|
Lacedaimonius
Lacedaemonius ( el, Λακεδαιμόνιος) was an Athenian general of the Philaid clan. He served Athens, notably in the naval Battle of Sybota against the Corinthians in 433 BC. Biography Lacedaemonius was the son of Cimon, a pro-Sparta general and Athenian political figure, and Isodice who was the daughter of Euryptolemus, a cousin of Pericles. He was a grandson of the famous Miltiades IV. An accounted cited that he had a twin called Oulius. He was also the brother of Miltiades VII, who was the ''oikist'' in the Adriatic in 324. Lacedaemonius comes from Lacedaemon, another name for the city state of Sparta. His father so admired the Spartans he showed them a sign of goodwill by naming his son after their city. Lacedaemonius was also identified as the ''proxenos'' of the Spartans at Athens. Accounts cited Lacedaemonius as one of the Athenian generals sent to aid Corcyra in its conflict with Corinth after an alliance agreement concluded in 433. This is part of the serie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philaidae
The Philaidae or Philaids were a powerful noble family of ancient Athens. They were conservative land owning aristocrats and many of them were very wealthy. The Philaidae produced two of the most famous generals in Athenian history: Miltiades the Younger and Cimon. The Philaids claimed descent from the mythological Philaeus, son of Ajax. The family originally came from Brauron in Attica. Later a prominent branch of the clan were based at Lakiadae west of Athens. In the late 7th century BC a Philaid called Agamestor married the daughter of Cypselus, the powerful tyrant of Corinth. In 597 BC a man named Cypselus was archon of Athens. This Cypselus was probably grandson of the Corinthian tyrant of the same name and son of Agamestor. Some years before 566 BC, a member of the Philaid clan, Hippocleides, was a suitor for the hand of Agariste, the daughter of the influential tyrant of Sicyon, Cleisthenes. However Hippocleides lost out to Megacles from the rival Alcmaeonid clan when Cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
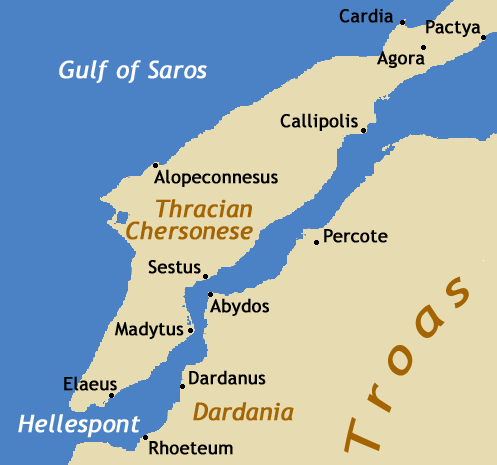
Battle Of Sybota
The Battle of Sybota ( grc, Σύβοτα) took place in 433 BCE between Corcyra (modern Corfu) and Corinth. It was one of the immediate catalysts for the Peloponnesian War. History Corinth had been in dispute with Corcyra, an old Corinthian colony which no longer wanted to remain under Corinthian influence (see Affair of Epidamnus for background). Corcyra, which had the third largest navy in Greece at the time, allied itself with Athens, an enemy of Corinth (as Corinth was allied with Sparta). Athens sent ten ships to Corcyra to reinforce the Corcyraean fleet, with instructions not to fight the Corinthian fleet unless they attempted to land on the island. Corinth, meanwhile, assembled a fleet of ships under the command of Xenoclides and prepared to sail to Corcyra. Corcyra gathered a fleet under Miciades, Aisimides and Eurybatus, who made the Sybota islands their base of operations. The Athenian commanders, Lacedaimonius (the son of Cimon), Diotimus, and Proteas, sailed with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician. He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Battle of Salamis (480 BC), during the Second Persian invasion of Greece. Cimon was then elected as one of the ten ''strategoi'', to continue the Persian Wars against the Achaemenid Empire. He played a leading role in the formation of the Delian League against Persia in 478 BC, becoming its commander in the early Wars of the Delian League, including at the Siege of Eion (476 BC). In 466 BC, Cimon led a force to Asia Minor, where he destroyed a Persian fleet and army at the Battle of the Eurymedon river. From 465 to 463 BC he suppressed the Thasian rebellion, in which the island of Thasos attempted to leave the Delian League. This event marked the transformation of the Delian League into the Athenian Empire. Cimon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proxeny
Proxeny or ( grc-gre, προξενία) in ancient Greece was an arrangement whereby a citizen (chosen by the city) hosted foreign ambassadors at his own expense, in return for honorary titles from the state. The citizen was called (; plural: or , "instead of a foreigner") or (). The proxeny decrees, which amount to letters patent and resolutions of appreciation were issued by one state to a citizen of another for service as ''proxenos'', a kind of honorary consul looking after the interests of the other state's citizens. A common phrase is (benefactor) and (). A proxenos would use whatever influence he had in his own city to promote policies of friendship or alliance with the city he voluntarily represented. For example, Cimon was Sparta's proxenos at Athens and during his period of prominence in Athenian politics, previous to the outbreak of the First Peloponnesian War, he strongly advocated a policy of cooperation between the two states. Cimon was known to be so fond of Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltiades The Younger
