|
Lumitrack
Lumitrack is a motion capture technology developed by Robert Xiao, Chris Harrison and Scott Hudson at Carnegie Mellon University. It combines projectors and sensors to provide high-fidelity motion-tracking. These types of sensors are used in video game controllers, such as Microsoft's Kinect, and in motion capture for movie and television production. Although the research prototype of Lumitrack currently uses visible light, it could be adapted to utilize invisible infrared light. According to the university, the sensors require little power and should be cheap to mass-produce. They could even be built into smartphones. Technology The projectors cover the tracked area with structured patterns called a binary m-sequence that resemble barcodes. The series of bars encodes a series of an assortment of vertical lines of varying thicknesses, without repeating any combination of seven adjacent line types anywhere in the projected image. The sensors read the bars to assess motion. The ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chris Harrison (computer Scientist)
Chris Harrison is a British-born, American computer scientist and entrepreneur, working in the fields of human–computer interaction, machine learning and sensor-driven interactive systems. He is a professor at Carnegie Mellon University and director of the Future Interfaces Group within the Human–Computer Interaction Institute. He has previously conducted research at AT&T Labs, Microsoft Research, IBM Research and Disney Research. He is also the CTO and co-founder of Qeexo, a machine learning and interaction technology startup. Harrison has authored more than 80 peer-reviewed papers and his work appears in more than 40 books. For his contributions in human–computer interaction, Harrison was named a top 35 innovator under 35 by MIT Technology Review (2012), a top 30 scientist under 30 by Forbes (2012), one of six innovators to watch by Smithsonian (2013), and a top Young Scientist by the World Economic Forum (2014). Over the course of his career, Harrison has been awarded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Hudson (computer Scientist)
Scott E. Hudson is a professor in the Human-Computer Interaction Institute at Carnegie Mellon University. He was previously an associate professor in the College of Computing at the Georgia Institute of Technology, and prior to that, an assistant professor of computer science at the University of Arizona. He earned his Ph.D. in computer science at the University of Colorado in 1986. Hudson has published over 150 papers and is the 17th most prolific author in the field. "HCI Bibliography: Most Frequent Authors. URL retrieved 21 April 2008. "ACM Author Page: Scott E. Hudson. URL retrieved 22 April 2008. He is the most published author at the prestigious [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
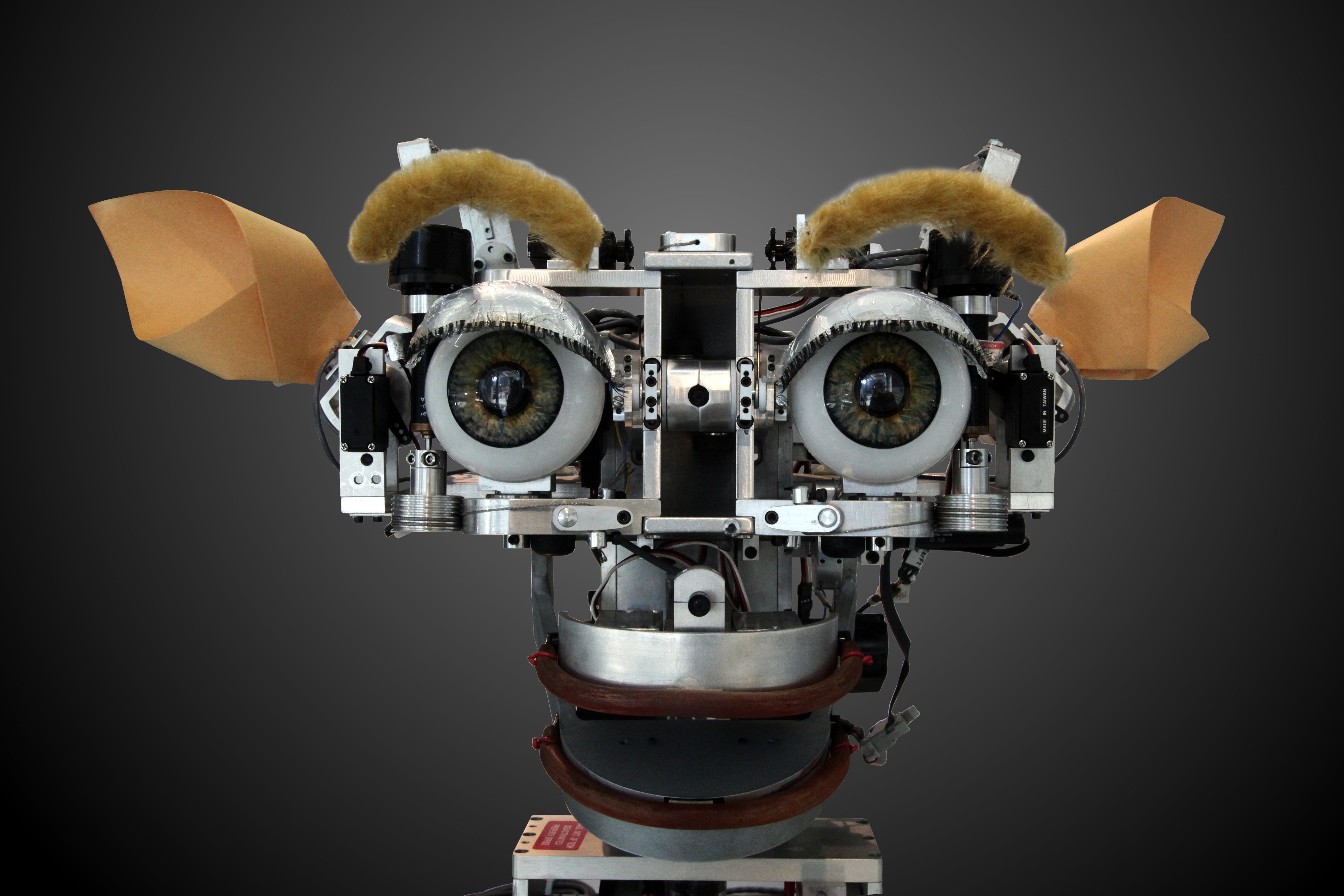
Motion Capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mo-cap or mocap, for short) is the process of recording the movement of objects or people. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robots. In filmmaking and video game development, it refers to recording actions of human actors, and using that information to animate digital character models in 2-D or 3-D computer animation.Andrew Harris Salomon, Feb. 22, 2013, Backstage MagazineGrowth In Performance Capture Helping Gaming Actors Weather Slump Accessed June 21, 2014, "..But developments in motion-capture technology, as well as new gaming consoles expected from Sony and Microsoft within the year, indicate that this niche continues to be a growth area for actors. And for those who have thought about breaking in, the message is clear: Get busy...."Ben Child, 12 August 2011, The GuardianAndy Serkis: why won't Oscars go ape over motion-capture acting? Star of Rise of the Planet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. One of its predecessors was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools; it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology in 1912 and began granting four-year degrees in the same year. In 1967, the Carnegie Institute of Technology merged with the Mellon Institute of Industrial Research, founded in 1913 by Andrew Mellon and Richard B. Mellon and formerly a part of the University of Pittsburgh. Carnegie Mellon University has operated as a single institution since the merger. The university consists of seven colleges and independent schools: The College of Engineering, College of Fine Arts, Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences, Mellon College of Science, Tepper School of Business, Heinz College of Information Systems and Public Policy, and the School of Computer Science. The university has its main campus located 5 miles (8 km) from Downto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office suite, and the Internet Explorer and Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Meta. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen on April 4, 1975, to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinect
Kinect is a line of motion sensing input devices produced by Microsoft and first released in 2010. The devices generally contain RGB cameras, and infrared projectors and detectors that map depth through either structured light or time of flight calculations, which can in turn be used to perform real-time gesture recognition and body skeletal detection, among other capabilities. They also contain microphones that can be used for speech recognition and voice control. Kinect was originally developed as a motion controller peripheral for Xbox video game consoles, distinguished from competitors (such as Nintendo's Wii Remote and Sony's PlayStation Move) by not requiring physical controllers. The first-generation Kinect was based on technology from Israeli company PrimeSense, and unveiled at E3 2009 as a peripheral for Xbox 360 codenamed "Project Natal". It was first released on November 4, 2010, and would go on to sell eight million units in its first 60 days of availability. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary M-sequence
Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1) * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that takes two arguments * Binary relation, a relation involving two elements * Binary-coded decimal, a method for encoding for decimal digits in binary sequences * Finger binary, a system for counting in binary numbers on the fingers of human hands Computing * Binary code, the digital representation of text and data * Bit, or binary digit, the basic unit of information in computers * Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text ** Executable, a type of binary file that contains machine code for the computer to execute * Binary tree, a computer tree data structure in which each node has at most two children Astronomy * Binary star, a star system with two stars in it * Binary planet, two planetary bodies of comparable m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcodes
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers, of which there are several types. Later, two-dimensional (2D) variants were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons and other patterns, called ''matrix codes'' or ''2D barcodes'', although they do not use bars as such. 2D barcodes can be read using purpose-built 2D optical scanners, which exist in a few different forms. 2D barcodes can also be read by a digital camera connected to a microcomputer running software that takes a photographic image of the barcode and analyzes the image to deconstruct and decode the 2D barcode. A mobile device with an inbuilt camera, such as smartphone, can function as the latter type of 2D barcode reader using specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human–robot Interaction
Human–robot interaction is the study of interactions between humans and robots. It is often referred as HRI by researchers. Human–robot interaction is a multidisciplinary field with contributions from human–computer interaction, artificial intelligence, robotics, natural-language understanding, design, and psychology. Origins Human–robot interaction has been a topic of both science fiction and academic speculation even before any robots existed. Because much of active HRI development depends on natural-language processing, many aspects of HRI are continuations of human communications, a field of research which is much older than robotics. The origin of HRI as a discrete problem was stated by 20th-century author Isaac Asimov in 1941, in his novel ''I, Robot''. He states the Three Laws of Robotics as: # A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm. # A robot must obey the orders by human beings except where such orders would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking
Tracking may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Tracking, in computer graphics, in match moving (insertion of graphics into footage) * Tracking, composing music with music tracker software * Eye tracking, measuring the position of the eye relative to the head * Finger tracking, measuring the positions of the fingers * Optical motion tracking, or motion capture, recording the precise movements of objects or people * Position tracking, monitoring the location of a mechanical system in real-time by counting pulses; see * Positional tracking, an essential component of augmented reality * Video tracking, locating an object in each frame of a video sequence * Mobile phone tracking, monitoring the physical location of a mobile phone * Internet tracking, analyzing online activity * Web visitor tracking, the analysis of visitor behavior on a website * Sleep tracking, monitoring sleeping experience (deep, REM, duration etc.) Life sciences * Animal migration tracking, perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing Input Devices
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology and software engineering. The term "computing" is also synonymous with counting and calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by mechanical computing machines, and before that, to human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. Computing is intimately tied to the representation of numbers, though mathematical concepts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)