|
Lake Hannington
Lake Bogoria (formerly Lake Hannington) is a saline, alkaline lake that lies in a volcanic region in a half-graben basin south of Lake Baringo, Kenya, a little north of the equator. Lake Bogoria, like Lake Nakuru, Lake Elementeita, and Lake Magadi further south in the Rift Valley, and Lake Logipi to the north, is home at times to one of the world's largest populations of lesser flamingos. The lake is a Ramsar site and Lake Bogoria National Reserve has been a protected National Reserve since November 29, 1973. Lake Bogoria is shallow (about 10 m depth), and is about 34 km long by 3.5 km wide, with a drainage basin of 700 km2. It is Located in Baringo County. Local features include the Kesubo Swamp to the north and the Siracho Escarpment to the east, both within the National Reserve. The lake is also famous for geysers and hot springs along the bank of the lake and in the lake. In four locations around the lake can be observed at least 10 geysers, which erupt up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenyan Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues northward into Ethiopia. It was formed on the "Kenyan Dome" a geographical upwelling created by the interactions of three major tectonics: the Arabian, Nubian, and Somalian plates. In the past, it was seen as part of a "Great Rift Valley" that ran from Madagascar to Syria. Most of the valley falls within the former Rift Valley Province. The valley contains the Cherangani Hills and a chain of volcanoes, some of which are still active. The climate is mild, with temperatures usually below . Most rain falls during the March–June and October–November periods. The Tugen Hills to the west of Lake Baringo contain fossils preserved in lava flows from the period 14 to 4 million years ago. The relics of many hominids, ancestors of humans, have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
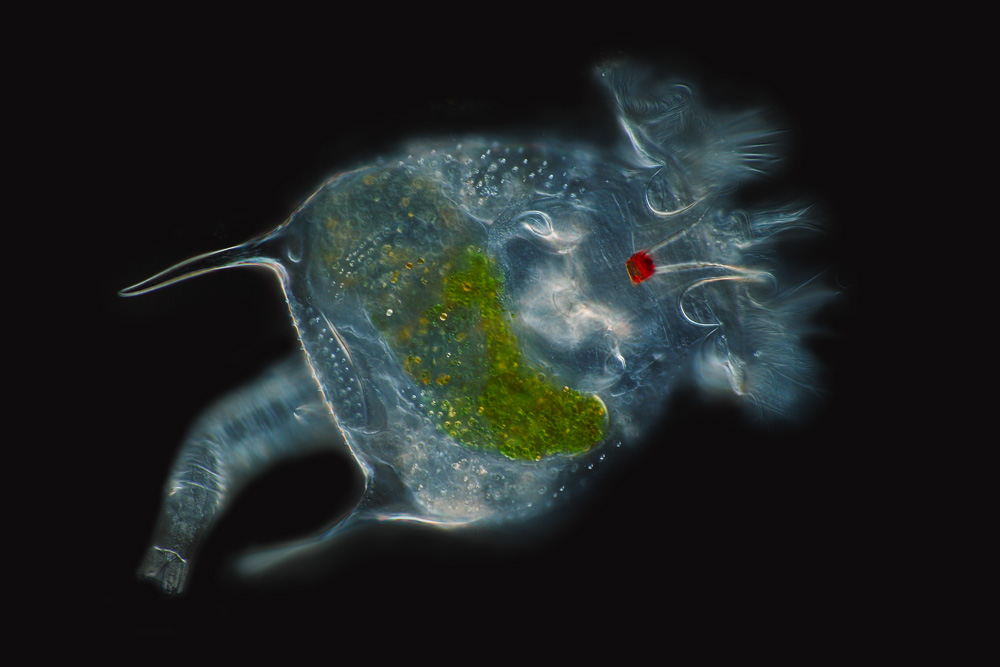
Brachionus Plicatilis
''Brachionus plicatilis'' is a euryhaline (tolerate a wide range of salinity) rotifer in the family ''Brachionidae'', and is possibly the only commercially important rotifer, being raised in the aquaculture industry as food for fish larvae. It has a broad distribution in salt lakes around the world and has become a model system for studies in ecology and evolution. Reproduction ''Brachionus'' species can normally reproduce asexually and sexually (cyclical parthenogenesis). Sexual reproduction (termed Mixis) is usually induced when population density increases. Mixis in Brachionus plicatilis has been shown to be induced by a density-dependent chemical cue. Genome size Haploid '1C' genome sizes in the ''Brachionus plicatilis'' species complex range at least from 0.056 to 0.416 pg. The complete mitochondrial genome of B. plicatilis sensu stricto NH1L has been sequenced. Cryptic species complex Brachionus plicatilis strains have long been divided into ‘L-’ and ‘S-type� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachionus
''Brachionus'' is a genus of planktonic rotifers occurring in freshwater, alkaline and brackish water. Species Species included in ''Brachionus'' include: * '' Brachionus amsterdamensis'' De Smet, 2001 * '' Brachionus angularis'' Gosse, 1851 * '' Brachionus asplanchnoides'' Charin, 1947 * ''Brachionus calyciflorus'' Pallas, 1766 * '' Brachionus diversicornis'' (Daday, 1883) * '' Brachionus havanaensis'' Rousselet, 1911 * ''Brachionus ibericus'' Ciros-Peréz, Gómez & Serra, 2001 * '' Brachionus leydigii'' Cohn, 1862 * '' Brachionus manjavacas'' Fontaneto, Giordani, Melone & Serra, 2007 * ''Brachionus nilsoni'' Ahlstrom * ''Brachionus plicatilis'' Müller, 1786 * ''Brachionus quadridentatus'' Hermann, 1783 * ''Brachionus rotundiformis'' Tschugunoff, 1921 * ''Brachionus rubens'' Ehrenberg, 1838 * ''Brachionus urceolaris'' Müller, 1773 * ''Brachionus variabilis'' Hempel, 1896 Use Rotifers such as ''Brachionus calyciflorus'' are favored test animals in aquatic toxicology because o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotifer
The rotifers (, from the Latin , "wheel", and , "bearing"), commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703. Most rotifers are around long (although their size can range from to over ), and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species. Some rotifers are free swimming and truly planktonic, others move by inchworming along a substrate, and some are sessile, living inside tubes or gelatinous holdfasts that are attached to a substrate. About 25 species are colonial (e.g., '' Sinantherina semibullata''), either sessile or planktonic. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton, being a major foodsource and with many species also contributing to the decomposition of soil organic matter. Most species of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirulina (dietary Supplement)
Spirulina is a biomass of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) that can be consumed by humans and animals. The three species are '' Arthrospira platensis'', ''A. fusiformis'', and ''A. maxima''. Cultivated worldwide, ''Arthrospira'' is used as a dietary supplement or whole food. It is also used as a feed supplement in the aquaculture, aquarium, and poultry industries.Vonshak, A. (ed.). ''Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira): Physiology, Cell-biology and Biotechnology.'' London: Taylor & Francis, 1997. Etymology and ecology The species ''A. maxima'' and ''A. platensis'' were once classified in the genus ''Spirulina''. The common name, spirulina, refers to the dried biomass of ''A. platensis'', which belongs to photosynthetic bacteria that cover the groups Cyanobacteria and Prochlorophyta. Scientifically, a distinction exists between spirulina and the genus ''Arthrospira''. Species of ''Arthrospira'' have been isolated from alkaline brackish and saline waters in tropical and subtro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in plast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
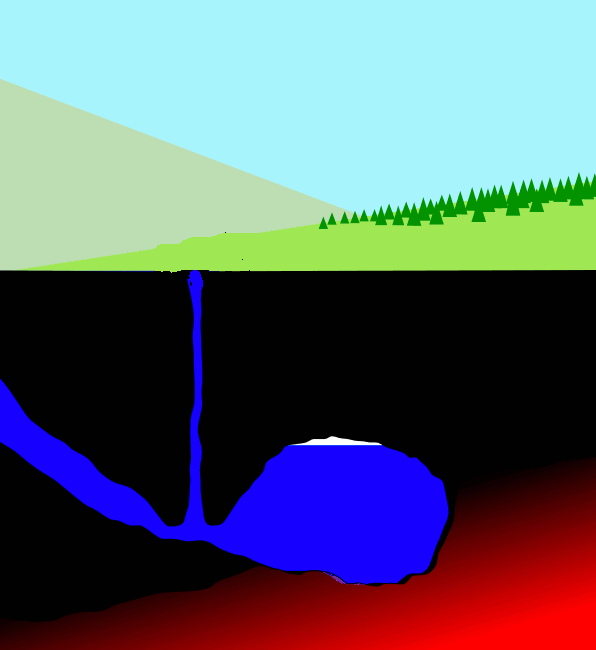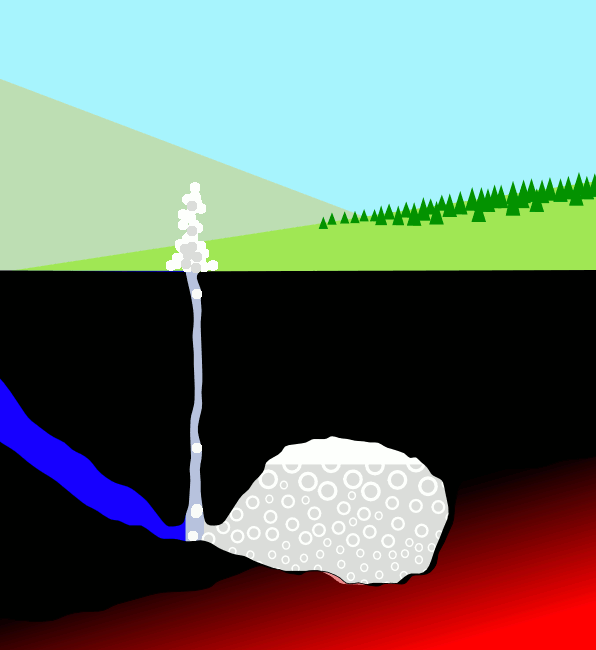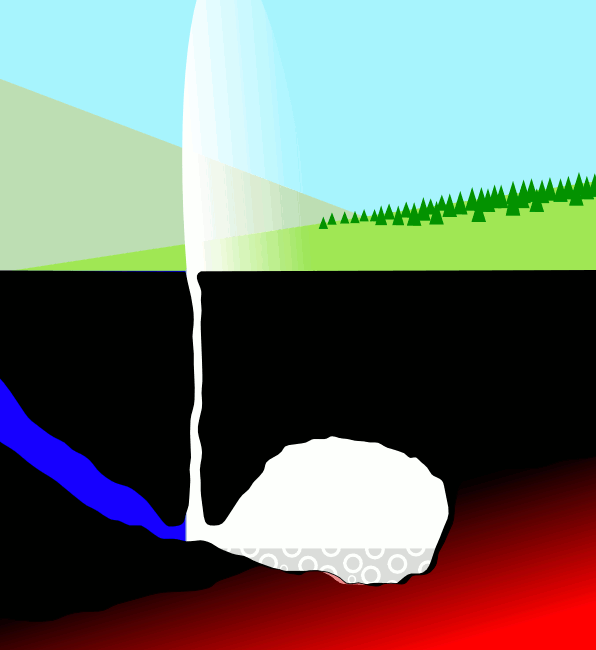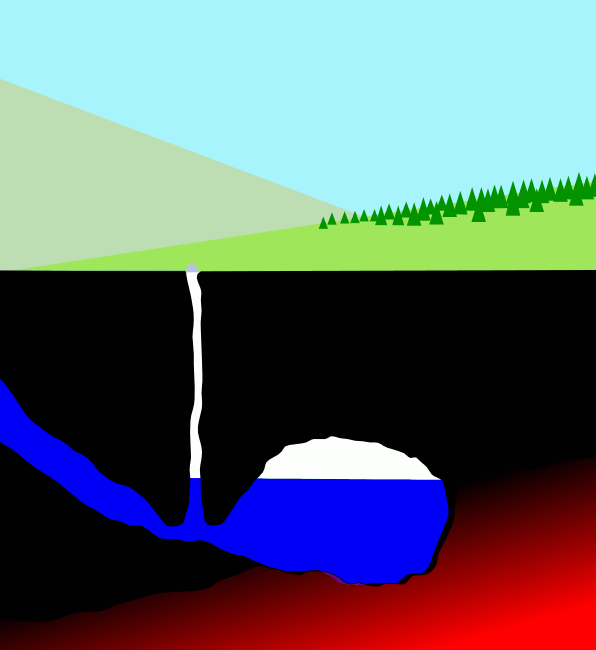
Geysers
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only in a few places on Earth. Generally all geyser field sites are located near active volcanic areas, and the geyser effect is due to the proximity of magma. Generally, surface water works its way down to an average depth of around where it contacts hot rocks. The resultant boiling of the pressurized water results in the geyser effect of hot water and steam spraying out of the geyser's surface vent (a hydrothermal explosion). A geyser's eruptive activity may change or cease due to ongoing mineral deposition within the geyser plumbing, exchange of functions with nearby hot springs, earthquake influences, and human intervention. Like many other natural phenomena, geysers are not unique to Earth. Jet-like eruptions, often referred to as cryoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circulation through faults to hot rock deep in the Earth's crust. In either case, the ultimate source of the heat is radioactive decay of naturally occurring radioactive elements in the Earth's mantle, the layer beneath the crust. Hot spring water often contains large amounts of dissolved minerals. The chemistry of hot springs ranges from acid sulfate springs with a pH as low as 0.8, to alkaline chloride springs saturated with silica, to bicarbonate springs saturated with carbon dioxide and carbonate minerals. Some springs also contain abundant dissolved iron. The minerals brought to the surface in hot springs often feed communities of extremophiles, microorganisms adapted to extreme conditions, and it is possible that life on Earth had its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geyser
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only in a few places on Earth. Generally all geyser field sites are located near active volcanic areas, and the geyser effect is due to the proximity of magma. Generally, surface water works its way down to an average depth of around where it contacts hot rocks. The resultant boiling of the pressurized water results in the geyser effect of hot water and steam spraying out of the geyser's surface vent (a hydrothermal explosion). A geyser's eruptive activity may change or cease due to ongoing mineral deposition within the geyser plumbing, exchange of functions with nearby hot springs, earthquake influences, and human intervention. Like many other natural phenomena, geysers are not unique to Earth. Jet-like eruptions, often referred to as cryoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Bogoria WW Satellite Image
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)