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer, and the father of Cimon, the noted Athenian statesman. Family Miltiades was a well-born Athenian, and considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, as well as a member of the prominent Philaid clan. He came of age during the tyranny of the Peisistratids. His family was prominent, due in good part to their success with Olympic chariot-racing.Creasy (1880) pg. 9 Plutarch claimed that Cimon, Miltiades' father, was known as "Coalemos", meaning "simpleton", because he had a reputation for being rough around the edges, but whose three successive chariot-racing victories at the Olympics made him popular, so popular in fact that, Herodotus claims, the sons of Peisistratos murdered him out of jea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Athenian Generals
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet built with Persian subsidies finally defeated Athens and started a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. The first phase (431–421 BC) was named the Ten Years War, or the Archidamian War, after the Spartan king Archidamus II, who launched several invasions of Attica with the full hoplite army of the Peloponnesian League, the alliance network dominated by Sparta. However, the Long Walls of Athens rendered this strategy ineffective, while the superior navy of the Delian League (Athens' alliance) raided the Peloponnesian coast to trigger rebellions within Sparta. The precarious Peace of Nicias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered by three municipalities with the islands of Othonoi, Ereikoussa, and Mathraki.https://corfutvnews.gr/diaspasi-deite-tin-tropologia/ The principal city of the island (pop. 32,095) is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University. The island is bound up with the history of Greece from the beginnings of Greek mythology, and is marked by numerous battles and conquests. Ancient Korkyra took part in the Battle of Sybota which was a catalyst for the Peloponnesian War, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time. Thucydides also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of fifth century BC Greece, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City State
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as Rome, Athens, Sparta, Carthage, and the Italian city-states during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, such as Florence, Venice, Genoa and Milan. With the rise of nation states worldwide, only a few modern sovereign city-states exist, with some disagreement as to which qualify; Monaco, Singapore and Vatican City are most commonly accepted as such. Singapore is the clearest example, with full self-governance, its own currency, a robust military and a population of 5.5 million. Several non-sovereign cities enjoy a high degree of autonomy and are sometimes considered city-states. Hong Kong, Macau, and members of the United Arab Emirates—most notably Dubai and Abu Dhabi—are often cited as such. Historical background Ancient and medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacedaemon
Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oikistes
The ''oikistes'' ( gr, οἰκιστής), often anglicized as oekist or oecist, was the individual chosen by an ancient Greek polis ''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ... as the leader of any new colonization effort. He was invested with the power of selecting a settling place, directing the initial labors of the colonists and guiding the fledgling colony through its hard early years. The oracle is also consulted during deliberations for choosing an ''oikistes''. After he is appointed and directed to found a colony, he also consults the Delphic oracle. Due to his authority, the ''oikistes'' was often accorded his own cult after his death, and his name was preserved even when all other details of the founding of a colony were forgotten. References Society of ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_Thucydides.jpg)

