|
Philaidae
The Philaidae or Philaids were a powerful noble family of ancient Athens. They were conservative land owning aristocrats and many of them were very wealthy. The Philaidae produced two of the most famous generals in Athenian history: Miltiades the Younger and Cimon. The Philaids claimed descent from the mythological Philaeus, son of Ajax. The family originally came from Brauron in Attica. Later a prominent branch of the clan were based at Lakiadae west of Athens. In the late 7th century BC a Philaid called Agamestor married the daughter of Cypselus, the powerful tyrant of Corinth. In 597 BC a man named Cypselus was archon of Athens. This Cypselus was probably grandson of the Corinthian tyrant of the same name and son of Agamestor. Some years before 566 BC, a member of the Philaid clan, Hippocleides, was a suitor for the hand of Agariste, the daughter of the influential tyrant of Sicyon, Cleisthenes. However Hippocleides lost out to Megacles from the rival Alcmaeonid clan when Clei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltiades The Younger
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer, and the father of Cimon, the noted Athenian statesman. Family Miltiades was a well-born Athenian, and considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, as well as a member of the prominent Philaid clan. He came of age during the tyranny of the Peisistratids. His family was prominent, due in good part to their success with Olympic chariot-racing.Creasy (1880) pg. 9 Plutarch claimed that Cimon, Miltiades' father, was known as "Coalemos", meaning "simpleton", because he had a reputation for being rough around the edges, but whose three successive chariot-racing victories at the Olympics made him popular, so popular in fact that, Herodotus claims, the sons of Peisistratos murdered him out of jealousy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocleides
Hippocleides (also Hippoclides) ( grc-gre, Ἱπποκλείδης), the son of Teisander (Τείσανδρος), was an Athenian nobleman, who served as Eponymous Archon for the year 566 BC – 565 BC. He was a member of the Philaidae, a wealthy Athenian family that was opposed to the Peisistratos family. During his term as archon, he set up the statue of Athena Promachos (πρὀμαχος) in Athens and oversaw a reorganization of the Panathenaia festival. As a young man, he competed for the hand of Agariste, the daughter of Cleisthenes, the tyrant of Sicyon. By the end of the competitions, only Hippocleides and Megacles remained. According to Herodotus (6.129-130), Hippocleides became intoxicated during a dinner party with Cleisthenes, and began to act like a fool; at one point he stood on his head and kicked his legs in the air, keeping time with the flute music. When Hippocleides was informed by Cleisthenes "Oh son of Teisander, you have just danced away your marriage," his r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltiades The Elder
Miltiades the Elder (ca. 590 – 525 BC) was an Athenian politician from the Philaid family. He is most famous for travelling to the Thracian Chersonese (modern-day Gallipoli) where, at the behest of the local peoples, he ruled as a tyrant. During his reign, Miltiades' best-attested action was the construction of a defensive wall across the peninsula. Miltiades was the uncle of Miltiades the Younger, who was a prominent commander in the Battle of Marathon. Early life and family Miltiades the Elder was born in Athens in around 590 BC. His father was Cypselus the archon; Miltiades also claimed descent from the mythological king Aeacus.Hammond, 117. During this time, the Philaids were one of the wealthiest families in the city. While living in Athens, Miltiades was a successful athlete. He owned a four-horse chariot,Herodotus, ''Histories,'' 6.35. and won an Olympic victory in the chariot race in 560 BC. In the Thracian Chersonese During this period, the Dolonci (a tribe from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimon Coalemos
Cimon Coalemos (ancient Greek Κίμων Κοάλεμος, ''Kìmon Koàlemos''), was a renowned ancient Olympic chariot-racer of the 6th century BC. Biography Cimon, called "Coalemos" (ancient Greek Κοάλεμος, ''Koàlemos'', "booby"),Plutarch, ''Life of Cimon'', 4,3. son of Stesagoras, was a member the Athenian clan of Philaidae, step-brother of Miltiades the Elder and father of Stesagoras, both tyrants of the Thracian Chersonese (now the Gallipoli Peninsula). Cimon was a well-known chariot race organizer, winning three consecutive times the chariot race, one of the most important competitions of the Ancient Olympic Games. In fact, the renown of the victory in the chariot race was given to the organizer of the team, who was funding the chariot, breeding the horses and hiring the charioteer. Banned from Athens for political reasons, Cimon was forgiven and called back to his homeland by the tyrant Peisistratos since he dedicated to the tyrant his second victory at the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician. He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Battle of Salamis (480 BC), during the Second Persian invasion of Greece. Cimon was then elected as one of the ten ''strategoi'', to continue the Persian Wars against the Achaemenid Empire. He played a leading role in the formation of the Delian League against Persia in 478 BC, becoming its commander in the early Wars of the Delian League, including at the Siege of Eion (476 BC). In 466 BC, Cimon led a force to Asia Minor, where he destroyed a Persian fleet and army at the Battle of the Eurymedon river. From 465 to 463 BC he suppressed the Thasian rebellion, in which the island of Thasos attempted to leave the Delian League. This event marked the transformation of the Delian League into the Athenian Empire. Cimon to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peisistratos
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular peninsula of Greece containing Athens, along with economic and cultural improvements laid the groundwork for the later preeminence of Athens in ancient Greece. His legacy lies primarily in his institution of the Panathenaic Games, historically assigned the date of 566 BC, and the consequent first attempt at producing a definitive version of the Homeric epics. Peisistratos' championing of the lower class of Athens is an early example of populism. While in power, he did not hesitate to confront the aristocracy and greatly reduce their privileges, confiscating their lands and giving them to the poor. Peisistratos funded many religious and artistic programs, in order to improve the economy and spread the wealth more equally among the Athenian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olorus
Olorus ( gr, Ὄλορος) was the name of a king of Thrace. His daughter Hegesipyle married the Athenian statesman and general Miltiades, who defeated the Persians at the Battle of Marathon The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination o ... in 490 BC.Herodotus. ''Histories'', 6.39.1. "Stesagoras met his end in this way. The sons of Pisistratus sent Miltiades, son of Cimon and brother of the dead Stesagoras, in a trireme to the Chersonese to take control of the country; they had already treated him well at Athens, feigning that they had not been accessory to the death of Cimon his father, which I will relate in another place. Reaching the Chersonese, Miltiades kept himself within his house, professing thus to honor the memory of his brother Stesagoras. When the people of the Chers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparchus (brother Of Hippias)
Hipparchus ( grc-gre, Ἵππαρχος ; died 514 BC) was a member of the ruling class of Athens and one of the sons of Pisistratus. He was a tyrant of the city of Athens from 528/7 BC until his assassination by the tyrannicides Harmodius and Aristogeiton in 514 BC. Life Hipparchus was said by some Greek authors to have been the tyrant of Athens, along with his brother Hippias, after the death of their father Peisistratos in about 528/7 BC. The word ''tyrant'' literally means "one who takes power by force", as opposed to a ruler who inherited a monarchy or was chosen in some way. It carried no pejorative connotation during the Archaic and early Classical periods. However, according to Thucydides, Hippias was the only 'tyrant'. Both Hipparchus and his father Pisistratus enjoyed the popular support of the people. Hipparchus was a patron of the arts; it was he who invited Simonides of Ceos to Athens.Aristotle, '' The Athenian Constitution'', Part 18 In 514 BC, Hipparchus wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippias (tyrant)
Hippias ( grc-gre, Ἱππίας; c. 570 BC – 490 BC) was the last tyrant of Athens, ruling from 527 to 510 BC. He was one of a group of tyrants known as the Peisistratids, which was a group of three tyrants in Ancient Greece. Pisistratus first, and then his son, Hippias, followed after him by Hippias' illegitimate son, Hegesistratos. He was deposed when Cleomenes I of Sparta successfully invaded Athens and forced him to flee to Persia. Early life Hippias was born around 570 BC as the eldest son of Pisistratus, the first tyrant of Athens. When his father was forced to flee to Eretria after insulting Megakles by having intercourse with his daughter in an indecent way, Peisistratos held counsel with his sons. Hippias suggested that they should retake the tyranny, which his father agreed to. Preparations began for which Athens fell to Peisistratos for the third time in 546 BC. Tyrant of Athens Hippias succeeded Peisistratos as tyrant of Athens in 528/7 BC when his father d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games (Ὀλυμπιακοὶ ἀγῶνες; la, Olympia, neuter plural: "the Olympics") were a series of athletic competitions among representatives of city-states and were one of the Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece. They were held in honor of Zeus, and the Greeks gave them a mythological origin. The originating Olympic Games are traditionally dated to 776 BC. The games were held every four years, or Olympiad, which became a unit of time in historical chronologies. They continued to be celebrated when Greece came under Roman rule, 2nd century BC. Their last recorded celebration was in AD 393, under the emperor Theodosius I, but archeological evidence indicates that some games were still held after this date.Hamlet, Ingomar. "Theodosius I. And The Olympic Games". Nikephoros 17 (2004): pp. 53-75. The games likely came to an end under Theodosius II, possibly in connection with a fire that burned down the temple of the Olympian Zeus during his reign. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
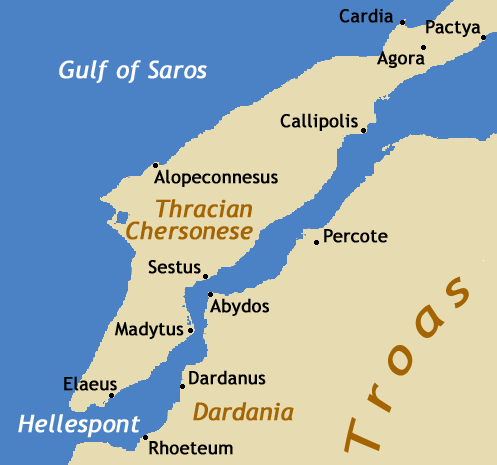
Thracian Chersonese
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area between northern Greece, southern Russia, and north-western Turkey. They shared the same language and culture... There may have been as many as a million Thracians, diveded among up to 40 tribes." Thracians resided mainly in the Balkans (mostly modern day Bulgaria, Turkey and Greece) but were also located in Anatolia (Asia Minor) and other locations in Eastern Europe. The exact origin of Thracians is unknown, but it is believed that proto-Thracians descended from a purported mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers, arriving from the rest of Asia and Africa through the Asia Minor (Anatolia). The proto-Thracian culture developed into the Dacian, Getae, and several other smaller Thracian cultures. Thracian cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |