|
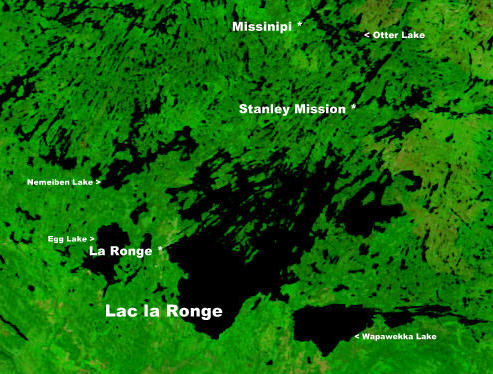
La Ronge
La Ronge is a northern town in the boreal forest of central Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is approximately north of Prince Albert where Highway 2 becomes Highway 102. La Ronge lies on the western shore of Lac la Ronge, is adjacent to Lac La Ronge Provincial Park, and is on the edge of the Canadian Shield. This town is also the namesake of the larger La Ronge population centre comprising the community, the Northern Village of Air Ronge and the Kitsakie 156B and Lac La Ronge 156 reserves of the Lac La Ronge First Nation. History The name of La Ronge comes from the lake. The origin of the name is uncertain; the most likely explanation is that early French fur traders named it ''la ronge'' (literally ''the chewed'') because of the large amount of beaver activity along the shoreline—many of the trees would have been chewed down for beaver dam construction. In 1782, Swiss born fur trader Jean-Étienne Waddens had a fur trade post on Lac La Ronge. In March 1782, Wadde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the United States, U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and List of lakes in Saskatchewan, lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, Saskatchewan, Melfort, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Saskatchewan Provincial Highways
This is a list of Saskatchewan's highways: Only Highways 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 16, and 39 contain sections of divided highway. Speed limits range from 90 km/h (55 mph) to 110 km/h (70 mph). Saskatchewan is the only province bordering the United States with no direct connection to the Interstate Highway System. Named routes * Can Am Highway *Circle Drive *Hanson Lake Road * Little Swan Road *Louis Riel Trail * McBride Lake Road *Northern Woods and Water Route * Ring Road *Red Coat Trail *Regina Bypass *Saskatoon Freeway * Saskota Travel Route * Trans-Canada Highway * Veterans Memorial Highway * Yellowhead Highway Primary (1–99) These are primary highways maintained by the provincial government. Almost all of these highways are paved for most of their length. Highways 1, 11, and 16 are the most important highways and are divided highways for much of their lengths, with some sections at expressway or freeway standards. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Centre (Canada)
The census geographic units of Canada are the Census division, census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct Census in Canada, the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation; they have no government of their own. They exist on four levels: the top-level (first-level) divisions are Canada's Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories; these are divided into second-level census divisions, which in turn are divided into third-level census subdivisions (often corresponding to List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, municipalities) and fourth-level dissemination areas. In some provinces, census divisions correspond to the province's second-level administrative divisions such as a county or another similar unit of political organization. In the Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces, census divisions do not corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Centre
In demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to different geographical locations; these are often confused. Definitions Three commonly used (but different) center points are: # the ''mean center'', also known as the ''centroid'' or ''center of gravity''; # the '' median center'', which is the intersection of the median longitude and median latitude; # the ''geometric median'', also known as ''Weber point'', ''Fermat–Weber point'', or ''point of minimum aggregate travel''. A further complication is caused by the curved shape of the Earth. Different center points are obtained depending on whether the center is computed in three-dimensional space, or restricted to the curved surface, or computed using a flat map projection. Mean center The mean center, or centroid, is the point on which a rigid, weig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the Shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the United States. Geographical extent The Canadian Shield is a physiographic division comprising four smaller physiographic provinces: the Laurentian Upland, Kazan Region, Davis and James. The shield extends into the United States as the Adirondack Mountains (connected by the Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lac La Ronge Provincial Park
Lac La Ronge Provincial Park is located in the boreal forest of the north central part of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Canadian Shield. Situated in the Churchill River system, this provincial park has close to 100 lakes and more than 30 canoe routes, many of which follow old fur trade routes. Summer activities include camping, hiking, boating, fishing, and swimming. In the winter, there's cross-country skiing, snowmobiling, and ice fishing. Saskatchewan's highest waterfall is in the park. Nistowiak Falls are located north of Lac La Ronge along the Rapid River. A little more than half of Lac La Ronge Provincial Park's area is water with Lac la Ronge being the largest lake. The park boundary begins on the western shore of Lac la Ronge at La Ronge and extends north to the Churchill River. Highway 102 forms this western boundary with one exception. 13 km (8 miles) north of the town of La Ronge the park goes further west to include a section of Nemeibe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lac La Ronge
Lac la Ronge is a glacial lake in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is the fifth largest lake in the province and is approximately north of Prince Albert, on the edge of the Canadian Shield. La Ronge, Air Ronge, and the Lac La Ronge First Nation are on the western shore. The lake is a popular vacation spot. Recreational activities include fishing, boating, canoeing, hiking, and camping. Recreation and access Lac La Ronge Provincial Park extends around the lake on three sides, starting at La Ronge and ending along the east shore. The park contains four RV parks, two of which are on the west shore of the lake, one is in the town of Missinipe (Missinipe is the Woodland Cree name for the Churchill River which is on the south-west shore of Otter Lake, which flows through the north side of the park), and the fourth one is on the east shore of Nemeiben Lake. There is also a hunting and fishing lodge 26 km north of La Ronge. Nistowiak Falls, on the Rapid R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Albert, Saskatchewan
Prince Albert is the third-largest city in Saskatchewan, Canada, after Saskatoon and Regina. It is situated near the centre of the province on the banks of the North Saskatchewan River. The city is known as the "Gateway to the North" because it is the last major centre along the route to the resources of northern Saskatchewan. Prince Albert National Park is located north of the city and contains a wealth of lakes, forest, and wildlife. The city itself is located in a transition zone between the aspen parkland and boreal forest biomes. Prince Albert is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Prince Albert No. 461, of which it is the seat, but is politically separate. History The area was named ''kistahpinanihk'' by the Cree, which translates to "sitting pretty place", "great meeting place" or "meeting place". The first trading post set up in the area was built in 1776 by Peter Pond. James Isbister, an Anglo-Métis employee of the Hudson's Bay Company, settled on the site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreal Forest Of Canada
Boreal may refer to: Climatology and geography *Boreal (age), the first climatic phase of the Blytt-Sernander sequence of northern Europe, during the Holocene epoch *Boreal climate, a climate characterized by long winters and short, cool to mild summers *Boreal ecosystem, an ecosystem with a subarctic climate in the Northern Hemisphere *Boreal forest, a biome characterized by coniferous forests *Boreal Sea, a Mesozoic-era seaway Companies and organizations * Boreale, a Quebec microbrewery *Boreal Mountain Resort, a ski resort in the Lake Tahoe area of California * Boreal Norge, a Norwegian public transport operator *Collège Boréal, a francophone college in Ontario, Canada Other uses * Boreal (horse), a racehorse * Carlo Boreal, a fictional character in Philip Pullman's ''His Dark Materials'' trilogy *''Le Boreal'', a French cruise ship * Borealism, the exoticisation of the northern regions of the Earth and their cultures See also *Boreal forest of Canada, a region covering muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities In Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is the Population of Canada by province and territory, sixth-most populous provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada with 1,132,505 residents as of Canada 2021 Census, 2021 and is the List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, fifth-largest in land area at . In 2021, Saskatchewan's 774 municipality, municipalities covered of the province's land mass and were home to of its population. These 774 municipalities are local government "creatures of provincial jurisdiction" with natural persons power. One of the key purposes of Saskatchewan's municipalities are "to provide services, facilities and other things that, in the opinion of council, are necessary or desirable for all or a part of the municipality". Other purposes are to: "provide good government"; "develop and maintain a safe and viable community"; "foster economic, social and environmental well-being" and "provide wise stewardship of public assets." The Government of Saskatchewan's Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least one month) must have a 24-hour average temperature of at least to fall into this category of climate, and the coldest month should ave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |