|
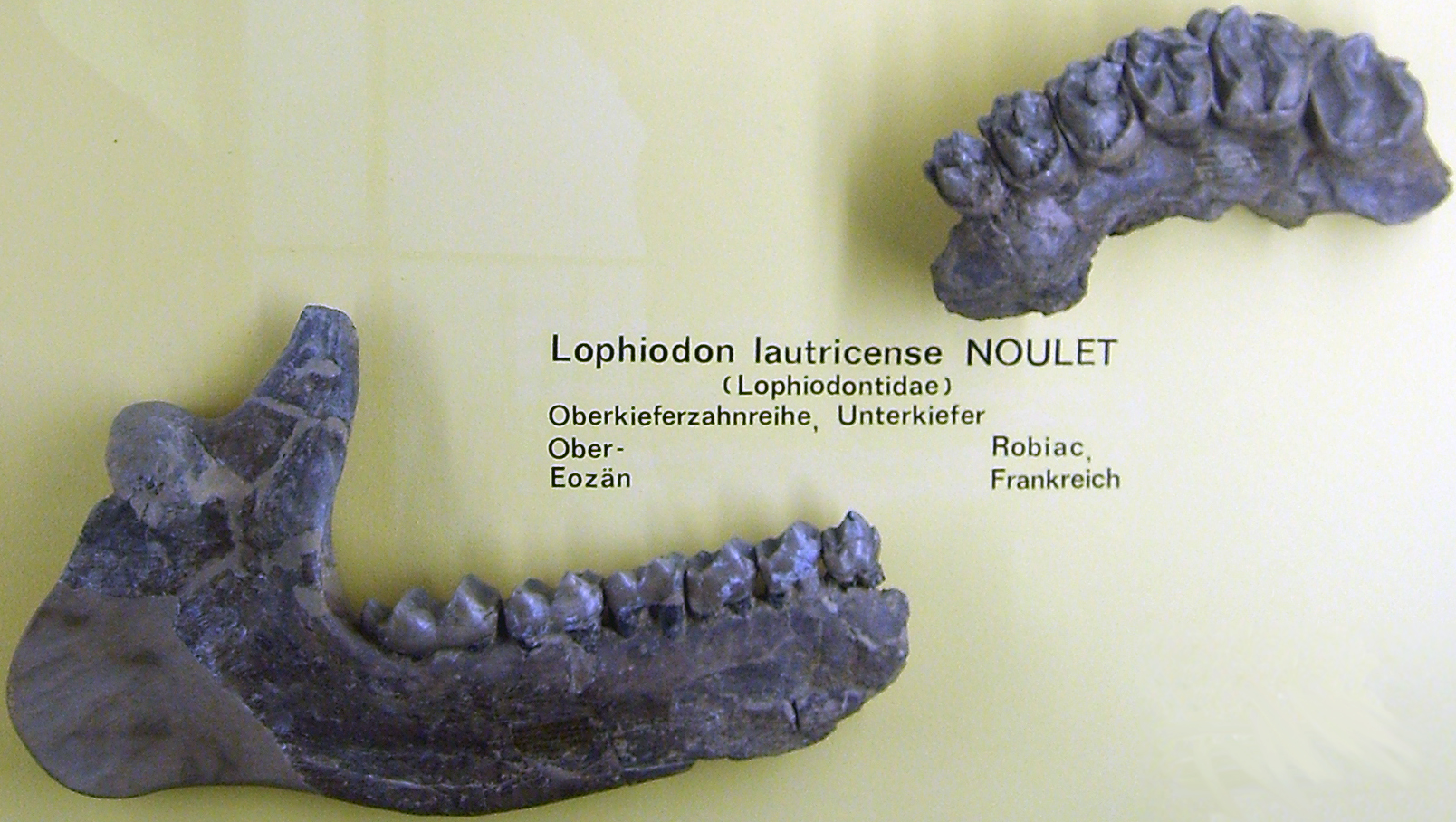
Lophiodon
''Lophiodon'' (from el, λόφος , 'crest' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') is an extinct genus of mammal related to chalicotheres. It lived in Eocene Europe Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ... between , and was previously thought to be closely related to '' Hyrachyus''. References Eocene odd-toed ungulates Fossil taxa described in 1822 Taxa named by Georges Cuvier Extinct mammals of Europe {{paleo-oddtoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophiodon
''Lophiodon'' (from el, λόφος , 'crest' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') is an extinct genus of mammal related to chalicotheres. It lived in Eocene Europe Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ... between , and was previously thought to be closely related to '' Hyrachyus''. References Eocene odd-toed ungulates Fossil taxa described in 1822 Taxa named by Georges Cuvier Extinct mammals of Europe {{paleo-oddtoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophiodon NT
''Lophiodon'' (from el, λόφος , 'crest' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') is an extinct genus of mammal related to chalicotheres. It lived in Eocene Europe between , and was previously thought to be closely related to ''Hyrachyus ''Hyrachyus'' (from '' Hyrax'' and grc, ὗς "pig") is an extinct genus of perissodactyl mammal that lived in Eocene Europe, North America, and Asia. Its remains have also been found in Jamaica. It is closely related to ''Lophiodon''.Hayden, F. ...''. References Eocene odd-toed ungulates Fossil taxa described in 1822 Taxa named by Georges Cuvier Extinct mammals of Europe {{paleo-oddtoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalicothere
Chalicotheres (from Greek '' chalix'', "gravel" and '' therion'', "beast") are an extinct clade of herbivorous, odd-toed ungulate (perissodactyl) mammals that lived in North America, Eurasia, and Africa from the Middle Eocene until the Early Pleistocene, existing from 48.6 to 1.806 mya. They are one of the five major radiations of perissodactyls, with three groups living (horses, plus the extinct paleotheres; rhinoceroses; tapirs), and two extinct (brontotheres and chalicotheres). Description Unlike modern perissodactyls, chalicotheres had clawed feet. They had longer forelimbs and shorter hind limbs, lower incisors that cropped food against a toothless pad in the upper jaw, low-crowned molar teeth, and were browsers on trees and shrubs throughout their history. They evolved in two different directions, which became separate subfamilies, the Schizotheriinae and the Chalicotheriinae. Schizotherine chalicotheres such as ''Moropus'' lived in a variety of forest, woodland, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyrachyus
''Hyrachyus'' (from '' Hyrax'' and grc, ὗς "pig") is an extinct genus of perissodactyl mammal that lived in Eocene Europe, North America, and Asia. Its remains have also been found in Jamaica. It is closely related to ''Lophiodon''.Hayden, F.V''Report of the United States Geological Survey of the Territories'', Volume III (1883) Description The 1.5-m-long beast was related to palaeotheres, and suspected to be the ancestor of modern tapirs and rhinoceros A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...es. Physically, it would have looked very similar to modern tapirs, although it probably lacked the tapir's characteristic proboscis. Its teeth, however, resembled those of a rhinoceros, supporting the idea of its relationship with that group. References Eocene odd-toed u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, Baron Cuvier (; 23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier, was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils. Cuvier's work is considered the foundation of vertebrate paleontology, and he expanded Linnaean taxonomy by grouping classes into phylum, phyla and incorporating both fossils and living species into the classification. Cuvier is also known for establishing extinction as a fact—at the time, extinction was considered by many of Cuvier's contemporaries to be merely controversial speculation. In his ''Essay on the Theory of the Earth'' (1813) Cuvier proposed that now-extinct species had been wiped out by periodic catastrophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Odd-toed Ungulates
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1822
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Georges Cuvier
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |