|
Lorraine-Dietrich 12D
The Lorraine 12D, also referred to as Lorraine-Dietrich 12D, was a series of water-cooled V12 engines produced by the French company Lorraine-Dietrich. The first variant began production in 1917, and the engines were used to power bombers for the French Navy during World War I. The Lorraine 12Da variant was the most powerful French engine at the time. After the war, the engines were licensed and produced by the Italian firm Isotta Fraschini until 1925. Design and development In 1916, French engineer Marius Barbarou began working a new V12 engine oriented at a 60-degree angle and a bore, to improve on the existing Lorraine-Dietrich 8B engine by adding two cylinders on each side. The Lorraine 12D was approved in January 1917 at . Lorraine produced 50 of the 12D engines. In 1917, the Lorraine 12Da was produced with an increase to and 400 units produced. The Lorraine 12Da variant became the most powerful French airplane engine at the time of World War I. The more powerful design re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Nature And Science
The is in the northeast corner of Ueno Park in Tokyo. The museum has exhibitions on pre-Meiji period, Meiji science in Japan. It is the venue of the taxidermied bodies of the legendary dogs Hachikō and Taro and Jiro. A life-size blue whale model and a steam locomotive are also on display outside. History file:NMNC02s3200.jpg , Blue whale Life size model. Opened in 1871, it has had several names, including Ministry of Education Museum, Tokyo Museum, Tokyo Science Museum, the National Science Museum of Japan, and the National Museum of Nature and Science as of 2007. It was renovated in the 1990s and 2000s, and offers a wide variety of natural history exhibitions and interactive scientific experiences. It was completed as the main building of the Tokyo Science Museum in September 1931 as part of the reconstruction project after the Great Kanto Earthquake. Neo-Renaissance style. Designed by Kenzo Akitani, an engineer of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potez
Potez (pronounced ) was a French aircraft manufacturer founded as Aéroplanes Henry Potez by Henry Potez at Aubervilliers in 1919 in aviation, 1919. The firm began by refurbishing war-surplus SEA IV aircraft, but was soon building new examples of an improved version, the Potez SEA VII. History During the inter-war years, Potez built a range of small passenger aircraft and a series of military reconnaissance biplanes that were also licence-built in Poland. In 1933 in aviation, 1933, the firm bought flying boat manufacturer Chantiers Aéro-Maritimes de la Seine, CAMS. The company was nationalization, nationalized in 1936 in aviation, 1936, following which it was merged with Chantiers aéronavals Étienne Romano, Lioré et Olivier, Chantiers Aéro-Maritimes de la Seine, CAMS and Société Provençale de Constructions Aéronautiques, SPCA in order to form the SNCASE, Société nationale des constructions aéronautiques du Sud-Est (SNCASE) on 1 February 1937. Potez's factories in Sar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
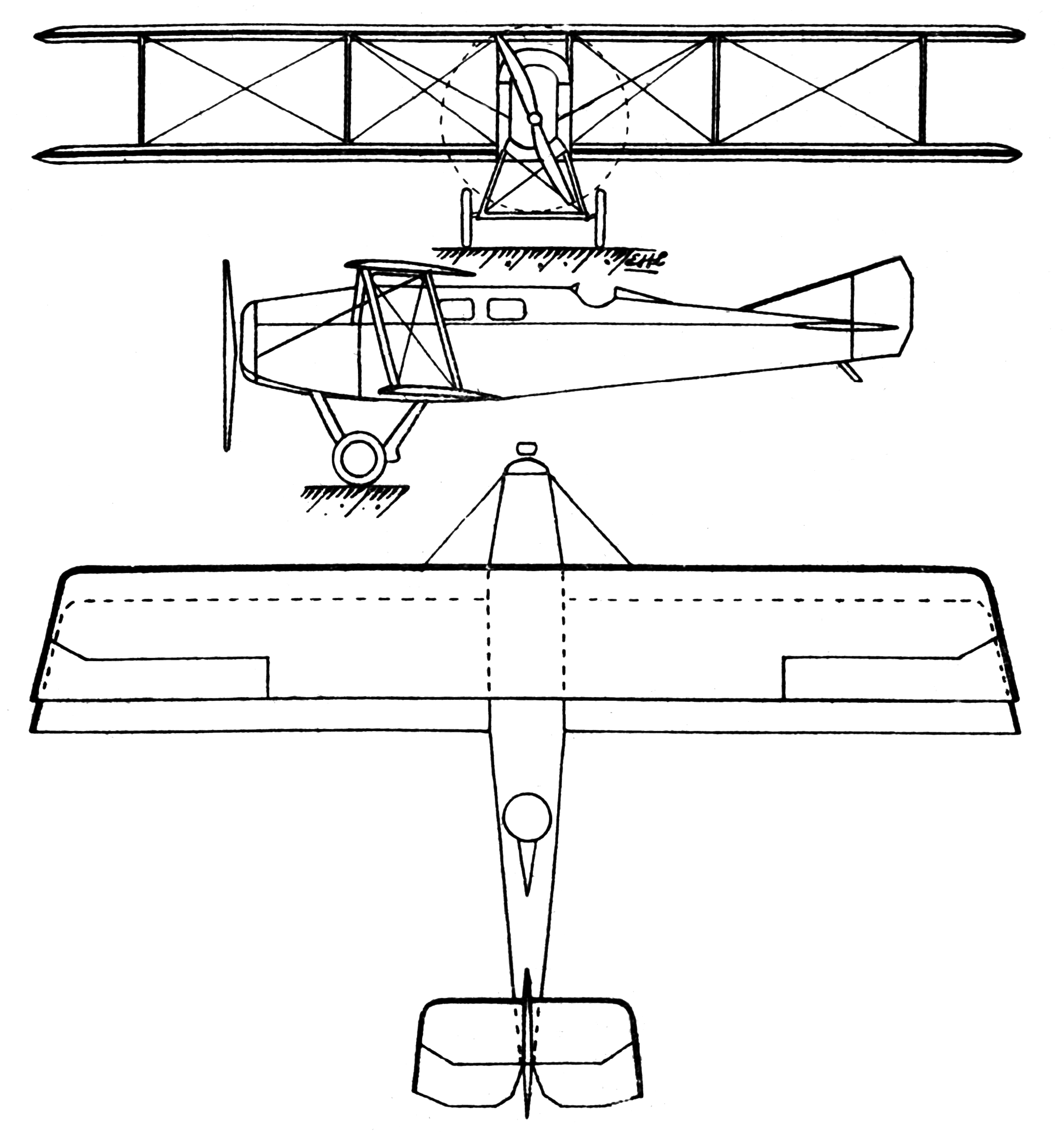
Potez XII
Potez (pronounced ) was a French aircraft manufacturer founded as Aéroplanes Henry Potez by Henry Potez at Aubervilliers in 1919. The firm began by refurbishing war-surplus SEA IV aircraft, but was soon building new examples of an improved version, the Potez SEA VII. History During the inter-war years, Potez built a range of small passenger aircraft and a series of military reconnaissance biplanes that were also licence-built in Poland. In 1933, the firm bought flying boat manufacturer CAMS. The company was nationalized in 1936, following which it was merged with Chantiers aéronavals Étienne Romano, Lioré et Olivier, CAMS and SPCA in order to form the Société nationale des constructions aéronautiques du Sud-Est (SNCASE) on 1 February 1937. Potez's factories in Sartrouville and Méaulte were taken over by SNCAN and the Berre factory went to SNCASE. After World War II, Potez was re-established as Société des Avions et Moteurs Henry Potez at Argenteuil but did not r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potez IX
The Potez IX was an early airliner produced in France in the 1920s, a further development of the SEA IV that Henry Potez had co-designed during the First World War.Taylor 1989, p.747''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft'', p.2760 Design and development The design mated an entirely new fuselage to the wing and tail structures of the earlier military aircraft."The Paris Aero Show 1921" 22 December 1921, p.841 This fuselage was very deep, nearly filling the interplane gap, and carried within it a fully enclosed cabin with seating for four passengers. The nose area was carefully streamlined with curved aluminium,"The Paris Aero Show 1921" 17 November 1921, p764/ref> but other aspects of the construction were conventional for the day; wooden structures skinned in plywood (the passenger cabin) or fabric (the rest of the aircraft)."The Paris Aero Show 1921" 22 December 1921, p.842 The pilot sat in an open cockpit aft of the cabin. The prototype flew in 1920,Stroud 1966, p. 176 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potez SEA VII
The Potez SEA VII, otherwise known simply as the Potez VII, was an early airliner developed in France shortly after the First World War.Taylor 1989, p.750 Design and development The SEA VII was a civil version of the SEA IV military aircraft that Henry Potez had developed with Louis Coroller and Marcel Bloch as the Société d'Etudes Aéronautiques."The Paris Aero Show 1919", p.69 With the end of hostilities, the French military cancelled its orders for the SEA IV and the company dissolved. Potez, however, believed that the design had potential in peacetime and founded Aéroplanes Henry Potez in 1919 to refurbish war-surplus machines for civil use.Gunston 1993, p.243 This soon led to a revision of the design as the SEA VII. This differed from its predecessor in having an enclosed cabin for two passengers occupying the rear fuselage. The wings were enlarged to reduce their loading and therefore to allow for slower, gentler landings than the military aircraft had been capable of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEA IV
The SEA IV was a French two-seat military aircraft of World War I and the immediate post-war era. Development The SEA IV was designed and built in 1917 by Henry Potez, Louis Coroller, and Marcel Bloch. It was a derivative of their previous SEA II design, equipped with a more powerful Lorraine engine of 261 kW (350 hp). It made its first flight during the first quarter of 1918, probably near Plessis-Belleville. It was initially tested by Gustave Douchy, a flying ace of 9 victories, then by the pilots of the Centre d'essais en Vol at Villacoublay. The " Ministère de l'Armement et des Fabrications de guerre" (Ministry of Armament and War Production) soon placed an order for 1,000 machines, making the SEA IV the first Dassault-designed aircraft to reach production. Operational history On August 24, 1918, General Duval, commander of Aéronautique at General Headquarters foresaw the need for two variants to equip the escadrilles at the beginning of 1919: the SEA IV A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lioré Et Olivier LeO H-10
The Lioré et Olivier LeO 10 or LeO H-10 was a prototype French Naval reconnaissance aircraft built. Only one example of this two seat, single engine biplane floatplane was built. Development The LeO H-10 (H for ''hydravion'' or waterplane) was a two-seat floatplane designed for reconnaissance work from Naval vessels. It was an unstaggered biplane with unswept wings of constant chord that could be folded for ease of onboard stowage. The interplane strut arrangement was unusual: outboard, there were conventional upright pairs but just inboard of these another pair ran diagonally in Warren girder style, replacing the conventional flying wires. The lower wing folded at a rear hinge on a short stub wing; outboard of the break was a single vertical strut. Central cabane struts provided an upper hinge so the wings, with their trailing edges folded downwards, leaned inwards over the fuselage when stowed. The fuselage of the LeO H.10 was a simple, flat sided structure with a wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latham 43
__NOTOC__ The Latham 43 was a flying boat bomber built in France in the 1920s for service with the French Navy. It was a conventional design for its day - a two-bay biplane with unstaggered wings, and engines mounted tractor-fashion on struts in the interplane gap. The pilot sat in an open cockpit, with a gunner in an open bow position, and another in an open position amidships. Two examples, designated Latham 42 powered by liquid-cooled Vee engines were evaluated by the navy in 1924, leading to a contract for 18 aircraft powered by air-cooled radial engines instead. Designated Latham 43 by the manufacturer and HB.3 in naval service (for ''Hydravion de bombardement'' - "Seaplane-bomber", 3 seats), they remained in service between 1926 and 1929. Eight other machines with the original liquid-cooled engine were sold to Poland. Variants * prototypes with Lorraine 12Da engines (2 built) * production version for France with Gnome et Rhône 9A The Bristol Jupiter was a British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latécoère 5
The Latécoère 5 was a French three-engined biplane bomber prototype of the early 1920s, based on the Latécoère 4 passenger aircraft. It did not fly until 1924 and only one was built. Design and development The Latécoère 5 was a revision of the second Latécoère 4 as a night bomber for the BN4 programme, which called for a 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) bomb load. The construction and general appearance of the two types was similar, both having fabric covered wings of wooden construction, three engines and a metal framed fuselage. The wings and tail of the Latécoère 4 and 5 appeared almost identical, using the single outer interplane strut of the Latécoère 4's early arrangement. In fact the bomber had a span 2 m (6 ft 7 in) greater and larger wing area. The fuselage behind the wing leading edge was again similar; as far as is known the defensive armament intended for the bomber was never fitted, and it had three windows on each side, though not the continuous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caproni Ca
Caproni, also known as ''Società de Agostini e Caproni'' and ''Società Caproni e Comitti'', was an Italian aircraft manufacturer. Its main base of operations was at Taliedo, near Linate Airport, on the outskirts of Milan. Founded by Giovanni Battista "Gianni" Caproni during 1908, the company produced several successful heavy bombers during the First World War. Following the acquisition of several other aviation firms throughout the interwar period, Caproni transformed into a sizable aviation-orientated syndicate, the ''Società Italiana Caproni, Milano''. The majority of its aircraft were bombers and transport aircraft. It played a pioneering role in the development of the Caproni Campini N.1, an experimental aircraft powered by a thermo-jet. It provided large numbers of combat aircraft for the Axis during the Second World War. The firm did not prosper in the postwar era, the Società Italiana Caproni collapsing during 1950. Many of the company's former assets were subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |