|
Lactocillin
Lactocillin is a thiopeptide antibiotic which is encoded for and produced by biosynthetic genes clusters in the bacteria ''Lactobacillus gasseri''. Lactocillin was discovered and purified in 2014. ''Lactobacillus gasseri'' is one of the four ''Lactobacillus'' bacteria found to be most common in the human vaginal microbiome. Due to increasing levels of pathogenic resistance to known antibiotics, novel antibiotics are increasingly valuable. Lactocillin could function as a new antibiotic that could help people fight off infections that are resistant to many other antibiotics. Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Lactocillin is produced by a biosynthetic gene cluster, which is a group of genes in bacteria that work together to make a secondary metabolite. Secondary metabolites are molecules with many different chemical structures and functions, and in this case, lactocillin functions as an antibiotic. Biosynthetic gene clusters are similar to operons in bacteria in that they both code for pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiopeptide
Thiopeptides (thiazolyl peptides) are a class of peptide antibiotics produced by bacteria. They have antibiotic activity against Gram-positive bacteria, but little or no activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Many of the members of this class show activity against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and are therefore subjects of research interest. There are over 100 members of this class known. Chemical structure Thiopeptides are sulfur-rich macrocyclic peptides containing highly-modified amino acids. They are characterized by a nitrogen-containing six-membered ring (such as piperidine, dehydropiperidine, or pyridine) substituted with multiple thiazole rings and dehydroamino acids. A macrocylic ring serves as a scaffold for a tail that also incorporates modified amino acids often with azole rings, such as thiazoles, oxazoles, and thiazolines which are derived from serine, threonine, and cysteine residues. Examples Examples of thiopeptides include thiostre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has led to the need for stricter requirements for scientific substantiation of putative benefits conferred by microorganism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcal Infection
A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the '' Staphylococcus'' genus of bacteria. These bacteria commonly inhabit the skin and nose where they are innocuous, but may enter the body through cuts or abrasions which may be nearly invisible. Once inside the body, the bacteria may spread to a number of body systems and organs, including the heart, where the toxins produced by the bacteria may cause cardiac arrest. Once the bacterium has been identified as the cause of the illness, treatment is often in the form of antibiotics and, where possible, drainage of the infected area. However, many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant; for those with these kinds of infection, the body's own immune system is the only defense against the disease. If that system is weakened or compromised, the disease may progress rapidly. Anyone can contract staph, but pregnant women, children, and people with chronic diseases or who are immuno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Sobrinus
''Streptococcus sobrinus'' is a Gram-positive, catalase-negative, non-motile, and Anaerobic organism, anaerobic member of the genus ''Streptococcus''. Pathology ''Streptococcus sobrinus'' in conjunction with the closely related species ''Streptococcus mutans'' are pathogenic within humans and enhances the formation of caries within teeth. Biofilm from the mixture of sugar and Dental plaque, plaque create a suitable environment for ''S. sobrinus'' to grow. ''S. sobrinus'' is more closely connected with the prevalence of caries than ''S. mutans''. ''S. sobrinus'' is also affiliated with early childhood caries, which are responsible for the majority of dental abscesses and toothaches in children. Children generally acquire ''S. sobrinus'' strains from their mother, but the relatively high consumption of sugars by minors facilitates bacterial growth and threatens the onset of early childhood tooth decay. ''S. sobrinus'' has also been documented within the teeth of rats. History ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobe, aerobic. They are bacillus (shape), bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club (weapon), club-shaped, which inspired the genus name (''coryneform'' means "club-shaped"). They are widely distributed in nature in the microbiota of animals (including the human microbiota) and are mostly innocuous, most commonly existing in commensalism, commensal relationships with their hosts. Some, such as ''Corynebacterium glutamicum, C. glutamicum'', are commercially useful. Others can cause human disease, including, most notably, diphtheria, which is caused by ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae, C. diphtheriae''. As with various species of amicrobiota (including their relatives in the genera ''Arcanobacterium'' and ''Trueperella''), they usually are not pathogenic, but can occasionally opportunistic infection, opportunistically capitalize on atypical access to tissue (biology), ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
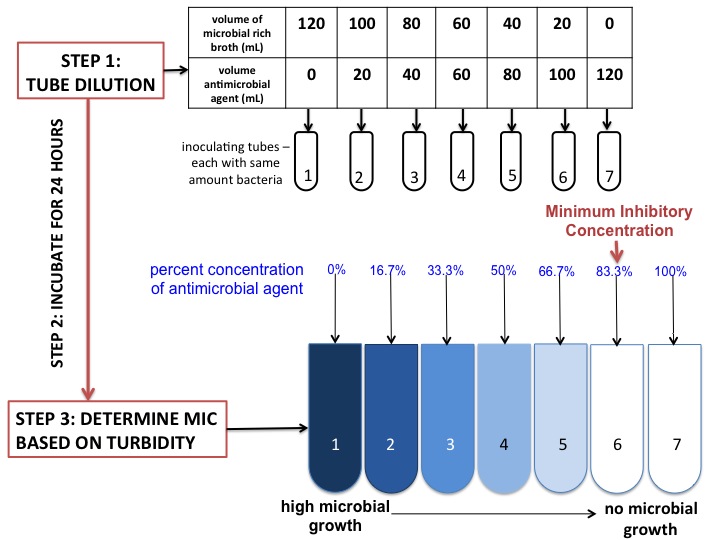
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible growth of a bacterium or bacteria. MIC depends on the microorganism, the affected human being (in vivo only), and the antibiotic itself. It is often expressed in micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). The MIC is determined by preparing solutions of the chemical in vitro at increasing concentrations, incubating the solutions with separate batches of cultured bacteria, and measuring the results using agar dilution or broth microdilution. Results have been graded into susceptible (often called sensitive), increased exposure, or resistant to a particular antimicrobial by using a breakpoint. Breakpoints are agreed upon values, published in guidelines of a reference body, such as the U.S. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) or the European Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposase
A transposase is any of a class of enzymes capable of binding to the end of a transposon and catalysing its movement to another part of a genome, typically by a cut-and-paste mechanism or a replicative mechanism, in a process known as transposition. The word "transposase" was first coined by the individuals who cloned the enzyme required for transposition of the Tn3 transposon. The existence of transposons was postulated in the late 1940s by Barbara McClintock, who was studying the inheritance of maize, but the actual molecular basis for transposition was described by later groups. McClintock discovered that some segments of chromosomes changed their position, jumping between different loci or from one chromosome to another. The repositioning of these transposons (which coded for color) allowed other genes for pigment to be expressed. Transposition in maize causes changes in color; however, in other organisms, such as bacteria, it can cause antibiotic resistance. Transposition is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created Bactericide, pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves Temperateness (virology), temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Gene Cluster
Metabolic gene clusters or biosynthetic gene clusters are tightly linked sets of mostly non-homologous genes participating in a common, discrete metabolic pathway. The genes are in physical vicinity to each other on the genome, and their expression is often coregulated. Metabolic gene clusters are common features of bacterial and most fungal genomes, and are less often found in other organisms. They are most widely known for producing secondary metabolites, which are the source or basis of most pharmaceutical compounds, natural toxins, and chemical communication and chemical warfare between organisms. Metabolic gene clusters are also involved in nutrient acquisition, toxin degradation, antimicrobial resistance, and vitamin biosynthesis. Given all these properties of metabolic gene clusters, they play a key role in shaping microbial ecosystems, including microbiome-host interactions. Thus several computational genomics tools have been developed to predict metabolic gene clusters. Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |