaciation, due to the cooling effects of aerosols or orbital forcing. Some press reports in the 1970s speculated about continued cooling; these did not accurately reflect the scientific literature of the time, which was generally more concerned with warming from an enhanced greenhouse effect. In the mid 1970s, the limited temperature series available suggested that the temperature had decreased for several decades up to then. As longer time series of higher quality became available, it became clear that global temperature showed significant increases overall. Introduction: general awareness and concern By the 1970s, scientists were becoming increasingly aware that estimates of global temperatures showed cooling since 1945, as well as the possibility of large scale warming due to emissions of greenhouse gases. In the scientific papers which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Cooling Map
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to: Entertainment * Global (Paul van Dyk album), ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003 * Global (Bunji Garlin album), ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007 * Global (Humanoid album), ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989 * Global (Todd Rundgren album), ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015 * Bruno J. Global, a character in the anime series ''The Super Dimension Fortress Macross'' Companies and brands Television * Global Television Network, in Canada ** Global BC, on-air brand of CHAN-TV, a television station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Okanagan, on-air brand of CHBC-TV, a television station in Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Toronto, a television station in Toronto ** Global Edmonton ** Global Calgary ** Global Montreal ** Global Maritimes ** Canwest Global, former parent company of Global Television Network * Global TV (Venezuela), a regional channel in Venezuela Other industries * Global (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
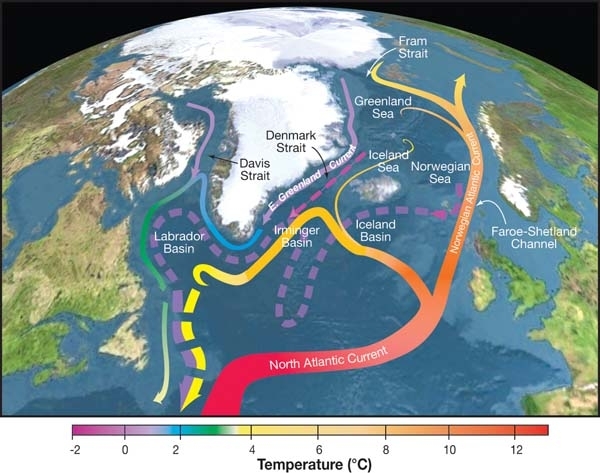
Shutdown Of Thermohaline Circulation
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is part of a global thermohaline circulation in the oceans and is the zonally integrated component of surface and deep currents in the Atlantic Ocean. It is characterized by a northward flow of warm, salty water in the upper layers of the Atlantic, and a southward flow of colder, deep waters. These "limbs" are linked by regions of overturning in the Nordic and Labrador Seas and the Southern Ocean, although the extent of overturning in the Labrador Sea is disputed. The AMOC is an important component of the Earth's climate system, and is a result of both atmospheric and thermohaline drivers. Climate change has the potential to weaken the AMOC through increases in ocean heat content and elevated freshwater flows from the melting ice sheets. Oceanographic reconstructions generally suggest that the AMOC is already weaker than it was before the Industrial Revolution, although there is a robust debate over the role of climate c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels may be burned to provide heat for use directly (such as for cooking or heating), to power engines (such as internal combustion engines in motor vehicles), or to generate electricity. Some fossil fuels are refined into derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and propane before burning. The origin of fossil fuels is the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, containing organic molecules created by photosynthesis. The conversion from these materials to high-carbon fossil fuels typically require a geological process of millions of years. In 2019, 84% of primary energy consumption in the world and 64% of its electricity was from fossil fuels. The large-scale burning of fossil fuels causes serious environmental damage. Over 80% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at Hydroelectric dam, hydroelectric dams, Irrigation, irrigation mist, Perfume, perfume from atomizers, smoke, steam from a kettle, Pesticide, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic aerosol. The liquid or solid particles in an aerosol have diameters typically less than micrometre, 1 μm (larger particles with a significant settling speed make the mixture a Suspension (chemistry), suspension, but the distinction is not clear-cut) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Aerosols
The term sulfate aerosols is used for a suspension of fine solid particles of a sulfate or tiny droplets of a solution of a sulfate or of sulfuric acid (hydrogen sulfate). They are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception of sea salt sulfate and gypsum dust particles). The two main sulfuric acid precursors are sulfur dioxide (SO2) from anthropogenic sources and volcanoes, and dimethyl sulfide (DMS) from biogenic sources, especially marine plankton. These aerosols can cause a cooling effect on earth. However the UNFCCC has noted that sulfate aerosols remain in the atmosphere for only a short amount of time in comparison to well-mixed greenhouse gases, and therefore their cooling is localized and temporary. Other side effects of sulfate aerosols in the environment include poor air quality.http://unfccc.int/essential_background/background_publications_htmlpdf/climate_change_information_kit/items/72.php UNFCC, Climate Change Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Climate Model
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources (radiation, latent heat). These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs (AGCM and OGCM) are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components. GCMs and global climate models are used for weather forecasting, understanding the climate, and forecasting climate change. Versions designed for decade to century time scale climate applications were originally created by Syukuro Manabe and Kirk Bryan at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) in Princeton, New Jersey. These models are based on the integration of a variety of fluid dynamical, chemical and sometimes biological equations. Terminology The acronym ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earth's energy balance. System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts, encompassing other factors that also influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Positive radiative forcing means Earth receives more incoming energy from sunlight than it radiates to space. This net gain of energy will cause warming. Conversely, negative radiative forcing means that Earth loses more energy to space than it receives from the sun, which produces cooling. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of space can be characterized by net zero radiative forcing and by a planetary equilibrium temperature. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Climate Model
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources (radiation, latent heat). These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs (AGCM and OGCM) are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components. GCMs and global climate models are used for weather forecasting, understanding the climate, and forecasting climate change. Versions designed for decade to century time scale climate applications were originally created by Syukuro Manabe and Kirk Bryan at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) in Princeton, New Jersey. These models are based on the integration of a variety of fluid dynamical, chemical and sometimes biological equations. Terminology The acronym ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to temperature and ' referring to salt content, factors which together determine the density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling en route, and eventually sinking at high latitudes (forming North Atlantic Deep Water). This dense water then flows into the ocean basins. While the bulk of it upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of about 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific. Extensive mixing therefore takes place between the ocean basins, reducing differences between them and making the Earth's oceans a global system. The water in these circuits transport both energy (in the form of heat) and mass (dissolved solids and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts to prepare IPCC reports. It draws the experts from nominations by governments and observer organisations. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC informs governments about the state of knowledge of climate change. It does this by examining all the relevant scientific literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an Event (probability theory), event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th Ed, (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', (Vol 1), 3rd Ed, (1968), Wiley, . The higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |