|
La Pacana
La Pacana is a Miocene age caldera in northern Chile's Antofagasta Region. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, it is part of the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex, Altiplano-Puna volcanic complex, a major caldera and silicic ignimbrite volcanic field. This volcanic field is located in remote regions at the Zapaleri tripoint between Chile, Bolivia and Argentina. La Pacana along with other regional volcanoes was formed by the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate in the Peru–Chile Trench, Peru-Chile Trench. La Pacana is situated in a basement (geology), basement formed by various Paleozoic Geological formation, formations and Tertiary ignimbrites and volcanoes. Several major fault (geology), faults cross the region at La Pacana and have influenced its volcanic activity. La Pacana is a supervolcano and is responsible for the eruption of the giant Atana ignimbrite, which reaches a volume of and constitutes the List of largest volcanic eruption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru–Chile Trench
The Peru–Chile Trench, also known as the Atacama Trench, is an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean, about off the coast of Peru and Chile. It reaches a maximum depth of below sea level in Richards Deep () and is approximately long; its mean width is and it covers an expanse of some . The trench delineates the boundary between the subducting Nazca Plate and the overriding South American Plate. Geology The trench is a result of a convergent plate boundary, where the eastern edge of the oceanic Nazca Plate is being subducted beneath the continental South American Plate. The trench is also a part of the Chile Triple Junction, an unusual junction that consists of a mid-oceanic ridge and the Chile Rise being subducted under the South American plate at the Peru-Chile Trench. Two seamount ridges within the Nazca Plate enter the subduction zone along this trench: the Nazca Ridge and the Juan Fernández Ridge. From the Chile Triple Junction to Juan Fernández Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socaire
Socaire is a village located southeast of the town of San Pedro de Atacama, in the San Pedro de Atacama province of Chile's northern Antofagasta Region. It offers views overlooking the Salar de Atacama. The local economy is dominated by agriculture and non-metallic mining. Ancient agricultural terraces are part of the landscape of the area. See also *Atacama Desert *Laguna Miscanti *Chiliques *Laguna Lejía Laguna (Italian and Spanish for lagoon) may refer to: People * Abe Laguna (born 1992), American DJ known as Ookay * Andrés Laguna (1499–1559), Spanish physician, pharmacologist, and botanist * Ana Laguna (born 1955), Spanish-Swedish ballet ... ReferencesSernatur - Socaire {{coord, 23, 35, 25, S, 67, 53, 25, W, display=title Oases of Chile Populated places in El Loa Province Climbing areas of Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paso De Jama
The Paso de Jama is a mountain pass through the Andes between Chile and Argentina, at an elevation of at the border. It is the northernmost road border crossing between the two countries. The pass is reached via Chile Route 27 and via National Route 52 (Argentina). The Chile Route 27 reaches an altitude according to OpenStreetMap of at OpenStreetMap Knoten 423099875called 2019-09-18 in a road distance of west of the border, making it one of the highest highways in South America. The pass links the city of Jujuy in Argentina with San Pedro de Atacama in Chile. The road was opened on 6 December 1991, and has been paved throughout 2005. It is open throughout the year, although occasionally closed by snow. It is used by truck traffic between northern Argentina and Paraguay Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropic Of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reaches 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight on the June Solstice. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of Cancer. The Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five major circles of latitude marked on maps of Earth. Its latitude is currently south of the Equator, but it is very gradually moving northward, currently at the rate of 0.47 arcseconds, or 15 metres, per year. Less than 3% of the world's population lives south of it; this is equivalent to about 30% of the population of the Southern Hemisphere. Name When this line of latitude was named in the last centuries BC, the Sun was in the constellation Capricornus at the December solstice. This is the date each year when the Sun reaches zenith at this latitude, the southernmost l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
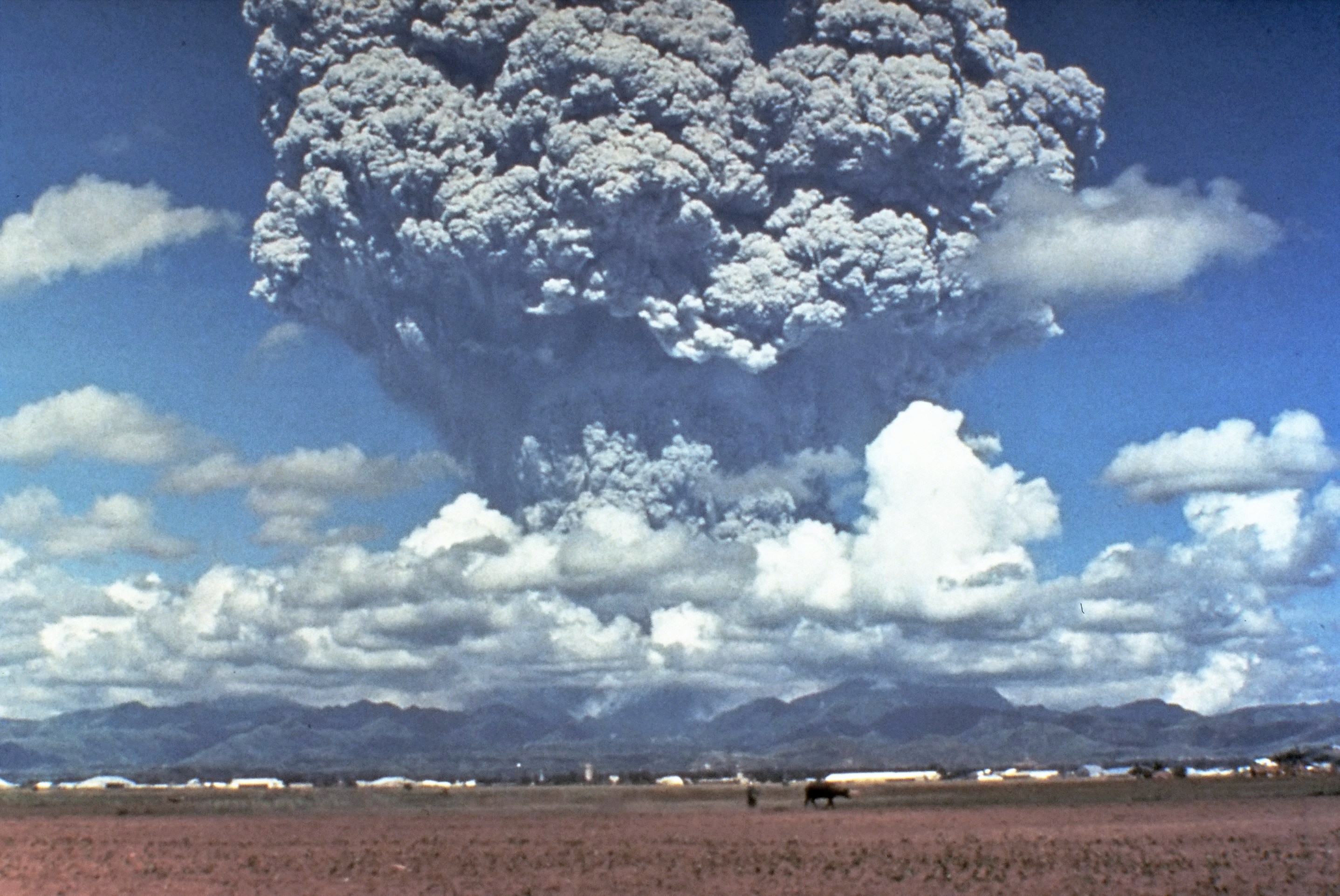
Explosive Eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma such that expelled lava violently froths into volcanic ash when pressure is suddenly lowered at the vent. Sometimes a lava plug will block the conduit to the summit, and when this occurs, eruptions are more violent. Explosive eruptions can expel as much as per second of rocks, dust, gas and pyroclastic material, averaged over the duration of eruption, that travels at several hundred meters per second as high as into the atmosphere. This cloud may subsequently collapse, creating a fast-moving pyroclastic flow of hot volcanic matter. Stages of an explosive eruption An explosive eruption begins with some form of blockage in the crater of a volcano that prevents the release of gases trapped in highly viscous andesitic or rhyolitic magma. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Largest Volcanic Eruptions
In a volcanic eruption, lava, volcanic bombs and ash, and various gases are expelled from a volcanic vent and fissure. While many eruptions only pose dangers to the immediately surrounding area, Earth's largest eruptions can have a major regional or even global impact, with some affecting the climate and contributing to mass extinctions. Volcanic eruptions can generally be characterized as either explosive eruptions, sudden ejections of rock and ash, or effusive eruptions, relatively gentle outpourings of lava. A separate list is given below for each type. There have probably been many such eruptions during Earth's history beyond those shown in these lists. However erosion and plate tectonics have taken their toll, and many eruptions have not left enough evidence for geologists to establish their size. Even for the eruptions listed here, estimates of the volume erupted can be subject to considerable uncertainty. Explosive eruptions In explosive eruptions, the eruption of magma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
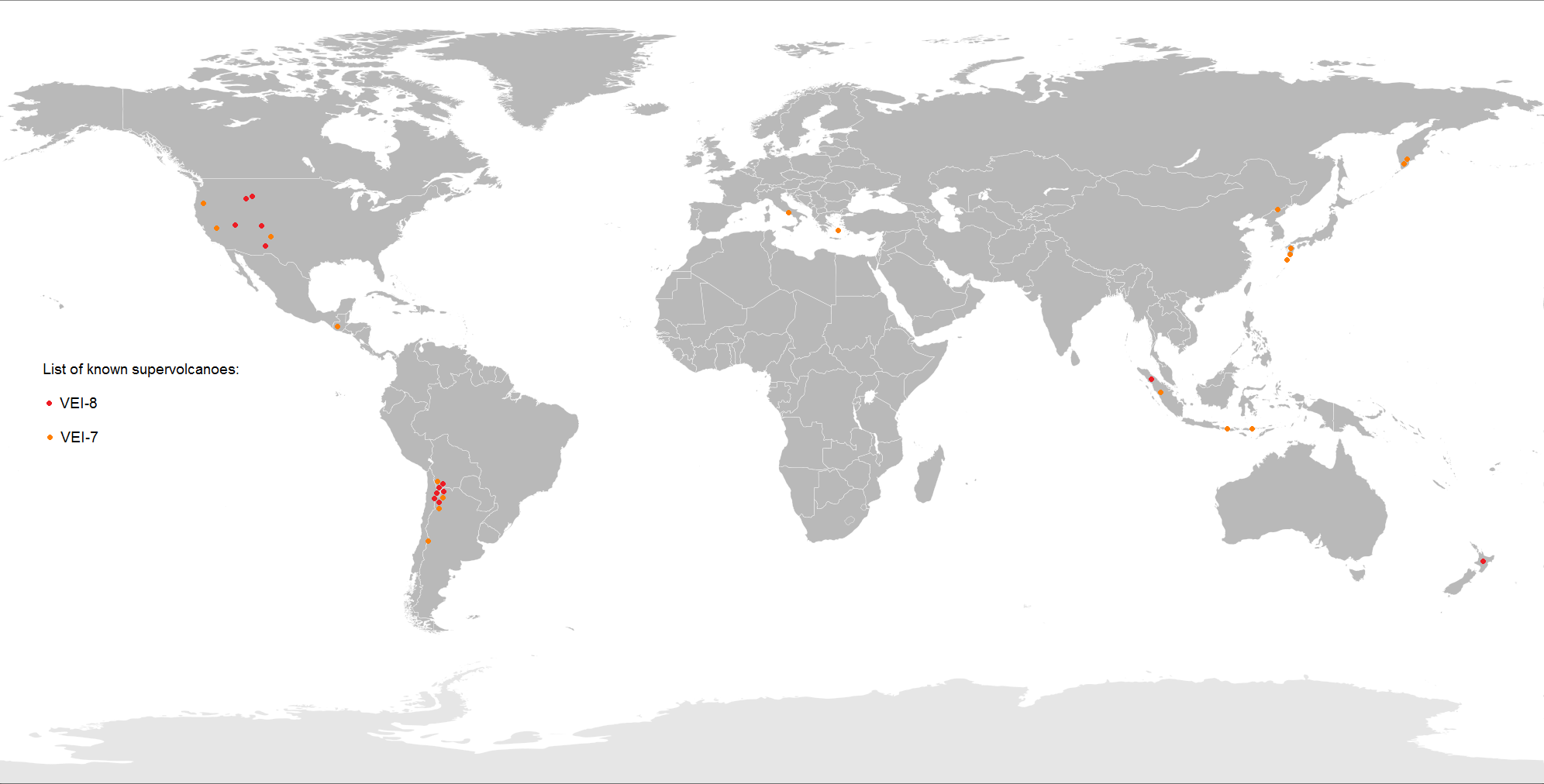
Supervolcano
A supervolcano is a volcano that has had an eruption with a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 8, the largest recorded value on the index. This means the volume of deposits for such an eruption is greater than 1,000 cubic kilometers (240 cubic miles). Supervolcanoes occur when magma in the mantle rises into the crust but is unable to break through it. Pressure builds in a large and growing magma pool until the crust is unable to contain the pressure and ruptures. This can occur at hotspots (for example, Yellowstone Caldera) or at subduction zones (for example, Toba). Large-volume supervolcanic eruptions are also often associated with large igneous provinces, which can cover huge areas with lava and volcanic ash. These can cause long-lasting climate change (such as the triggering of a small ice age) and threaten species with extinction. The Oruanui eruption of New Zealand's Taupō Volcano (about 26,500 years ago) was the world's most recent VEI-8 eruption. Terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the merged Paleogene and Neogene periods, which are informally called the Early Tertiary and the Late Tertiary, respectively. The Tertiary established the Antarctic as an icy island continent. Historical use of the term The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied. In the early d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)