|
Lustratio
''Lustratio'' was an ancient Greek and ancient Roman purification ritual. It included a procession and in some circumstances the sacrifice of a pig (''sus''), a ram (''ovis''), and a bull (''taurus'') (''suovetaurilia''). Purpose One reason for a ''lustratio'' was to rid newborn children of any harmful spirits that may have been acquired at birth prior to the ''dies lustricus''. The ceremony took place at the age of nine days for baby boys and eight days for baby girls. In the ceremony, the procession traced a magical boundary around the child to be purified. At the end of the ceremony, if the child was male, he was presented with a small charm, usually of gold, called a ''bulla'' and kept in a leather bag around the boy's neck. This ''bulla'' would be worn until the boy became a man and exchanged the child's purple-lined toga ''toga praetexta'' for the plain '' toga virilis'' of an adult. The ''lustratio'' ceremony culminated with the naming of the child, the name being added to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
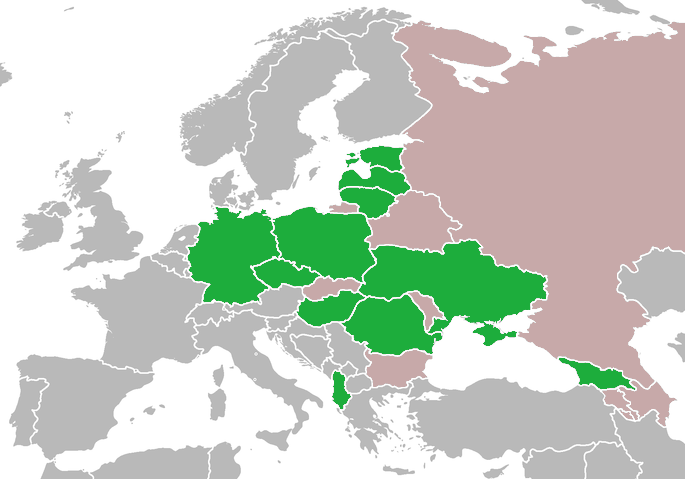
Lustration
Lustration is the purge of government officials in Central and Eastern Europe. Various forms of lustration were employed in post-communist Europe. Etymology Lustration in general is the process of making something clear or pure, usually by means of a propitiatory offering. The term is taken from the ancient Roman lustratio purification rituals. Background According to a 1992 constitutional amendment in the Czech Republic, a person who publicly denies, puts in doubt, approves, or tries to justify Nazi or Communist genocide or other crimes of Nazis or Communists will be punished with a prison term of six months to three years. In 1992, Barbara Harff wrote that no Communist country or governing body had been convicted of genocide. In his 1999 foreword to ''The Black Book of Communism'', Martin Malia wrote: "Throughout the former Communist world, moreover, virtually none of its responsible officials has been put on trial or punished. Indeed, everywhere Communist parties, tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrifice
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly existed before that. Evidence of ritual human sacrifice can also be found back to at least pre-Columbian civilizations of Mesoamerica as well as in European civilizations. Varieties of ritual non-human sacrifices are practiced by numerous religions today. Terminology The Latin term ''sacrificium'' (a sacrifice) derived from Latin ''sacrificus'' (performing priestly functions or sacrifices), which combined the concepts ''sacra'' (sacred things) and ''facere'' (to do or perform). The Latin word ''sacrificium'' came to apply to the Christian eucharist in particular, sometimes named a "bloodless sacrifice" to distinguish it from blood sacrifices. In individual non-Christian ethnic religions, terms translated as "sacrifice" include the Indic ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
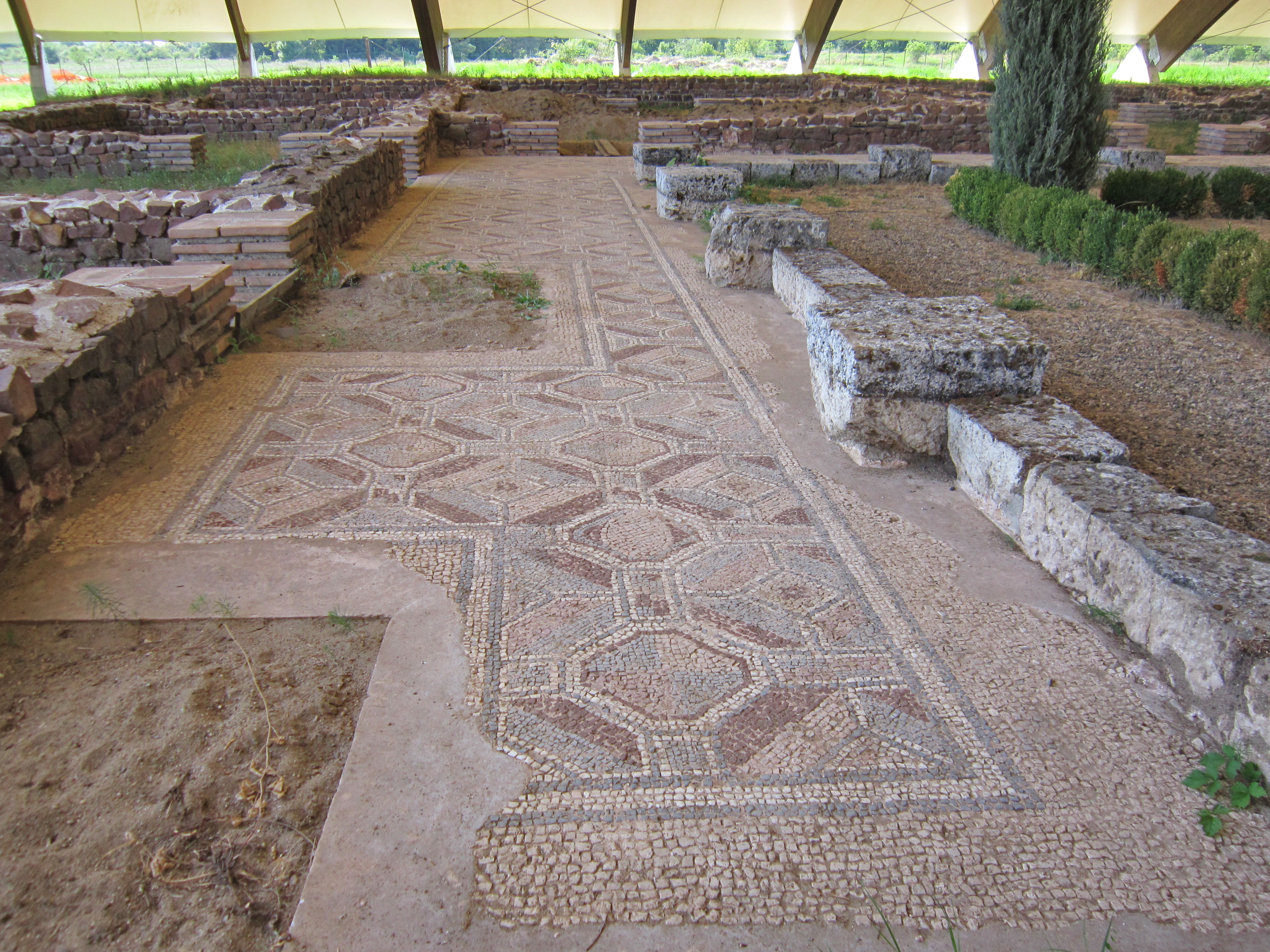
Suovetaurilia
The or was one of the most sacred and traditional rites of Roman religion: the sacrifice of a pig (), a sheep () and a bull () to the deity Mars to bless and purify land (). Summary There were two kinds: * ("suckling suovetaurilia") of a male pig, a lamb and a calf, for purifying private fields * ("greater suovtaurilia") of a boar, a ram and a bull, for public ceremonies. The ritual for private fields is preserved in Cato the Elder's , "On Agriculture". The first step was to lead the three animals around the boundaries of the land to be blessed, pronouncing the following words: : :"That with the good help of the gods success may crown our work, I bid thee, Manius, to take care to purify my farm, my land, my ground with this suovetaurilia, in whatever part thou thinkest best for them to be driven or carried around." "Manius" in this passage may be an obscure minor deity, related to the Manes, or may be the equivalent of English John Doe. Then, before the sacrifice is pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dies Lustricus
In ancient Rome the ''dies lustricus'' ("day of lustration" or "purification day") was a traditional naming ceremony in which an infant was purified and given a ''praenomen'' (given name). This occurred on the eighth day for girls and the ninth day for boys, a difference Plutarch explains by noting that "it is a fact that the female grows up, and attains maturity and perfection before the male." Until the umbilical cord fell off, typically on the seventh day, the baby was regarded as "more like a plant than an animal," as Plutarch expresses it. The ceremony of the ''dies lustricus'' was thus postponed until the last tangible connection to the mother's body was dissolved and the child was seen "as no longer forming part of the mother, and in this way as possessing an independent existence which justified its receiving a name of its own and therefore a fate of its own." The day was celebrated with a family feast. The childhood goddess Nundina presided over the event, and the goddess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylonian Affair
Cylon (Greek: Κύλων ''Kylon'') was an Athenian associated with the first reliably dated event in Athenian history, the Cylonian Affair, an attempted seizure of power in the city. Cylon, one of the Athenian nobles and a previous victor of the Olympic Games, attempted a coup in 632 BC with support from Megara, where his father-in-law, Theagenes, was tyrant. The oracle at Delphi had advised him to seize Athens during a festival of Zeus, which Cylon understood to mean the Olympics. However, the coup was opposed, and Cylon and his supporters took refuge in Athena's temple on the Acropolis. Cylon and his brother escaped, but his followers were cornered by Athens' nine archons. According to Plutarch and Thucydides (1.126), they were persuaded by the archons to leave the temple and stand trial after being assured that their lives would be spared. In an effort to ensure their safety, the accused tied a rope to the temple's statue and went to the trial. On the way, the rope (again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Religion
Religion in ancient Rome consisted of varying imperial and provincial religious practices, which were followed both by the people of Rome as well as those who were brought under its rule. The Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, and attributed their success as a world power to their collective piety ''(pietas)'' in maintaining Pax deorum, good relations with the gods. Their Polytheism, polytheistic religion is known for having honored List of Roman deities, many deities. The presence of Magna Graecia, Greeks on the Italian peninsula from the beginning of the historical period influenced Culture of ancient Rome, Roman culture, introducing some religious practices that became fundamental, such as the ''Cult (religious practice), cultus'' of Apollo. The Romans looked for common ground between their major gods and those of the Greeks (''interpretatio graeca''), adapting Greek mythology, Greek myths and iconography for Latin literature and Roman art, as the Etruscans h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Rituals
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Religions have sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolution
Absolution is a traditional theological term for the forgiveness imparted by ordained Christian priests and experienced by Christian penitents. It is a universal feature of the historic churches of Christendom, although the theology and the practice of absolution vary between denominations. Some traditions see absolution as a sacrament — the Sacrament of Penance. This concept is found in the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox Church, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Assyrian Church of the East and the Lutheran Church. In other traditions, including the Anglican Communion and Methodism, absolution is seen as part of the sacramental life of the church, although both traditions are theologically predicated upon the Book of Common Prayer, which counts absolution amongst the five rites described as "Commonly called Sacraments, but not to be counted for Sacraments of the Gospel". Confession and Absolution is practiced in the Irvingian Churches, though it is not a sacrament. The concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fausta
Flavia Maxima Fausta ''Augusta'' (289–326 AD) was a Roman empress. She was the daughter of Maximian and second wife of Constantine the Great, who had her executed and excluded from all official accounts for unknown reasons. Historians Zosimus and Zonaras reported that she was executed for adultery with her stepson, Crispus. Family Fausta was the daughter of Emperor Maximian. To seal the alliance between them for control of the Tetrarchy, in 307 Maximianus married her to Constantine I, who set aside his wife, Minervina, in her favour. As the sister of Emperor Maxentius, Fausta had a part in their father's downfall. In 310 Maximian died as a consequence of an assassination plot against Constantine. Maximian decided to involve his daughter Fausta, but she revealed the plot to her husband, and the assassination was disrupted. Maximian died, by suicide or by assassination, in July of that same year. Fausta was held in high esteem by Constantine, and proof of his favour was that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crispus
Flavius Julius Crispus (; 300 – 326) was the eldest son of the Roman emperor Constantine I, as well as his junior colleague ( ''caesar'') from March 317 until his execution by his father in 326. The grandson of the ''augustus'' Constantius I, Crispus was the elder half-brother of the future ''augustus'' Constantine II and became co-''caesar'' with him and with his cousin Licinius II at Serdica, part of the settlement ending the Cibalensean War between Constantine and his father's rival Licinius I. Crispus ruled from Augusta Treverorum (Trier) in Roman Gaul between 318 and 323 and defeated the navy of Licinius I at the Battle of the Hellespont in 324, which with the land Battle of Chrysopolis won by Constantine forced the resignation of Licinius and his son, leaving Constantine the sole ''augustus'' and the Constantinian dynasty in control of the entire empire. It is unclear what was legal status of the relationship Crispus's mother Minervina had with Constantine; Crispus ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Constantius Chlorus, Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrians, Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helena, was a Greeks, Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Sasanian Empire, Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Roman Britain, Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |