|
Luke Foxe
Luke Foxe (or Fox) (20 October 1586 – c. 15 July 1635) was an English explorer, born in Kingston-upon-Hull, Yorkshire, who searched for the Northwest Passage across North America. In 1631, he sailed much of the western Hudson Bay before concluding no such passage was possible. Foxe Basin, Foxe Channel and Foxe Peninsula were named after him. He left the Thames in May 1631 in the ''Charles'', took 20 days to work through Hudson Strait, reaching the Bay on 11 July. Blocked by ice to the northward, he went south of Southampton Island to Roes Welcome Sound and south along the west shore to Port Nelson, Manitoba where he found Thomas Button's winter camp of 18 years before, turned north-east, met Thomas James on 29 August, went north into Foxe Channel and into the lower part of Foxe Basin, turned back at 66°47'N, passed Hudson Strait in 10 days and reached England in October without any deaths among his crew. Early life The son of Richard Fox, seaman and assistant of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston-upon-Hull
Kingston upon Hull, usually abbreviated to Hull, is a port city and unitary authority in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It lies upon the River Hull at its confluence with the Humber Estuary, inland from the North Sea and south-east of York, the historic county town. With a population of (), it is the fourth-largest city in the Yorkshire and the Humber region after Leeds, Sheffield and Bradford. The town of Wyke on Hull was founded late in the 12th century by the monks of Meaux Abbey as a port from which to export their wool. Renamed ''Kings-town upon Hull'' in 1299, Hull had been a market town, military supply port, trading centre, fishing and whaling centre and industrial metropolis. Hull was an early theatre of battle in the English Civil Wars. Its 18th-century Member of Parliament, William Wilberforce, took a prominent part in the abolition of the slave trade in Britain. More than 95% of the city was damaged or destroyed in the blitz and suffered a pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the World War II, Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Pinnace
The full-rigged pinnace was the larger of two types of vessel called a pinnace in use from the sixteenth century. Etymology The word ''pinnace'', and similar words in many languages (as far afield as Indonesia, where the boat "pinisi" took its name from the Dutch ''pinas''), came ultimately from the Spanish ''pinaza'' c. 1240, from ''pino'' (pine tree), from the wood of which the ships were constructed. The word came into English from the Middle French ''pinasse''. Design "The pinnace is perhaps the most confusing of all the early seventeenth-century types of vessels. Pinnace was more of a use than a type name, for almost any vessel could have been a pinnace or tender to a larger one. Generally speaking, pinnaces were lightly built, single-decked, square-sterned vessels suitable for exploring, trading, and light naval duties. On equal lengths, pinnaces tended to be narrower than other types. Although primarily sailing vessels, many pinnaces carried sweeps for moving in calms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Briggs (mathematician)
Henry Briggs (1 February 1561 – 26 January 1630) was an English mathematician notable for changing the original logarithms invented by John Napier into common (base 10) logarithms, which are sometimes known as Briggsian logarithms in his honour. The specific algorithm for long division in modern use was introduced by Briggs 1600 AD. Briggs was a committed Puritan and an influential professor in his time. Personal life Briggs was born at Daisy Bank, Sowerby Bridge, near Halifax, in Yorkshire, England. After studying Latin and Greek at a local grammar school, he entered St John's College, Cambridge, in 1577, and graduated in 1581. In 1588, he was elected a Fellow of St John's. In 1592, he was made reader of the physical lecture founded by Thomas Linacre; he also read some of the mathematical lectures. During this period, he took an interest in navigation and astronomy, collaborating with Edward Wright. In 1596, he became first professor of geometry in the recently f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Waymouth
George Weymouth (Waymouth) () was an English explorer of the area now occupied by the state of Maine. Voyages George Weymouth was a native of Cockington, Devon, who spent his youth studying shipbuilding and mathematics. In 1602 Weymouth was hired to seek a northwest passage to India by the recently formed East India Company. He sailed the ship ''Discovery'' 300 miles into Hudson Strait but turned back on July 26, as the year was far spent and many men were ill. Weymouth reached Dartmouth on September 5, 1602. 1605 expedition In March 1605 Thomas Arundell, 1st Baron Arundell of Wardour and Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton sent Captain Weymouth to found a colony in Virginia under the ruse of searching again for a northwest passage. Weymouth sailed from England on March 31, 1605 on the ship ''Archangel''Drake, Samuel Adams. ''The Pine-tree Coast'', (Estes & Lauriat, 1890), 218. and landed near Monhegan off the coast of Maine on May 17, 1605. A report of the voyage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
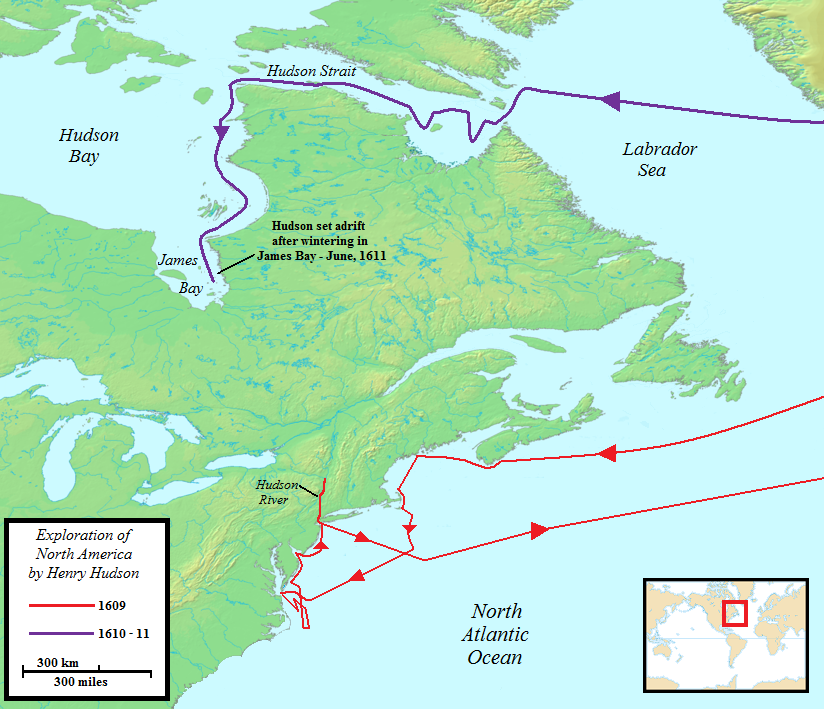
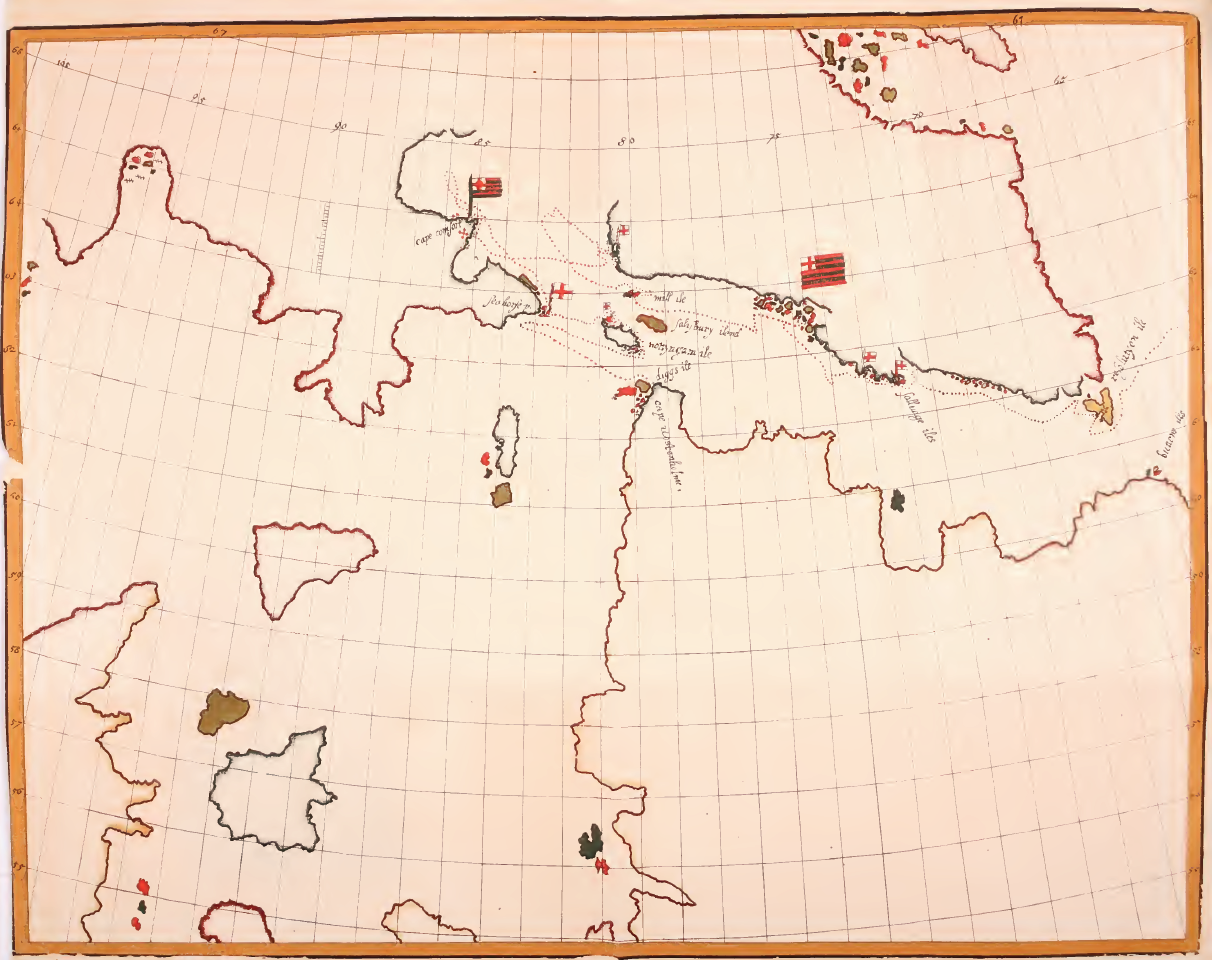
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States. In 1607 and 1608, Hudson made two attempts on behalf of English merchants to find a rumoured Northeast Passage to Cathay via a route above the Arctic Circle. In 1609, he landed in North America on behalf of the Dutch East India Company and explored the region around the modern New York metropolitan area. Looking for a Northwest Passage to Asia on his ship '' Halve Maen'' ("Half Moon"), he sailed up the Hudson River, which was later named after him, and thereby laid the foundation for Dutch colonization of the region. On his final expedition, while still searching for the Northwest Passage, Hudson became the first European to see Hudson Strait and the immense Hudson Bay. In 1611, after wintering on the shore of James Bay, Hudson wanted to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Thomas Button
Sir Thomas Button (died April, 1634) was a Welsh officer of the Royal Navy, notable as an explorer who in 1612–1613 commanded an expedition that unsuccessfully attempted to locate explorer Henry Hudson and to navigate the Northwest Passage. Early life Born about 1575, he was the fourth son of Miles Button of Worlton, Glamorgan, and his wife Margaret, daughter of Edward Lewis. His father's family had been landowners, originally at Bitton in Gloucestershire, since the 1100s. Around 1595 he married Elizabeth, daughter of landowner Sir Walter Rice of Newton House, Llandeilo, and his wife Elizabeth, daughter of Sir Edward Mansell of Margam. This made him a nephew of the prominent naval officer Sir Robert Mansell, from whose patronage he benefited for the rest of his career. Arctic exploration In April 1612 he was given command of two navy ships, ''Resolution'' and ''Discovery'', to lead an expedition in search of the North-West Passage. Sailing from England about the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Baffin
William Baffin ( – 23 January 1622) was an English navigator, explorer and cartographer. He is primarily known for his attempt to find a Northwest Passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific, during the course of which he was the first European to discover Baffin Bay situated between Canada and Greenland. He was also responsible for exceptional surveys of the Red Sea and Persian Gulf on behalf of the East India Company. Life Nothing is known about Baffin's early life (an estimated year of birth, 1584, originated in the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' in the 19th century, but without known documentary support). It has been conjectured that he was born to a humble station in London and gradually raised himself through his diligence and perseverance. In printing his journals, Samuel Purchas wrote of him as a "learned-unlearned Mariner and Mathematician... wanting art of words" who "really employed himself to those industries, whereof here you see so evident fruits." His earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bylot
Robert Bylot () was an English explorer who made four voyages to the Arctic. He was uneducated and from a working-class background, but was able to rise to rank of master in the English Royal Navy. Voyages Robert Bylot First voyage, 1610–1611 Bylot was first mate on the during Henry Hudson's 1610–1611 expedition into what is now known as Hudson Bay. In the spring of 1611, Hudson wanted to continue the expedition, but the crew wanted to return home. There was discontent between the captain and members of the crew, and Bylot was stripped of his rank. Later there was a mutiny in which Hudson, his son and several sailors were set adrift in an open boat in James Bay. It was due to Bylot's navigational skills that ''Discovery'' was able to return from the Arctic safely; Hudson and his party were never seen again. Upon return to England, Bylot was tried as a mutineer but was pardoned. Second voyage, 1612–1613 Bylot returned to Hudson Bay in 1612 with Sir Thomas Butto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(1906).jpg)