|
Louis Auguste Blanqui
Louis Auguste Blanqui (; 8 February 1805 – 1 January 1881) was a French socialist and political activist, notable for his revolutionary theory of Blanquism. Biography Early life, political activity and first imprisonment (1805–1848) Blanqui was born in Puget-Théniers, Alpes-Maritimes, where his father, Jean Dominique Blanqui, of Italian descent, was subprefect. He was the younger brother of the liberal economist Jérôme-Adolphe Blanqui. He studied both law and medicine, but found his real vocation in politics, and quickly became a champion of the most advanced opinions. A member of the Carbonari society since 1824, he took an active part in most republican conspiracies during this period. In 1827, under the reign of Charles X (1824–1830), he participated in a street fight in Rue Saint-Denis, during which he was seriously injured. In 1829, he joined Pierre Leroux's ''Globe'' newspaper before taking part in the July Revolution of 1830. He then joined the '' Amis d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget-Théniers
Puget-Théniers (; oc, Lo Puget Tenier; it, Poggetto Tenieri) is a commune in the Alpes-Maritimes department in southeastern France. Geography It is situated on in the valley of the Var. History It was part of the historic County of Nice until 1860 as ''Poggetto Tenieri''. Personalities It is the birthplace of Auguste Blanqui, Jean-Pierre Papon and Aimé Teisseire. Population See also *Communes of the Alpes-Maritimes department References External links Puget-Théniers Tourist Information* & (Occitan Occitan may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain. * Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France. * Occitan language Occitan (; ...Dance and traditional music from Puget-Théniers Communes of Alpes-Maritimes Alpes-Maritimes communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{AlpesMaritimes-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Buonarroti
:''See also Filippo Buonarroti (1661–1733).'' Filippo Giuseppe Maria Ludovico Buonarroti, more usually referred to under the French version Philippe Buonarroti (11 November 1761 – 16 September 1837), was an Italian utopian socialist, writer, agitator, freemason, and conspirator; he was active in Corsica, France, and Geneva. His '' History of Babeuf’s Conspiracy of Equals'' (1828) became a quintessential text for revolutionaries, inspiring such socialists as Blanqui and Marx. He proposed a mutualist strategy that would revolutionize society by stages, starting from monarchy to liberalism, then to radicalism, and finally to communism. Life Early activism Born in Pisa in the Grand Duchy of Tuscany to a family of local nobility, Buonarroti studied jurisprudence at the University of Pisa, where he founded what was seen by the authorities of Grand Duke Peter Leopold as a subversive paper, the ''Gazetta Universale'' (1787). It is thought that he joined a Masonic Lod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded language to produce an emotional rather than a rational response to the information that is being presented. Propaganda can be found in news and journalism, government, advertising, entertainment, education, and activism and is often associated with material which is prepared by governments as part of war efforts, political campaigns, health campaigns, revolutionaries, big businesses, ultra-religious organizations, the media, and certain individuals such as soapboxers. In the 20th century, the English term ''propaganda'' was often associated with a manipulative approach, but historically, propaganda has been a neutral descriptive term of any material that promotes certain opinions or ideologies. Equivalent non-English terms have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxists
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, no single, definitive Marxist theory exists. In addition to the schools of thought which emphasize or modify elements of classical Marxism, various Marxian concepts have been incorporated and adapted into a diverse array of social theories leading to widely varying conclusions. Alongside Marx's critique of political economy, the defining characteristics of Marxism have often been described using the terms dialectical materialism and historical materialism, though these terms were coined after Marx's death and their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Revolutions Of 1848 In France
The French Revolution of 1848 (french: Révolution française de 1848), also known as the February Revolution (), was a brief period of civil unrest in France, in February 1848, that led to the collapse of the July Monarchy and the foundation of the French Second Republic. It sparked the wave of revolutions of 1848. The revolution took place in Paris, and was preceded by the French government's crackdown on the campagne des banquets. Starting on 22 February as a large-scale protest against the government of François Guizot, it later developed into a violent uprising against the monarchy. After intense urban fighting, large crowds managed to take control of the capital, leading to the abdication of King Louis Philippe on 24 February and the subsequent proclamation of the Second Republic. Background Under the Charter of 1814, Louis XVIII ruled France as the head of a constitutional monarchy. Upon Louis XVIII's death, his brother, the Count of Artois, ascended to the throne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Imprisonment
Life imprisonment is any sentence (law), sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes for which, in some countries, a person could receive this sentence include murder, torture, terrorism, child abuse resulting in death, rape, espionage, treason, drug trafficking, drug possession, human trafficking, severe fraud and financial crimes, aggravated criminal damage, arson, kidnapping, burglary, and robbery, piracy, aircraft hijacking, and genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes or any three felony, felonies in case of three-strikes law. Life imprisonment (as a maximum term) can also be imposed, in certain countries, for traffic offences causing death. Life imprisonment is not used in all countries; Portugal was the first country to abolish life imprisonment, in 1884. Where life imprisonment is a possible sentenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Société Des Saisons
Lactalis is a French multinational dairy products corporation, owned by the Besnier family and based in Laval, Mayenne, France. The company's former name was Besnier SA. Lactalis is the largest dairy products group in the world, and is the second largest food products group in France, behind Danone. It owns brands such as Parmalat, Président, Siggi's Dairy, Skånemejerier, Rachel's Organic, and Stonyfield Farm. History André Besnier started a small cheesemaking company in 1933 and launched its ''Président'' brand of Camembert in 1968. In 1990, it acquired Group Bridel (2,300 employees, 10 factories, fourth-largest French dairy group) with a presence in 60 countries. In 1992, it acquired United States cheese company Sorrento. In 1999, ''la société Besnier'' became ''le groupe Lactalis'' owned by Belgian holding company BSA International SA. In 2006, they bought Italian group Galbani, and in 2008, bought Swiss cheesemaker Baer. They bought Italian group Parmalat in a 2011 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist League
The Communist League (German: ''Bund der Kommunisten)'' was an international political party established on 1 June 1847 in London, England. The organisation was formed through the merger of the League of the Just, headed by Karl Schapper, and the Communist Correspondence Committee of Brussels, Belgium, in which Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels were the dominant personalities. The Communist League is regarded as the first Marxist political party and it was on behalf of this group that Marx and Engels wrote the ''Communist Manifesto'' late in 1847. The Communist League was formally disbanded in November 1852, following the Cologne Communist Trial. Organisational history Background During the decade of the 1840s the word "communist" came into general use to describe those who supposedly hailed from the left wing of the Jacobin Club of the French Revolution.David Fernbach, "Introduction" to Karl Marx, ''The Revolutions of 1848.'' New York: Random House, 1973; pg. 23. This politica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
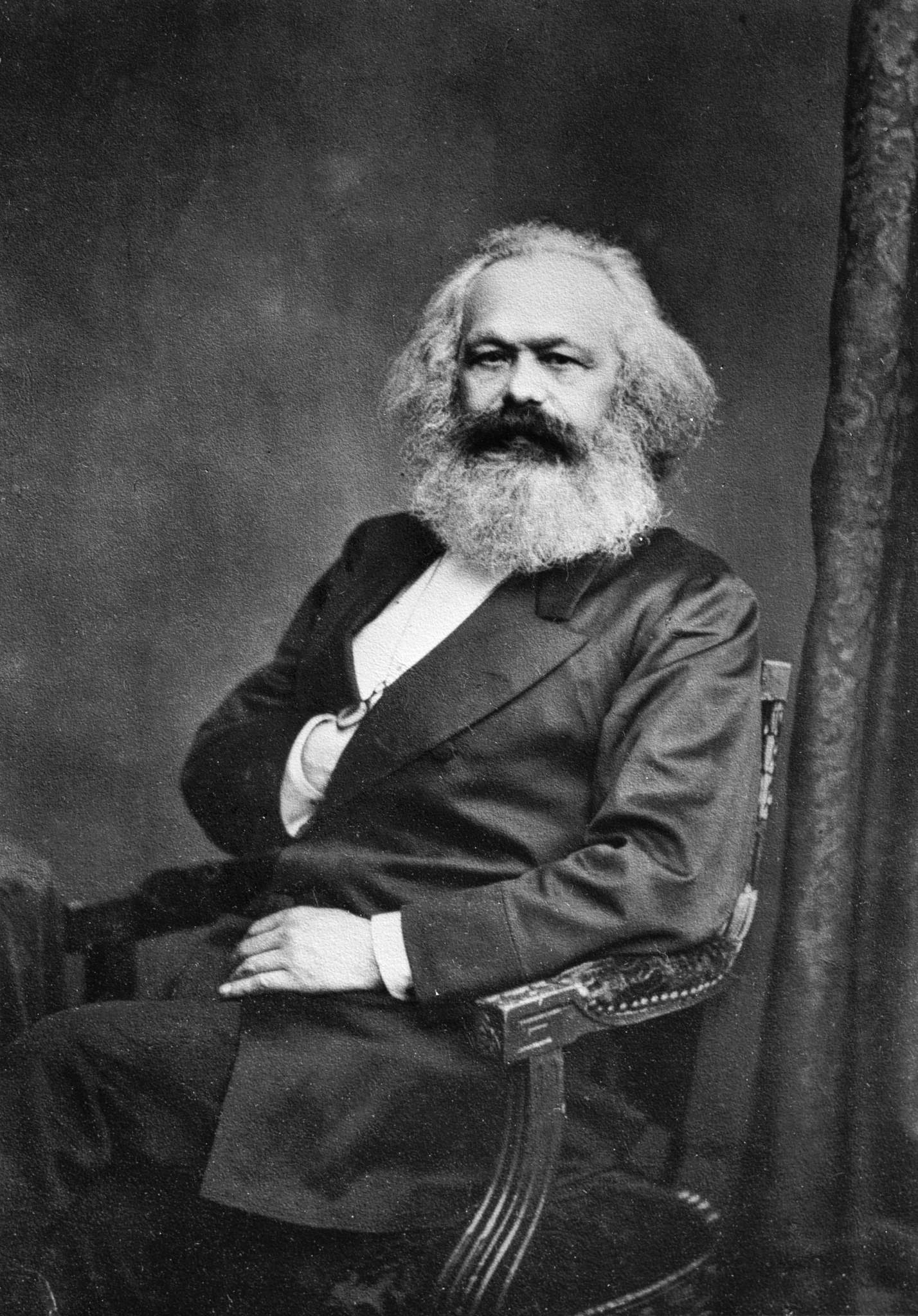
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' and the four-volume (1867–1883). Marx's political and philosophical thought had enormous influence on subsequent intellectual, economic, and political history. His name has been used as an adjective, a noun, and a school of social theory. Born in Trier, Germany, Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin. He married German theatre critic and political activist Jenny von Westphalen in 1843. Due to his political publications, Marx became stateless and lived in exile with his wife and children in London for decades, where he continued to develop his thought in collaboration with German philosopher Friedrich Engels and publish his writings, researching in the British Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of The Just
The League of the Just (German: ''Bund der Gerechten'') or League of Justice was a Christian communist international revolutionary organization. It was founded in 1836 by branching off from its ancestor, the League of Outlaws (German: ''Bund der Geächteten''), which had formed in Paris in 1834. The League of the Just was largely composed of German emigrant artisans. In 1847, the League of the Just merged with the Communist Correspondence Committee (German: ''Kommunistisches Korrespondenzkomitee''), an organization led by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, creating the Communist League. The new group tasked Marx and Engels with writing a political platform for itself. The resulting document was ''The Communist Manifesto''. History Jacob Venedey and Theodore Schuster founded the League of Outlaws in Paris in 1834. They modeled the organization closely after Philippe Buonarroti's vision of the "Universal Democratic Carbonari" as an egalitarian international revolutionary fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cour D'assises
In France, a ''cour d'assises'', or Court of Assizes or Assize Court, is a criminal trial court with original and appellate limited jurisdiction to hear cases involving defendants accused of felonies, meaning crimes as defined in French law. It is the only French court consisting in a jury trial. Justiciable matters Under French law, the definition of a ''crime ( m)'' is limited to any criminal act punishable by over 10 years of prison, including murder and rape. Previous death penalty application The ''cour d'assises'', uniquely outside military law, could sentence proven convicts for serious crimes, e.g. murder (''assassinat'' or ''meurtre'') to the death penalty, until it was abolished from French law in September 1981. In the sentencing phase, a qualified majority would vote on the verdict, or 2/3 of the jury, the same procedure as in rendering the guilty verdict. One of the last famous death penalty trials, that of Patrick Henry in 1977, famously ended in a life sente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amis Du People
Amis may refer to: * Amis (surname) * Amis people (or ''Amis''), a tribe of Taiwanese aborigines * Amis language, an indigenous language of Taiwan * AMIS (ISP), an Internet service provider (ISP) in Slovenia and Croatia * Amis et Amiles, an old French romance The acronym AMIS may stand for: * Association for Music in International Schools, an association "dedicated to the promotion of excellence in all levels of music education." * African Union Mission in Sudan (AMIS) * American Musical Instrument Society (AMIS) * AMI Semiconductor, designer and manufacturer of silicon chips * Atari Message Information System, a bulletin board system for 8-bit Atari computers * Audio Messaging Interchange Specification, a method to move messages from one voice mail system to another * Alternate Multiplex Interrupt Specification, a method of sharing a software interrupt by many TSR programs * Abandoned Mines Information System, a database containing abandoned and inactive mines in Ontario, Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)