|
Ludwig Bruns
Ludwig Bruns (25 June 1858 – 9 November 1916) was a German neurologist who was a native of Hanover. He studied medicine in Göttingen (since 1878: member of Corps Hannovera Göttingen) and Munich, receiving his doctorate in 1882. Subsequently, he was an assistant to Eduard Hitzig (1839-1907) at the insane asylum in Nietleben as well as at the psychiatric and nerve clinic in Halle. Afterwards he worked with Karl Westphal (1833-1890) and Hermann Oppenheim (1858-1919) at the Charité Hospital in Berlin. Bruns would maintain a working relationship with Oppenheim throughout his professional career. He also studied in Paris (under Jean Charcot) and England, later returning to his hometown of Hanover, where in 1903 he became a professor of neurology. Bruns was the first director of the ''Gesellschaft Deutscher Nervenärzte'' (German Society of Neurologists). Bruns was interested in all aspects of neurology, however he is best known for his work in the fields of child neurology and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Cramer
Johann Baptist August Cramer (10 November 1860 – 5 September 1912) was a Swiss-German neuropathologist and psychiatrist who was a native of the canton St. Gallen. He studied medicine in Marburg and Freiburg, earning his medical doctorate in 1887. In 1889 be began work at a mental asylum in Eberswalde, and in 1895 received his habilitation in psychiatry at the University of Göttingen, where he subsequently became a professor and director of the psychiatric clinic. At Göttingen he helped establish the ''Provinzial-Jugendheim'', an institution for treatment and education of psychopathic youth. Cramer published numerous essays on clinical psychiatry, brain pathology, pathological anatomy, et al. Among his better known books were a treatise on forensic psychiatry titled ''Gerichtliche Psychiatrie. Ein Leitfaden für Mediziner und Juristen'', and a textbook of nervous disorders in children that he co-authored with Ludwig Bruns (1858–1916) and Theodor Ziehen Georg Theodor Zi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a " bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
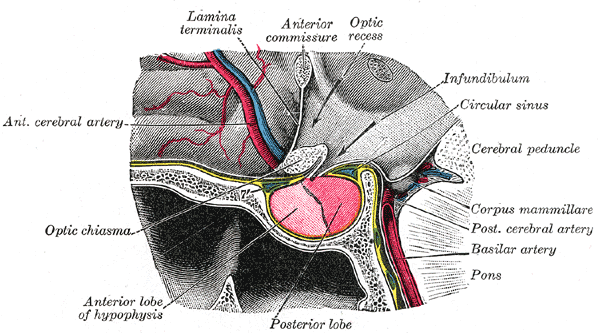
Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Structure The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner of the third ventricle itself forms a bulb, known as the ''anterior recess'' (it is also known as the ''bulb of the ventricl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to Motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in Fine motor skill, fine movement, Equilibrioception, equilibrium, Human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Ventricle
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The fourth ventricle has a characteristic diamond shape in cross-sections of the human brain. It is located within the pons or in the upper part of the medulla oblongata. CSF entering the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct can exit to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord through two lateral apertures and a single, midline median aperture. Boundaries The fourth ventricle has a roof at its ''upper'' (posterior) surface and a floor at its ''lower'' (anterior) surface, and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles (nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties walking. It is typically worse when the head is moved. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. The most common disorders that result in vertigo are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Ménière's disease, and labyrinthitis. Less common causes include stroke, brain tumors, brain injury, multiple sclerosis, migraines, trauma, and uneven pressures between the middle ears. Physiologic vertigo may occur following being exposed to motion for a prolonged period such as when on a ship or simply following spinning with the eyes closed. Other causes may include toxin exposures such as to carbon monoxide, alcohol, or aspirin. Vertigo typically indicates a problem in a part of the vestibular system. Other causes of dizziness include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication (especially in case of migraine or cluster headache). A headache is one of the most commonly experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe (though not well-defined) is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is covered by the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex includes the premotor cortex, and the primary motor cortex – parts of the motor cortex. The front part of the frontal cortex is covered by the prefrontal cortex. There are four principal gyri in the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus is directly anterior to the central sulcus, running parallel to it and contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |