|
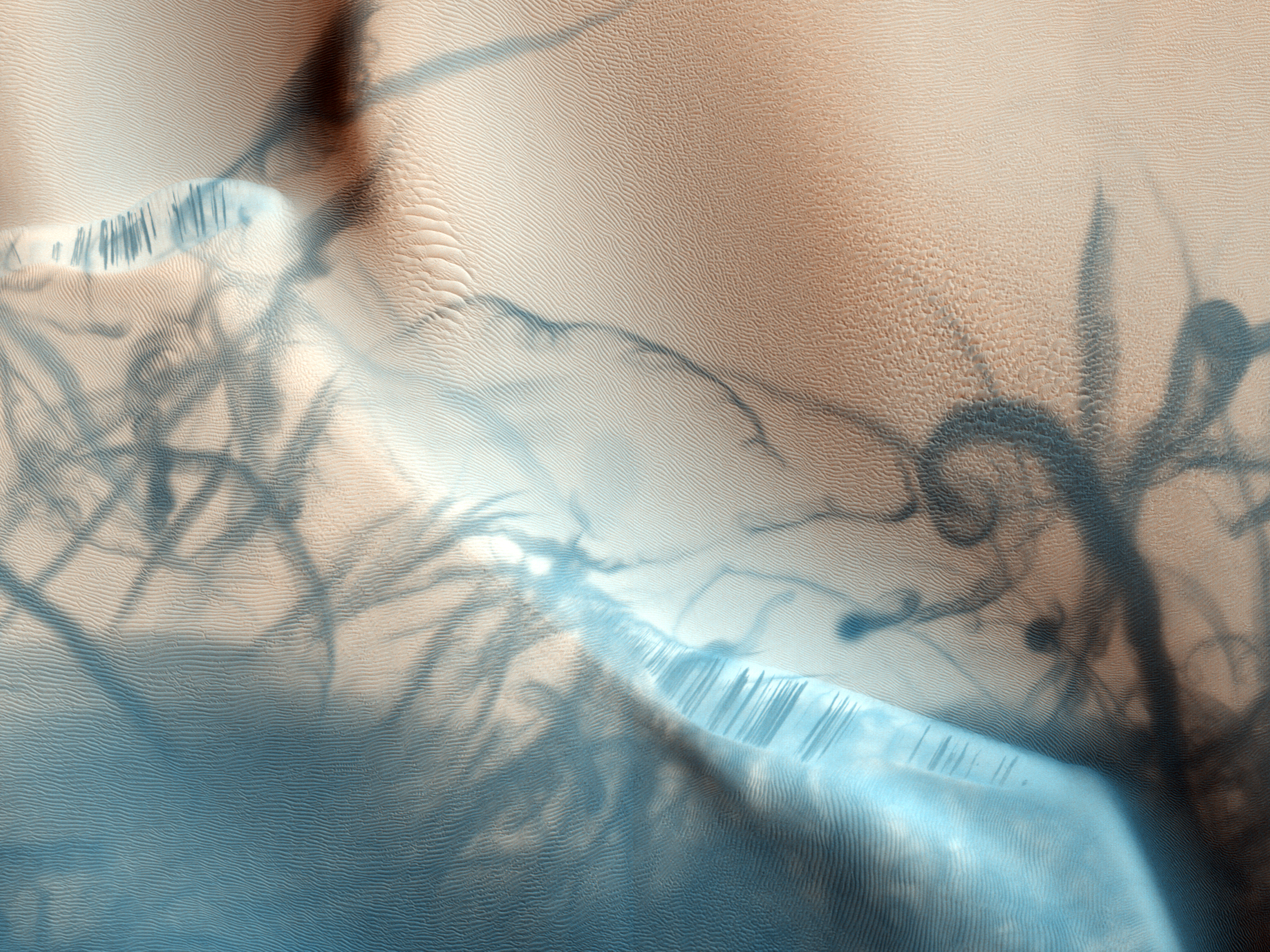
Lycus Sulci
Lycus Sulci is a feature in the Amazonis quadrangle on Mars, with its location centered at 24.6° north latitude and 141.1° west longitude. It is 1,350 km long and is named after a classical albedo feature name. The term "sulci" is applied to subparallel furrows and ridges. Gallery Image:Lycus Sulci from HiRISE.JPG, Surface features of Lycus Sulci, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program. File:27356ovalcraterwall.png, Crater wall and floor in Lycus Sulci, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The crater floor contains many mounds and ridges. The part in the box is enlarged in the next photo. File:27356ridgesclose.jpg, Close-up of a mound and ridges, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. ESP 046002 2115layers.jpg, Layers and dark slope streak Dark slope streaks are narrow, avalanche-like features common on dust-covered slopes in the equatorial regions of Mars.Chuang, F.C.; Beyer, R.A.; Bridges, N.T. (2010). Modification of Martian Slope Streaks by Eolian Processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THEMIS
In Greek mythology and religion, Themis (; grc, Θέμις, Themis, justice, law, custom) is one of the twelve Titan children of Gaia and Uranus, and the second wife of Zeus. She is the goddess and personification of justice, divine order, fairness, law, and custom, and her symbols include the Scales of Justice. She is also associated with oracles and prophecies, including the Oracle of Delphi. Name ''Themis'' means "divine law" rather than human ordinance, literally "that which is put in place", from the Greek verb ''títhēmi'' ( τίθημι), meaning "to put." To the ancient Greeks she was originally the organizer of the "communal affairs of humans, particularly assemblies." Moses Finley remarked of ''themis'', as the word was used by Homer in the 8th century BCE, to evoke the social order of the 10th- and 9th-century Greek Dark Ages: Finley adds, "There was ''themis''—custom, tradition, folk-ways, ''mores'', whatever we may call it, the enormous power of 'it is ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonis Quadrangle
The Amazonis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Amazonis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-8 (Mars Chart-8). The quadrangle covers the area from 135° to 180° west longitude and 0° to 30° north latitude on Mars. The Amazonis quadrangle contains the region called Amazonis Planitia. This area is thought to be among the youngest parts of Mars because it has a very low density of craters. The Amazonian Epoch is named after this area. This quadrangle contains special, unusual features called the Medusae Fossae Formation and Sulci. Medusae Fossae Formation The Amazonis quadrangle is of great interest to scientists because it contains a big part of a formation, called the Medusae Fossae Formation. It is a soft, easily eroded deposit that extends for nearly 1,000 km along the equator of Mars. The surface of the formation has been eroded by the wind into a series o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus (geology)
Sulcus (plural: sulci ) is, in astrogeology, an area of complex parallel or subparallel ridges and furrows on a planet or moon. For example, Uruk Sulcus is a bright region of grooved terrain adjacent to Galileo Regio on Jupiter Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandt ...'s moon Ganymede. References Planetary geology {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiWish Program
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016. Glacial features Some landscapes look just like glaciers moving out of mountain valleys on Earth. Some have a hollowed-out appearance, looking like a glacier after almost all the ice has disappeared. What is left are the moraines—the dirt and debris carried by the glacier. The center is hollowed out because the ice is mostly gone. These supposed alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Slope Streak
Dark slope streaks are narrow, avalanche-like features common on dust-covered slopes in the equatorial regions of Mars.Chuang, F.C.; Beyer, R.A.; Bridges, N.T. (2010). Modification of Martian Slope Streaks by Eolian Processes. ''Icarus,'' 205 154–164. They form in relatively steep terrain, such as along escarpments and crater walls.Schorghofer, N.; Aharonson, O.; Khatiwala, S. (2002). Slope Streaks on Mars: Correlations with Surface Properties and the Potential Role of Water. ''Geophys. Res. Lett.,'' 29(23), 2126, . Although first recognized in Viking Orbiter images from the late 1970s,Morris, E.C. (1982). Aureole Deposits of the Martian Volcano Olympus Mons. ''J. Geophys. Res.,'' 87(B2), 1164–1178.Ferguson, H.M.; Lucchitta, B.K. (1984). Dark Streaks on Talus Slopes, Mars in ''Reports of the Planetary Geology Program 1983, NASA Tech. Memo., TM-86246,'' pp. 188–190. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19840015363_1984015363.pdf. dark slope streaks were not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |