|
Lu Kai
Lu Kai (198 – December 269 or January 270), courtesy name Jingfeng, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Born in the influential Lu clan of the Wu region towards the end of the Eastern Han dynasty, Lu Kai started his career around the beginning of the Three Kingdoms period as a county chief and later a military officer under Sun Quan, the founding emperor of Eastern Wu. During the reign of Sun Liang, he participated in some battles against bandits and Eastern Wu's rival state Cao Wei, and was promoted to the rank of General. Throughout the reign of Sun Xiu and early reign of Sun Hao, Lu Kai continued to hold military commands until September or October 266, when Sun Hao appointed him and Wan Yu as the Left and Right Imperial Chancellors of Eastern Wu respectively. Well known for being outspoken and candid, Lu Kai strongly objected to Sun Hao's decision to move the imperial capital from J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor (China)
The grand chancellor (, among other titles), also translated as counselor-in-chief, chancellor, chief councillor, chief minister, imperial chancellor, lieutenant chancellor and prime minister, was the highest-ranking executive official in the imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history, and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly, even during a particular dynasty. Professor Zhu Zongbin of Peking University outlined the role of "grand chancellor" as one with the power to oversee all jurisdictional matters, the right to decide and to draft edicts with other ministers, and the position of chief advisor to the emperor. This extended even to the ability to criticize the emperor's edicts and decisions. Thus, the grand chancellor served as the emperor's chief of staff and main political advisor, often exercising power second only to the emperor. In practice, the grand chancellor was often a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy Name
A courtesy name ( zh, s=字, p=zì, l=character), also known as a style name, is an additional name bestowed upon individuals at adulthood, complementing their given name. This tradition is prevalent in the East Asian cultural sphere, particularly in China, Japan, Korea, Taiwan and Vietnam. Courtesy names are a marker of adulthood and were historically given to men at the age of 20, and sometimes to women upon marriage. Unlike art names, which are more akin to pseudonyms or pen names, courtesy names served a formal and respectful purpose. In traditional Chinese society, using someone's given name in adulthood was considered disrespectful among peers, making courtesy names essential for formal communication and writing. Courtesy names often reflect the meaning of the given name or use homophonic characters, and were typically disyllabic after the Qin dynasty. The practice also extended to other East Asian cultures, and was sometimes adopted by Mongols and Manchu people, Manchus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu County
Wu County or Wuxian (; 221 B.C. – December 2000) is a former county and city located in modern Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province. Its name refers to its former status as the capital of the state of Wu during the Spring and Autumn period. History In 221 BC, Emperor Qin Shi Huang established Wu County as the capital of Kuaiji Commandery. The city itself was often known as Kuaiji from this role, prior to return of Kuaiji's administration to present-day Shaoxing on the southern shore of Hangzhou Bay. In 1928, the government of the Republic of China split the urban area of Wu County and set up Suzhou City. Two years later, the decision was withdrawn. After the establishment of the People's Republic of China, Suzhou City was divided from Wu County again in 1949. In March 1983, Wu County became a county of prefecture-level city Suzhou. In June 1995, Wu County was renamed to Wuxian City, a county-level city. In December 2000, it was divided into two districts, currently known as Wuzh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A commandery ( zh, s=郡, p=jùn) was a historical administrative division of China that was in use from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). Several neighboring countries adopted Chinese commanderies as the basis for their own administrative divisions. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou dynasty, Zhou's Chinese feudalism, vassal states—including Qin (state), Qin, Jin (Chinese state), Jin and Wei (state), Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into Counties of the People's Republic of China#History, counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, commanderies were developed as marchlands between the Warring States period, major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (265–420)
Jin may refer to: States Jìn 晉 * Jin (Chinese state) (晉國), major state of the Zhou dynasty, existing from the 11th century BC to 376 BC * Jin dynasty (266–420) (晉朝), also known as Liang Jin and Sima Jin * Jin (Later Tang precursor) (晉國; 907–923), Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Later Jin (Five Dynasties) (後晉; 936–947), Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Jīn 金 * Jin dynasty (1115–1234) (金朝), also known as the Jurchen Jin * Later Jin (1616–1636) (後金; 1616–1636), precursor of the Qing dynasty Others * Jin (Korean state) (辰國), precursor of the Jinhan Confederation * Balhae (698–713), originally known as Jin (震) Places * Jin Prefecture (Shanxi) (晉州), a former Chinese prefecture centered on present-day Linfen, Shanxi * Jin Prefecture (Shaanxi) (金州), a former Chinese efecture centered on present-day Ankang, Shaanxi * Jin Prefecture (Hunan) (锦州), a former Chinese prefecture centered on Luyang in present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400. Situated in the Yangtze River Delta, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and Chinese culture, culture, having served as the historical capitals of China, capital of various Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to Port of Nanjing, one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial city, sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China, administrative structure, enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiankang
Jiankang (), or Jianye (), as it was originally called, was the capital city of the Eastern Wu (229–265 and 266–280 CE), the Jin dynasty (265–420), Eastern Jin dynasty (317–420 CE) and the Southern Dynasties (420–552), including the Chen dynasty (557–589 CE). Its walls are extant as ruins in the modern prefecture-level city, municipal region of Nanjing. Jiankang was an important city of the Song dynasty. Its name was changed to Nanjing during the Ming dynasty. History Before the Eastern Jin the city was known as Jianye, and it was the capital of the kingdom of Eastern Wu, Wu during the Three Kingdoms period. It was renamed Jiankang during the Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin dynasty, in order to observe the naming taboo for Emperor Min of Jin. Renamed Jiankang in 313 CE, it served as the capital of the Eastern Jin, following the retreat from the north due to Xiongnu raids. Jiankang remained the capital of the Southern Dynasties: Liu Song (420–479), Southern Qi (479 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dynasty. Its capital was initially located at Xuchang, and was later moved to Luoyang. The name ''Wei'' first became associated with Cao Cao when he was named the Duke of Wei by the Eastern Han government in 213, and became the name of the state when Cao Pi proclaimed himself emperor in 220. Historians often add the prefix "Cao" to distinguish it from other Chinese states known as ''Wei (other), Wei''. The authority of the ruling Cao family dramatically weakened following the deposition and execution of Cao Shuang, a regent for the dynasty's third emperor Cao Fang. Beginning in 249, another regent in Sima Yi gradually consolidated state authority for himself and his relatives, with the last Wei emperors largely being puppet ruler, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Quan
Sun Quan (; 182 – 21 May 252), courtesy name Zhongmou (), posthumous name, posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of Eastern Wu, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime established by his elder brother, Sun Ce, in 200. He declared formal independence and ruled from November 222 to May 229 as the King of Wu and from May 229 to May 252 as the Emperor of Wu. Unlike his rivals Cao Cao and Liu Bei, Sun Quan was much younger and governed his state mostly separate of politics and ideology. He is sometimes portrayed as neutral considering he adopted a flexible foreign policy between his two rivals with the goal of pursuing the greatest interests for the country. Sun Quan was born while his father Sun Jian served as the adjutant of Xiapi County. After Sun Jian's death in the early 190s, he and his family lived at various cities on the lower Yangtze, until Sun Ce carved out a warlord regime in the Jiangnan, Jiangdong region, based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
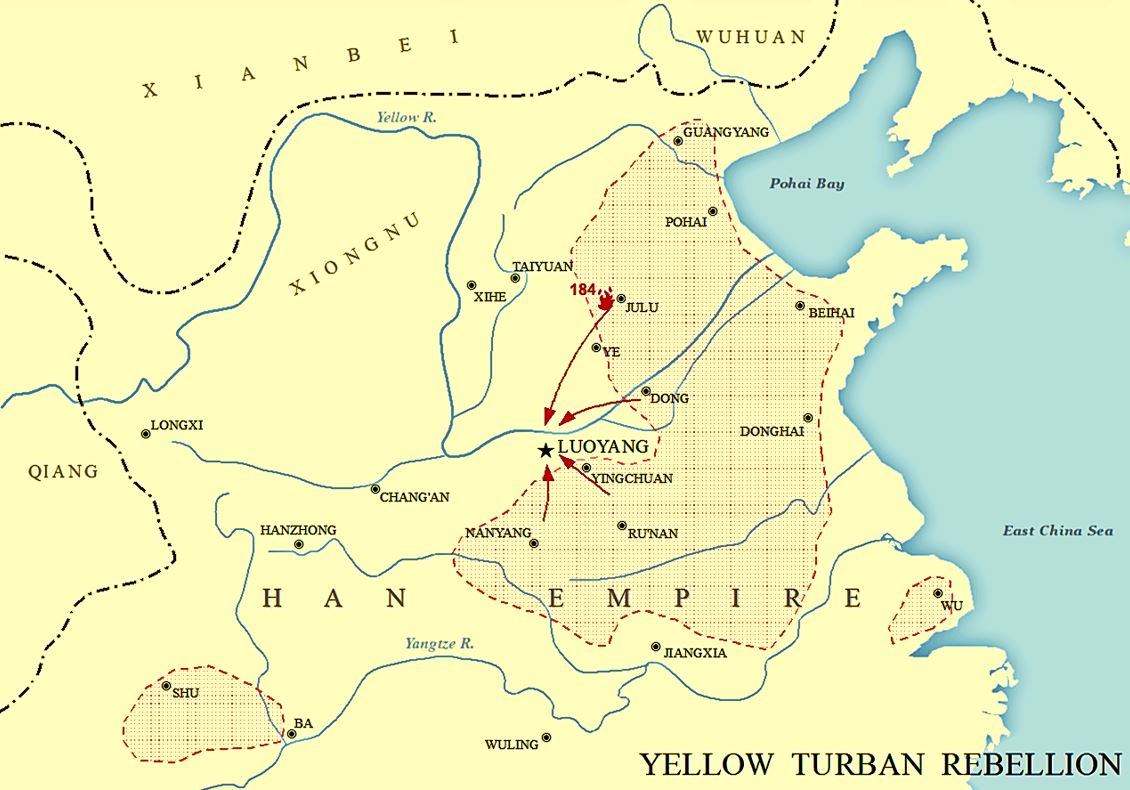
End Of The Han Dynasty
The end of the (Eastern) Han dynasty was the period of History of China, Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian. It was followed by the Three Kingdoms era (220–280 CE). During the end of the Han dynasty, the country was thrown into turmoil by the Yellow Turban Rebellion (184–205). Meanwhile, the Han Empire's institutions were destroyed by the warlord Dong Zhuo and fractured into regional regimes ruled by various warlords, some of whom were nobles and officials of the Han imperial court. The warlord Cao Cao took control of Emperor Xian and his court in 196 and began gradually reunifying the empire. Cao Cao ostensibly operated under Emperor Xian's rule, though in reality the emperor was a hostage. Cao Cao's efforts to reunify China were rebuffed at the Battle of Red Cliffs in 208-209, when his armies were defeated by the allied forces of Sun Quan and Liu Bei. The Han d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
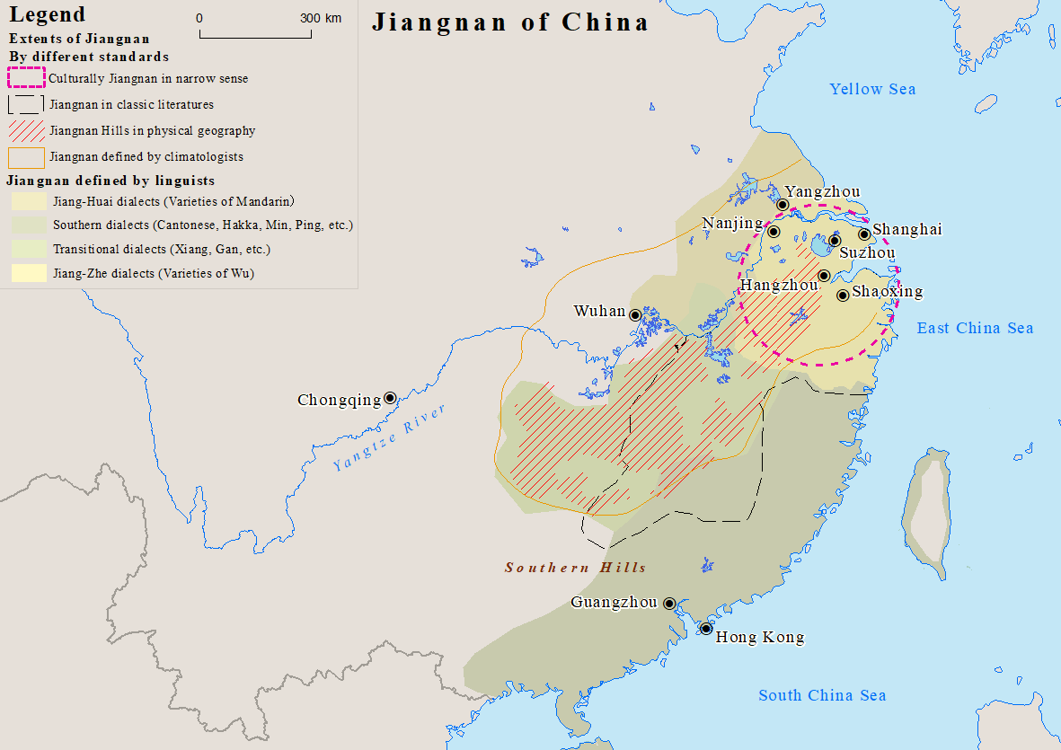
Wu (region)
Jiangnan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze, Yangtze River, including the southern part of its Yangtze Delta, delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, Yangzhou and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high list of administrative divisions of Greater China by Human Development Index, human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The name Jiangnan is the pinyin romanization of Chinese, romanization of the Standard Mandarin pronunciation of , meaning "[Lands] South of the Yangtze Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |