|
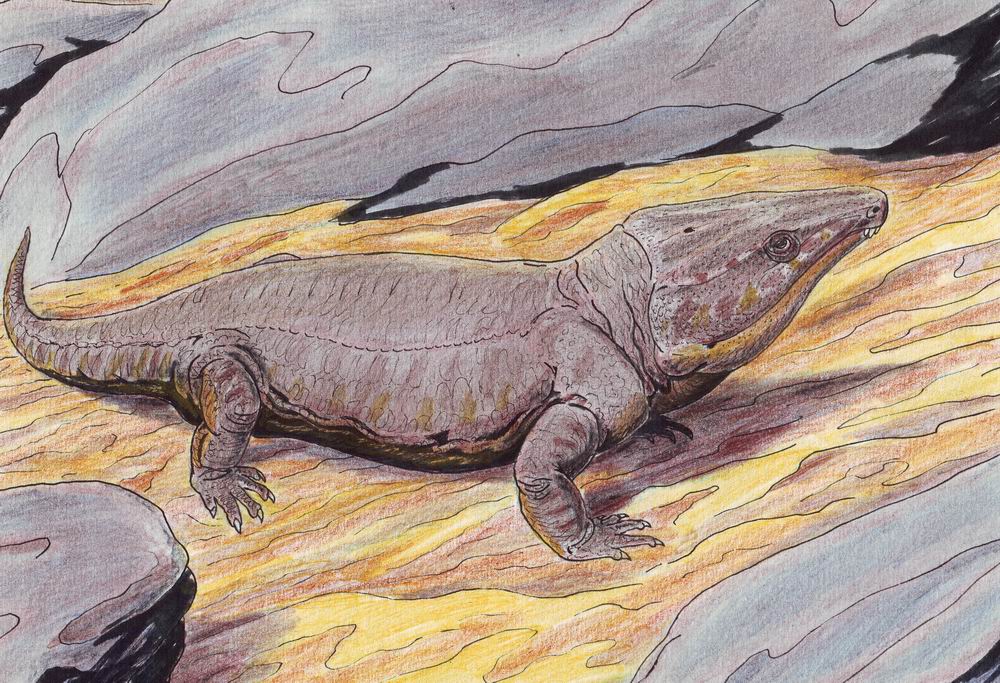
Labidosaurikos
''Labidosaurikos'' is a genus of extinct captorhinid anapsid reptile that lived around 279 to 272 million years ago during Kungurian age of the lower Permian. The American paleontologist John Willis Stovall first described ''Labidosaurikos'' in 1950, naming it "Labidosaurus like" for the striking similarity of the holotype skull of his specimen to the cranial anatomy of another captorhinid ''Labidosaurus hamatus''.Stovall, J.W., 1950. A new cotylosaur from north central Oklahoma. ''American Journal of Science'', 248(1), pp.46-54. ''Labidosaurus'' or generally called "lipped lizard" is another genus of the family Captorhinidae whose name is derived from the Greek for "forceps lizard" based on () ("forceps" or "pinsers") and () ("lizard") ''Labidosaurikos'' is an important find in Permian red beds of North America, where captorhinids are commonly found, as it is a key discovery in the evolution of herbivory in large captorhinids given its multi-row tooth plates.LeBlanc, A.R., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinid
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs) is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like reptiles that date from the late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the Protorothyrididae, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is very similar to that of advanced reptiliomorph amphibians, so much in fact that the amphibian Seymouriamorpha and Diadectomorpha were thought to be reptiles and grouped together in "Cotylosauria" as the first reptiles in the early 20th century. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorhinid, the herbivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinids
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs) is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like reptiles that date from the late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the Protorothyrididae, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is very similar to that of advanced reptiliomorph amphibians, so much in fact that the amphibian Seymouriamorpha and Diadectomorpha were thought to be reptiles and grouped together in "Cotylosauria" as the first reptiles in the early 20th century. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorhinid, the herbivor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinidae
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs) is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like reptiles that date from the late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the Protorothyrididae, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is very similar to that of advanced reptiliomorph amphibians, so much in fact that the amphibian Seymouriamorpha and Diadectomorpha were thought to be reptiles and grouped together in "Cotylosauria" as the first reptiles in the early 20th century. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorhinid, the herbivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Permian
01 or '01 may refer to: * The year 2001, or any year ending with 01 * The month of January * 1 (number) Music * '01 (Richard Müller album), 01'' (Richard Müller album), 2001 * 01 (Son of Dave album), ''01'' (Son of Dave album), 2000 * 01 (Urban Zakapa album), ''01'' (Urban Zakapa album), 2011 * O1 (Hiroyuki Sawano album), ''O1'' (Hiroyuki Sawano album), 2015 * 01011001, the seventh studio album from Arjen Anthony Lucassen's Ayreon project Other uses * 01 (telephone number), United Kingdom internal dialing code for London between the late 1950s and 1990 * Lynk & Co 01, a compact SUV built since 2017 * Zero One also known as ''Machine City'', a city-state from the ''The Matrix (series), Matrix'' series * Kolmogorov's zero-one law, a law of probability theory * Pro Wrestling ZERO1-MAX, a wrestling promotion formerly known as Pro Wrestling ZERO-ONE * BAR 01, a Formula One chassis * The number of the French department Ain * The codename given to the Wing Gundam by Oz in the anime ''G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate (or velum). Structure Innervation The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate. Development The hard palate forms before birth. Variation If the fusion is incomplete, a cleft palate results. Function When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth, the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolopalatal, and uvular consonants. History Etymology The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin ''palatum'' via Old French ''palat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Reptiles Of North America
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Reptile Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronoid Process , a triangular eminence projecting forward from the upper and front part of the ulna
{{disambig ...
The Coronoid process (from Greek , "like a crown") can refer to: * The coronoid process of the mandible, part of the ramus mandibulae of the mandible * The coronoid process of the ulna The coronoid process of the ulna is a triangular process projecting forward from the anterior proximal portion of the ulna. Structure Its ''base'' is continuous with the body of the bone, and of considerable strength. Anatomy Its ''apex'' is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians. Anatomy and function In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ... bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies Anatomical terms of location, ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the Postorbital bone, postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate bone, quadrate and Pterygoid bone, pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the Quadrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals. Anatomy In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two other lower jaw bones, the suprangular and the angular. Developmentally, it originates from the embryonic mandibular cartilage. The most caudal portion of the mandibular cartilage ossifies to form the articular bone, while the remainder of the mandibular cartilage either remains cartilaginous or disappears. In snakes In snakes, the articular, surangular, and prearticular bones have fused to form the compound bone. The mandible is suspended from the quadrate bone and articulates at this compound bone. Function In amphibians and reptiles In most tetrapods, the articular bone forms the lower portion of the jaw joint. The upper jaw articulates at the quadrate bone. In mammals In mammals, the articular bone evolves to form the malle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Tetrapods
The evolution of tetrapods began about 400 million years ago in the Devonian Period with the earliest tetrapods evolved from Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fishes. Tetrapods (under the Synapomorphy and apomorphy, apomorphy-based definition used on this page) are categorized as animals in the superclass (biology), biological superclass Tetrapoda, which includes all living and extinct amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. While most species today are terrestrial, little evidence supports the idea that any of the earliest tetrapods could move about on land, as their limbs could not have held their midsections off the ground and the known trackways do not indicate they dragged their bellies around. Presumably, the tracks were made by animals walking along the bottoms of shallow bodies of water. The specific aquatic ancestors of the tetrapods, and the process by which land colonization occurred, remain unclear. They are areas of active research and debate among palaeontologists at pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |