|
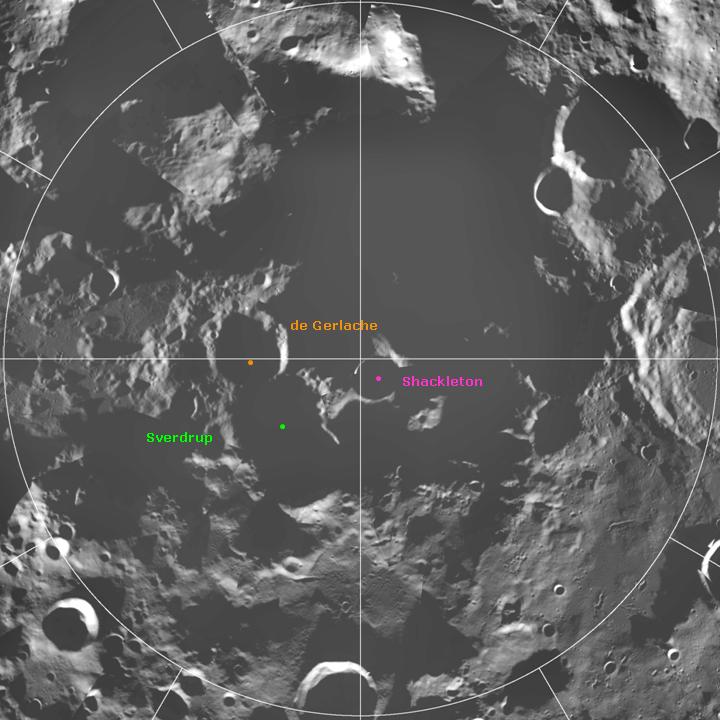
Lunar South Pole
The lunar south pole is the southernmost point on the Moon. It is of interest to scientists because of the lunar water, occurrence of water ice in Crater of eternal darkness, permanently shadowed areas around it. The lunar south pole region features craters that are unique in that the near-constant sunlight does not reach their interior. Such craters are cold trap (astronomy), cold traps that contain fossil records of hydrogen, water ice, and other volatiles dating from the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, early Solar System. In contrast, the lunar north pole region exhibits a much lower quantity of similarly sheltered craters. Geography The lunar south pole is located on the center of the polar Antarctic Circle (80°S to 90°S).Lunar South Pole. NASA. 2017. Accessed on 16 July 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
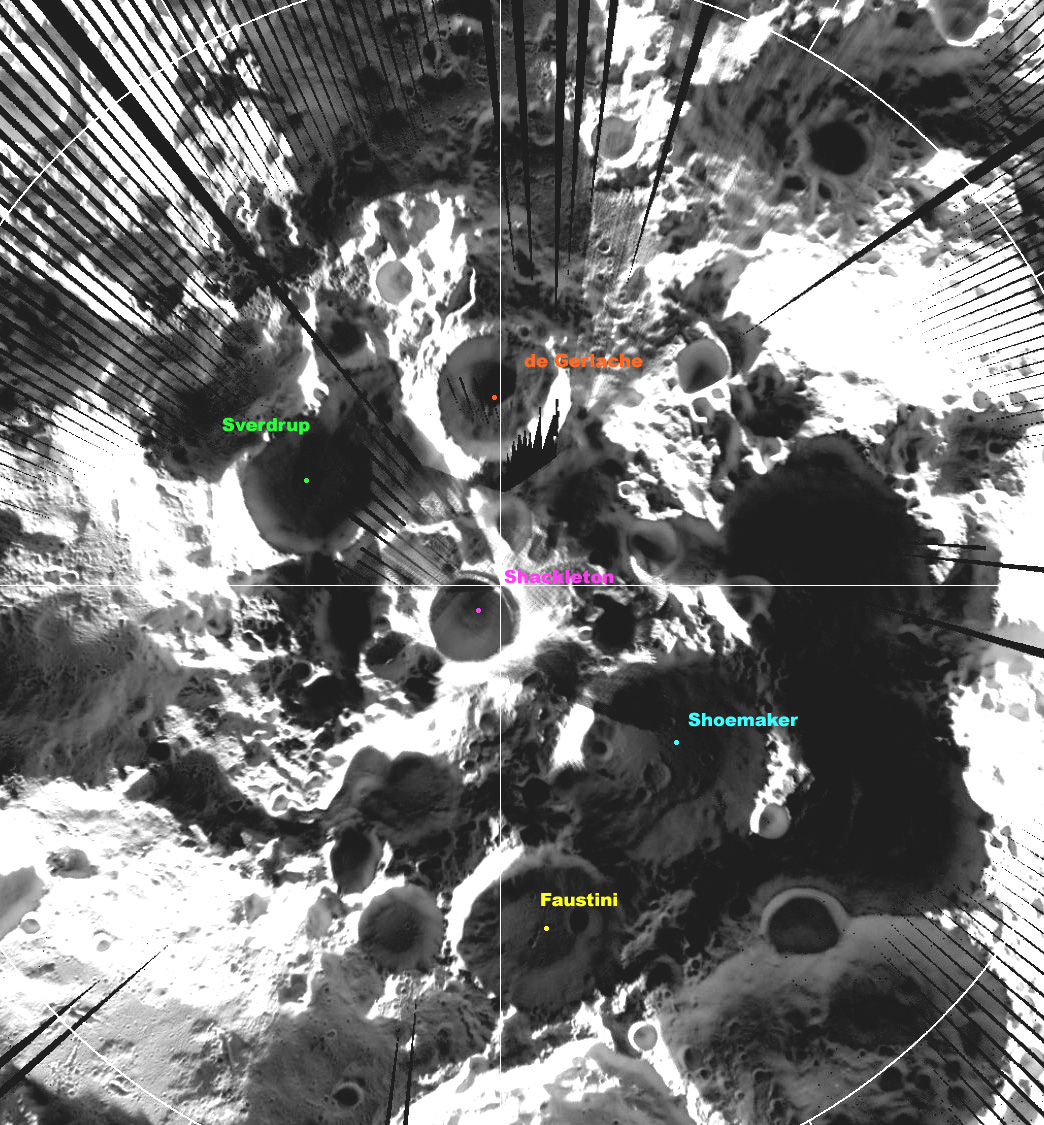
Shackleton Crater
Shackleton is an impact crater that lies at the lunar south pole. The peaks along the crater's rim are exposed to almost continual sunlight, while the interior is perpetually in shadow. The low-temperature interior of this crater functions as a cold trap that may capture and freeze volatiles shed during comet impacts on the Moon. Measurements by the ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft showed higher than normal amounts of hydrogen within the crater, which may indicate the presence of water ice. The crater is named after Antarctic explorer Ernest Shackleton. Description The rotational axis of the Moon passes through Shackleton, near the rim. The crater is in diameter and deep. From the Earth, it is viewed edge-on in a region of rough, cratered terrain. It is located within the South Pole–Aitken basin on a massif. The rim is slightly raised about the surrounding surface and it has an outer rampart that has been only lightly impacted. No significant craters intersect the rim, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sverdrup (crater)
Sverdrup is a lunar impact crater that is located about one crater diameter from the southern pole of the Moon. It lies on the far side of the Moon with respect to the Earth, in an area of the surface that is only illuminated by very oblique light from the Sun. The interior part of the crater is cloaked in perpetual darkness, and thus has not been mapped using photography. Portions of the rim are illuminated, however, and give the appearance of a worn formation that has been intruded upon by adjacent formations. The nearest craters of note to Sverdrup are de Gerlache to the east, and Shackleton at the south pole. References * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{cite news , title = Diviner lunar south pole image , publisher = UCLA The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheric gases cause it to heat up and radiate energy. It then becomes a meteor and forms a Meteoroid#Fireball, fireball, also known as a shooting star; astronomers call the brightest examples "Bolide#Astronomy, bolides". Once it settles on the larger body's surface, the meteor becomes a meteorite. Meteorites vary greatly in size. For geologists, a bolide is a meteorite large enough to create an impact crater. Meteorites that are recovered after being observed as they transit the atmosphere and Impact event, impact the Earth are called meteorite falls. All others are known as meteorite finds. Meteorites have traditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and may subtend an arc of 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religions. Comets usually have highly eccentric elliptical orbits, and they have a wide range of orbital periods, ranging from several years to potentially several mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Trap (astronomy)
A cold trap is a concept in planetary sciences that describes an area cold enough to freeze (trap) volatiles. Cold-traps can exist on the surfaces of airless bodies or in the upper layers of an adiabatic atmosphere. On airless bodies, the ices trapped inside cold-traps can potentially remain there for geologic time periods, allowing us a glimpse into the primordial solar system. In adiabatic atmospheres, cold-traps prevent volatiles (such as water) from escaping the atmosphere into space. Cold-traps on airless planetary bodies The obliquity (axial tilt) of some airless planetary bodies in our solar system such as Mercury, the Moon and Ceres is very close to zero. Harold Urey first noted that depressions or craters located near the poles of these bodies will cast persistent shadows that can survive for geologic time periods (millions–billions of years). The absence of an atmosphere prevents mixing by convection, rendering these shadows extremely cold. If molecules of volatiles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backscatter
In physics, backscatter (or backscattering) is the reflection of waves, particles, or signals back to the direction from which they came. It is usually a diffuse reflection due to scattering, as opposed to specular reflection as from a mirror, although specular backscattering can occur at normal incidence with a surface. Backscattering has important applications in astronomy, photography, and medical ultrasonography. The opposite effect is forward scatter, e.g. when a translucent material like a cloud diffuses sunlight, giving soft light. Backscatter of waves in physical space Backscattering can occur in quite different physical situations, where the incoming waves or particles are deflected from their original direction by different mechanisms: *Diffuse reflection from large particles and Mie scattering, causing alpenglow and gegenschein, and showing up in weather radar; * Inelastic collisions between electromagnetic waves and the transmitting medium (Brillouin scattering and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
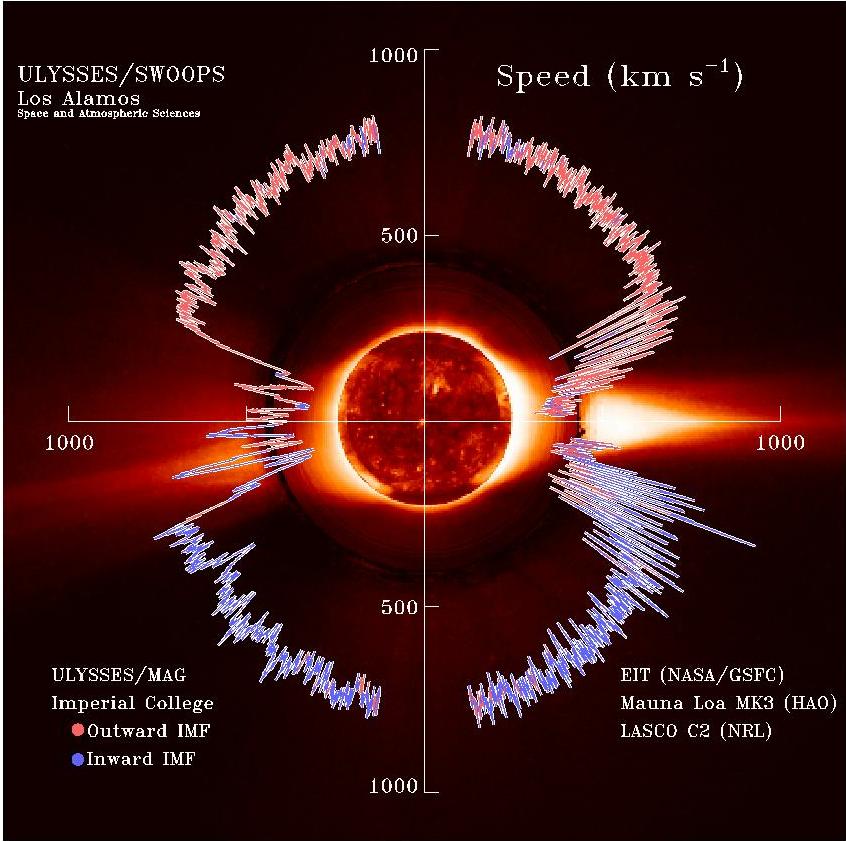
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions to the Moon. Its detailed mapping program is identifying safe landing sites, locating potential resources on the Moon, characterizing the radiation environment, and demonstrating new technologies. Launched on June 18, 2009, in conjunction with the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), as the vanguard of NASA's Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, LRO was the first United States mission to the Moon in over ten years. LRO and LCROSS were launched as part of the United States's Vision for Space Exploration program. The probe has made a 3-D map of the Moon's surface at 100-meter resolution and 98.2% coverage (excluding polar areas in deep shadow), including 0.5-meter resolution images of Apollo landing sites. The first images f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
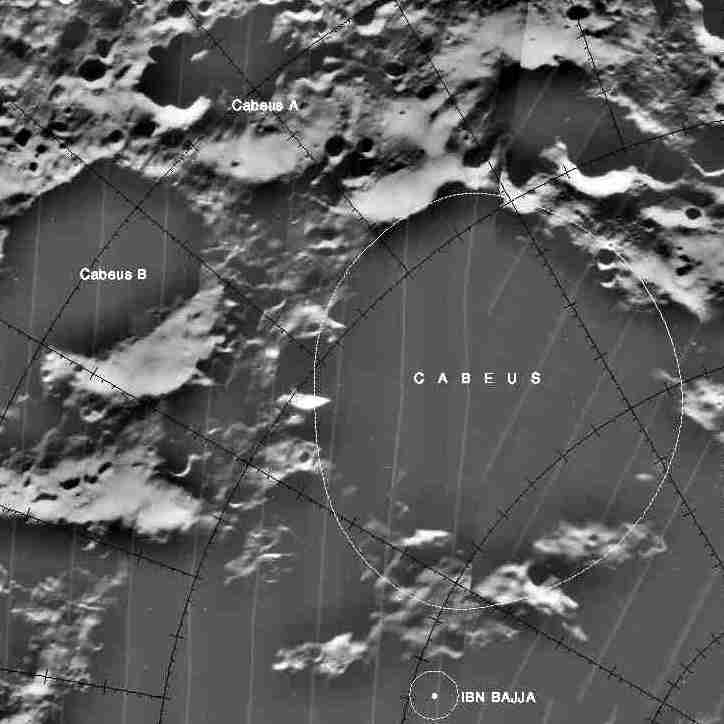
Cabeus (crater)
Cabeus is a lunar impact crater that is located about from the south pole of the Moon. At this location the crater is seen obliquely from Earth, and it is almost perpetually in deep shadow due to lack of sunlight. Hence, not much detail can be seen of this crater, even from orbit. Through a telescope, this crater appears near the southern limb of the Moon, to the west of the crater Malapert and to the south-southwest of Newton. Description The crater name ''Cabeus'' first appeared in the 1651 work ''Almagestum Novum'' by Giovanni Riccioli, who named it after Niccolò Cabeo. However, the position of the Cabeus crater was in the location later assigned to Newton crater.Whitaker (1999:61, 211) The official name and location for this crater was adopted by the IAU Commission 17, as established in the 1935 work ''Named Lunar Formations'' by Mary A. Blagg and Karl Müller. This crater is a worn formation that has been eroded by subsequent impacts. The rim is eroded and uneve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobile (crater)
Nobile is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southern pole of the Moon. It lies to the south of the crater Scott, along the western rim of Amundsen. Between Nobile and the southern pole lie the smaller craters Shoemaker and Faustini. This is an eroded crater formation that is almost constantly cloaked in deep shadows. When sunlight does enter the interior of this crater, it does so at a very oblique angle. The crater rim is overlaid by several lesser craters, the most notable being a formation about half the diameter of Nobile along the western rim. There are also small craters along the southwest and northern parts of the rim. The outer rampart of Amundsen overlies the eastern rim and inner wall. The interior floor of this crater is somewhat irregular, and there are a few small craterlets across the surface. Nobile was previously designated Scott A before being assigned a name by the IAU. On 20 September 2021, NASA selected the western edge of Nobile as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



_launches_with_LRO_and_LCROSS.jpg)

