|
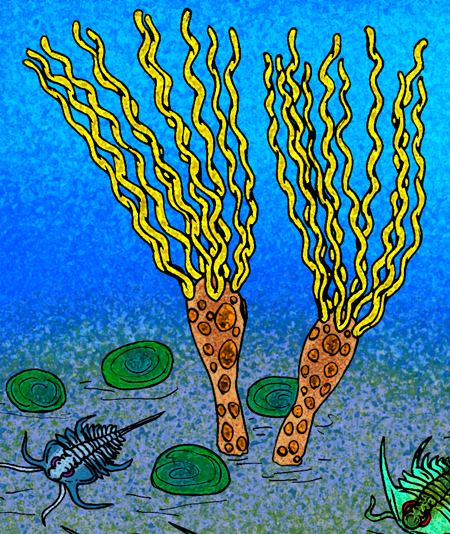
Lyracystis
''Lyracystis radiata'' is an extinct genus of Cambrian eocrinoid echinoderm, fossils of which are known from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. It is related to ''Gogia ''Gogia'' is a genus of primitive eocrinoid blastozoan from the early to middle Cambrian. ''G. ojenai'' dates to the late Early Cambrian; other species come from various Middle Cambrian strata throughout North America, but the genus has yet to ...''. References External links * Burgess Shale animals Blastozoa genera {{paleo-echinoderm-stub Cambrian genus extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gogiida
The Gogiida are an order of early echinoderms known from late Early to Middle Cambrian deposits. References Fossil taxa described in 1982 Cambrian first appearances Cambrian extinctions Blastozoa Prehistoric animal orders Echinoderm orders {{Paleo-echinoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Adult echinoderms are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are the largest entirely marine phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. The echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs, and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess Shale Animals
__NOTOC__ Burgess may refer to: People and fictional characters * Burgess (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * Burgess (given name), a list of people Places * Burgess, Michigan, an unincorporated community *Burgess, Missouri, United States * Burgess, South Carolina, United States *Burgess, Virginia, United States *Burgess Township, Bond County, Illinois, United States *Burgess Park, London, England *Burgess Field Oxford, England *Burgess Hill, Sussex, England *Mount Burgess, Canadian Rockies *Burgess Branch, a tributary of Missisquoi River, Vermont, United States Other uses *Burgess (title), a political official or representative *Burgess Company, an American airplane manufacturer *Burgess GAA, an athletic club in Ireland See also *Burgess House (other), several buildings named *Burgess model, or Concentric zone model, a theoretical model in urban geography *Burgess reagent, used in organic chemistry *Burgess Shale, a fossil-bearing formation near Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gogia
''Gogia'' is a genus of primitive eocrinoid blastozoan from the early to middle Cambrian. ''G. ojenai'' dates to the late Early Cambrian; other species come from various Middle Cambrian strata throughout North America, but the genus has yet to be described outside this continent. Notable localities where species are found include the Wheeler Shale of Utah, and the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The species of ''Gogia'', like other eocrinoids, were not closely related to the true crinoids, instead, being more closely related to the blastoids. ''Gogia'' is distinguished from sea lilies, and most other blastoids, in that the plate-covered body was shaped like a vase, or a bowling pin (with the pin part stuck into the substrate), and that the five ambulacra were split into pairs of coiled or straight, ribbon-like strands. Six specimens of ''Gogia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed The Phyllopod bed, designated by USNM locality number 35k, is the most famous fossil-be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver. The first known human inhabitants of the area settled in British Columbia at least 10,000 years ago. Such groups include the Coast Salish, Tsilhqotʼin, and Haida peoples, among many others. One of the earliest British settlements in the area was Fort Victoria, established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints. The rock unit is a black shale and crops out at a number of localities near the town of Field in Yoho National Park Yoho National Park ( ) is a National Parks of Canada, national park of Canada. It is located within the Canadian Rockies, Rocky Mountains along the western slope of the Continental Divide of the Americas in southeastern British Columbia, bordered ... and the Kicking Horse Pass. Another outcrop is in Kootenay National Park 42 km to the south. History and significance The Burgess Shale was discovered by palaeontologist Charles Doolittle Walcott, Charles Walcott on 30 August 1909, towards the end of the season's fieldwork. He returned in 1910 with his sons, daughter, and wif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocrinoidea
The Eocrinoidea are an extinct class of echinoderms that lived between the Early Cambrian and Late Silurian periods. They are the earliest known group of stalked, arm-bearing echinoderms, and were the most common echinoderms during the Cambrian. Eocrinoids were a paraphyletic group that may have been ancestral to six other classes: Rhombifera, Diploporita, Coronoidea, Blastoidea, Parablastoidea, and Paracrinoidea. They may also be the progenitors of the cystoids, who are believed to be ancestral to modern crinoids. The earliest genera had a short holdfast and irregularly structured plates. Later forms had a fully developed stalk with regular rows of plates. They were benthic suspension feeders, with five ambulacra on the upper surface, surrounding the mouth and extending into a number of narrow arms. An unusual Ordovician form was the conical '' Bolboporites'' with its single brachiole.Rozhnov, S.V. and Kushlina, V.B. 1994. Interpretation of new data on ''Bolboporites'' Pande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Adult echinoderms are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are the largest entirely marine phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. The echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs, and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
