|
Lactacystin
Lactacystin is an organic compound naturally synthesized by bacteria of the genus '' Streptomyces'' first identified as an inducer of neuritogenesis in neuroblastoma cells in 1991.Omura S, Fujimoto T, Otoguro K, Matsuzaki K, Moriguchi R, Tanaka H, Sasaki Y. (1991). Lactacystin, a novel microbial metabolite, induces neuritogenesis of neuroblastoma cells: S. Omura, et al. ''J. Antibiot.'' 44(1):113-6. The target of lactacystin was subsequently found to be the proteasome on the basis of its affinity for certain catalytic subunits of the proteasome by Fenteany and co-workers in 1995. The proteasome is a protein complex responsible for the bulk of proteolysis in the cell, as well as proteolytic activation of certain protein substrates. Lactacystin was the first non-peptidic proteasome inhibitor discovered and is widely used as a research tool in biochemistry and cell biology. The transformation product of lactacystin clasto-lactacystin β-lactone (also known as omuralide) covalently mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
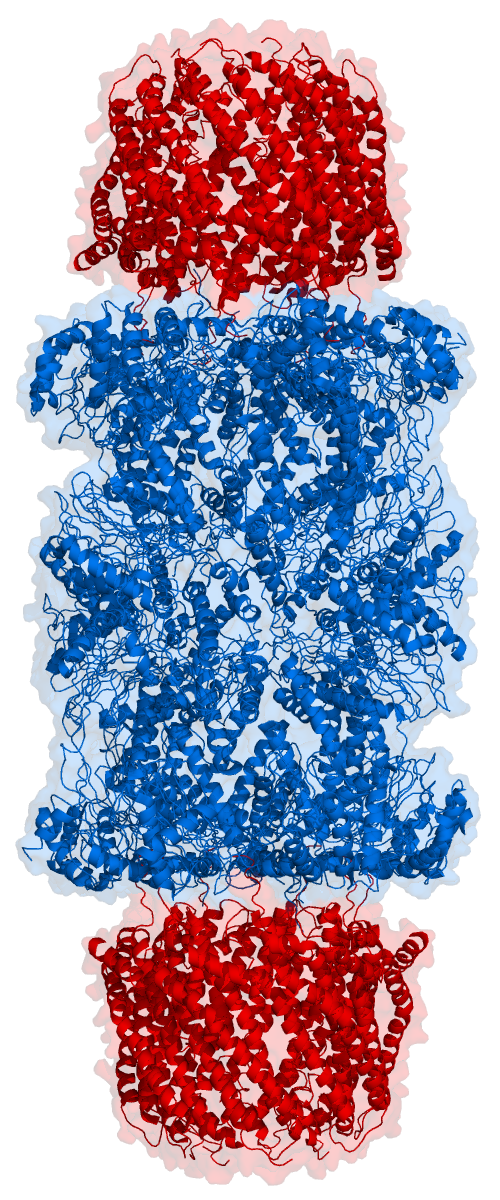
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satoshi Ōmura
is a Japanese biochemist. He is known for the discovery and development of hundreds of pharmaceuticals originally occurring in microorganisms. In 2015, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly with William C. Campbell for their role in the discovery of avermectins and ivermectin, the world's first endectocide and a safe and highly effective microfilaricide. It is believed that the large molecular size of ivermectin prevents it from crossing the blood/aqueous humour barrier, and renders the drug an important treatment of helminthically-derived blindness. Early life and education Satoshi Ōmura was born in Nirasaki, Yamanashi Japan in 1935, the second son of Ōmura family. After graduating from the University of Yamanashi in 1958, he was appointed to science teacher at Tokyo Metropolitan Sumida Tech High School. In 1960, he became an auditor of Koji Nakanishi’s course at Tokyo University of Education, one year later, he enrolled in the Tokyo Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Streptomycetes are characterised by a complex secondary metabolism. They produce over two-thirds of the clinically useful antibiotics of natural origin (e.g., neomycin, streptomycin, cypemycin, grisemycin, bottromycins and chloramphenicol). The antibiotic streptomycin takes its name directly from ''Streptomyces''. Streptomycetes are infrequent pathogens, though infections in humans, such as mycetoma, can be caused by '' S. somaliensis'' and '' S. sudanensis'', and in plants can be caused by '' S. cavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine Protease
Threonine proteases are a family of proteolytic enzymes harbouring a threonine (Thr) residue within the active site. The prototype members of this class of enzymes are the catalytic subunits of the proteasome, however the acyltransferases convergently evolved the same active site geometry and mechanism. Mechanism Threonine proteases use the secondary alcohol of their N-terminal threonine as a nucleophile to perform catalysis. The threonine must be N-terminal since the terminal amine of the same residue acts as a general base by polarising an ordered water which deprotonates the alcohol to increase its reactivity as a nucleophile. Catalysis takes place in two steps: * Firstly the nucleophile attacks the substrate to form a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate, releasing the first product. * Secondly the intermediate is hydrolysed by water to regenerate the free enzyme and release the second product. ** In ornithine acyltransferase, instead of water, the substrate ornithine (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells,Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs, as well as organism structure and function.Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, which is the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful. Often, the aim is to discover a new route of synthesis for a target molecule for which there already exist known routes. Sometimes, however, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PubMed
PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintain the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval. From 1971 to 1997, online access to the MEDLINE database had been primarily through institutional facilities, such as university libraries. PubMed, first released in January 1996, ushered in the era of private, free, home- and office-based MEDLINE searching. The PubMed system was offered free to the public starting in June 1997. Content In addition to MEDLINE, PubMed provides access to: * older references from the print version of ''Index Medicus'', back to 1951 and earlier * references to some journals before they were indexed in Index Medicus and MEDLINE, for instance ''Science'', ''BMJ'', and ''Annals of Surgery'' * very recent entries to records for an article before it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |