|
Laik-Gi
Laik-Gi ( my, လိုက်ဂီ, ) was governor of Pegu in the late 13th and early 14th centuries. He became governor of the province 1296 after his overlord King Wareru of Martaban had defeated the self-proclaimed king of Pegu Tarabya.Pan Hla 2005: 31 Prior to the appointment, Laik-Gi had served as the chief minister of Wareru's upstart Mon-speaking kingdom since its founding in 1287. He also led the diplomatic mission to the court of King Ram Khamhaeng of Sukhothai in 1286–1287 that secured Sukhothai's backing of Wareru's plan to declare independence from the Pagan Empire The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-da ....Pan Hla 2005: 24–25 Chronicles do not state when Laik-Gi's term at Pegu ended. References Bibliography * {{s-end Hanthawaddy dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wareru
Wareru ( mnw, ဝါရေဝ်ရောဝ်, my, ဝါရီရူး, ; also known as Wagaru; 20 March 1253 – 14 January 1307) was the founder of the Martaban Kingdom, located in present-day Myanmar (Burma). By using both diplomatic and military skills, he successfully carved out a Mon-speaking polity in Lower Burma, during the collapse of the Pagan Empire (Bagan Empire) in the 1280s. Wareru was assassinated in 1307 but his line ruled the kingdom until its fall in the mid-16th century. Wareru, a commoner, seized the governorship of Martaban (Mottama) in 1285, and after receiving the backing of the Sukhothai Kingdom, he went on to declare independence from Pagan in 1287. In 1295–1296, he and his ally Tarabya, the self-proclaimed king of Pegu (Bago), decisively defeated a major invasion by Pagan. Wareru eliminated Tarabya soon after, and emerged as the sole ruler of three Mon-speaking provinces of Bassein, Pegu and Martaban 1296. With his domain now much enlarged, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarabya Of Pegu
Tarabya of Pegu ( mnw, တယာဖျာ; my, ပဲခူး တရဖျား, ) was the self-proclaimed List of rulers of Pegu, king of Pegu (modern Bago, Myanmar) from 1287 to 1296. He was one of several regional strongmen who emerged after the fall of the Pagan Kingdom, Pagan Empire in 1287. Initially, Tarabya was allied with Wareru, the strongman of the nearby Martaban province. But after their decisive victory over Pagan in 1295–1296, the alliance turned into an intense rivalry, which culminated in the two men fighting a duel on elephant-back about two years later. Tarabya was defeated, and after a brief stay in Mottama, Martaban (Mottama), executed. Background Tarabya was originally a commoner by the name of Burmese name, Nga Pa-Mun (ငပမွန်, ),Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 253Yazawin Thit Vol. 1 2012: 148Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 359 or A-Che-Mun (အချဲမွန်, ).A-Che-Mun per (Pan Hla 2005: 30). (Phayre 1873: 41) transliterates his name as Akhyemwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Pegu
This is a list of rulers of Pegu (Bago), one of the three main Mon-speaking provinces, located on the south-central coast of modern Myanmar. This is not a list of monarchs of the Hanthawaddy Kingdom, who ruled Lower Burma from Pegu during three separate periods (1369–1539, 1550–1552, 1740–1757). Backgrounder Various Mon language chronicles state different foundation dates of Pegu (Bago), ranging from 573 CE to 1152 CE.A version of the 18th century chronicle ''Slapat Rajawan'' as reported by Arthur Phayre (Phayre 1873: 32) states that the settlement was founded in 1116 Buddhist Era (572/573 CE). But another version of the ''Slapat'', used by P.W. Schmidt (Schmidt 1906: 20, 101), states that it was founded on 1st waxing of Mak (Tabodwe) 1116 BE ( 19 January 573 CE), which it says is equivalent to year 514 of "the third era", without specifying what the era specifically was. However, per (Phayre 1873: 39), one of the "native records" used by Maj. Lloyd says that Pegu was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanthawaddy Kingdom
( Mon) ( Burmese) , conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Hongsarwatoi (Hanthawaddy) Pegu , common_name = Hongsarwatoi (Hanthawaddy) Kingdom / Ramannya (Ramam) , era = Warring states , status = Kingdom , event_pre = , date_pre = , event_start = , year_start = 1287 , date_start = 30 January , event_end = , year_end = 1552 , date_end = 12 March , event1 = Vassal of Sukhothai , date_event1 = 1287–1298, 1307–1317, 1330 , event2 = Forty Years' War , date_event2 = 1385–1424 , event3 = Golden Age , date_event3 = 1426–1534 , event4 = War with Toungoo , date_event4 = 1534–1541 , event_post = , date_post = , p1 = Pagan Kingdom , flag_p1 = , s1 = First Toungoo Empire , flag_s1 = , image_flag = Golden Hintar flag of Burma.svg , flag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon Language
The Mon language (, mnw, ဘာသာမန်, links=no, (Mon-Thai ဘာသာမည်) ; my, မွန်ဘာသာ; th, ภาษามอญ; formerly known as Peguan and Talaing) is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Mon people. Mon, like the related Khmer language, but unlike most languages in mainland Southeast Asia, is not tonal. The Mon language is a recognised indigenous language in Myanmar as well as a recognised indigenous language of Thailand. Mon was classified as a "vulnerable" language in UNESCO's 2010 ''Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger''. The Mon language has faced assimilative pressures in both Myanmar and Thailand, where many individuals of Mon descent are now monolingual in Burmese or Thai respectively. In 2007, Mon speakers were estimated to number between 800,000 and 1 million. In Myanmar, the majority of Mon speakers live in Southern Myanmar, especially Mon State, followed by Tanintharyi Region and Kayin State. History Mon is an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Khamhaeng
Ram Khamhaeng ( th, รามคำแหง, ) or Pho Khun Ram Khamhaeng Maharat ( th, พ่อขุนรามคำแหงมหาราช, ), also spelled Ramkhamhaeng, was the third king of the Phra Ruang Dynasty, ruling the Sukhothai Kingdom (a historical kingdom of Thailand) from 1279 to 1298, during its most prosperous era. He is credited for the creation of the Thai alphabet and the firm establishment of Theravada Buddhism as the state religion of the kingdom.Chakrabongse, C., 1960, ''Lords of Life'', London: Alvin Redman Limited Birth and name Ram Khamhaeng was a son of Pho Khun Bang Klang Hao, who ruled as Pho Khun Si Inthrathit, and his queen, Sueang,Prasert Na Nagara and Alexander B. Griswold (1992). "The Inscription of King Rāma Gāṃhèṅ of Sukhodaya (1292 CE)", p. 265, in ''Epigraphic and Historical Studies''. Journal of the Siam Society. The Historical Society Under the Royal Patronage of H.R.H. Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn: Bangkok. . though fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom ( th, สุโขทัย, , IAST: , ) was a post-classical Thai kingdom (mandala) in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. The kingdom was founded by Si Inthrathit in 1238 and existed as an independent polity until 1438, when it fell under the influence of the neighboring Ayutthaya after the death of Borommapan (Maha Thammaracha IV). Sukhothai was originally a trade center in Lavo—itself under the suzerainty of the Khmer Empire—when Central Thai people led by Pho Khun Bang Klang Hao, a local leader, revolted and gained their independence. Bang Klang Hao took the regnal name of Si Inthrathit and became the first monarch of the Phra Ruang dynasty. The kingdom was centralized and expanded to its greatest extent during the reign of Ram Khamhaeng the Great (1279–1298), who some historians considered to have introduced Theravada Buddhism and the initial Thai script to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
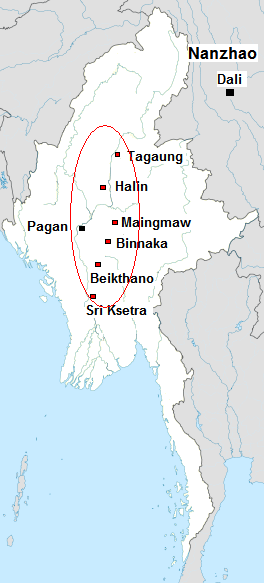
Pagan Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy River, Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and Burmese culture, culture, the spread of Bamar people, Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Bagan, Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Bamar, Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razadarit Ayedawbon
''Razadarit Ayedawbon'' ( my, ရာဇာဓိရာဇ် အရေးတော်ပုံ) is a Burmese chronicle covering the history of Ramanya from 1287 to 1421. The chronicle consists of accounts of court intrigues, rebellions, diplomatic missions, wars etc. About half of the chronicle is devoted to the reign of King Razadarit (r. 1384–1421), detailing the great king's struggles in the Forty Years' War against King Minkhaung I and Crown Prince Minye Kyawswa of Ava.Thaw Kaung 2010: 29–30 It is the Burmese translation of the first half of the ''Hanthawaddy Chronicle'' from Mon by Binnya Dala, an ethnic Mon minister and general of Toungoo Dynasty. It is likely the earliest ''extant'' text regarding the history of the Mon people in Lower Burma,Aung-Thwin 2005: 133–135 probably the only surviving portion of the original Mon language chronicle, which was destroyed in 1565 when a rebellion burned down Pegu (Bago).Harvey 1925: xviii Four oldest palm-leaf manuscri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
.jpg)