|
Loop (biochemistry)
A turn is an element of secondary structure in proteins where the polypeptide chain reverses its overall direction. Definition According to one definition, a turn is a structural motif where the Cα atoms of two residues separated by a few (usually 1 to 5) peptide bonds are close (less than ). The proximity of the terminal Cα atoms often correlates with formation of an inter main chain hydrogen bond between the corresponding residues. Such hydrogen bonding is the basis for the original, perhaps better known, turn definition. In many cases, but not all, the hydrogen-bonding and Cα-distance definitions are equivalent. Types of turns Turns are classified according to the separation between the two end residues: * In an α-turn the end residues are separated by ''four'' peptide bonds (''i'' → ''i'' ± 4). * In a β-turn (the most common form), by ''three'' bonds (''i'' → ''i'' ± 3). * In a γ-turn, by ''two'' bonds (''i'' → ''i'' ± 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Hairpins
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced bilabial fricative while in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter and the Cyrillic letters and . Name Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word ('house', compare and ). In Greek, the name was , pronounced in Ancient Greek. It is spelled in modern monotonic orthography and pronounced . History The letter beta was derived from the Phoenician letter beth . The letter Β had the largest number of highly divergent local forms. Besides the standard form (either rounded or pointed, ), there were forms as varied as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gajendra Pal Singh Raghava
Gajendra Pal Singh Raghava is an Indian bio-informatician and head of computational biology at the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology. Personal Early years and education Raghava was born in village Nagla Karan, Bulandshahr district (UP), India in 1963. He completed his primary education from his native place Bulandshahr and post graduation from Meerut, UP in 1984. After completing his MTech from Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi, he joined Institute of Microbial Technology as a computer scientist. There he continued to work on various projects and became the head of Bioinformatics Centre in 1994. In 1996 he received a doctorate in bioinformatics from Institute of Microbial Technology and Panjab University, Chandigarh. Career and higher studies Raghava joined the Institute of Microbial Technology, Chandigarh in 1986 as a computer scientist and developer. He is also coordinator of the distributed information centre supported by DBT under the BTISNET p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after Protein biosynthesis, synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of Amino acid, amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. This structure permits the protein to become biologically functional or active. The folding of many proteins begins even during the translation of the polypeptide chain. The amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, known as the protein's native state. This structure is determined by the amino-acid sequence or primary structure. The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins Intrinsically unstructured proteins, may remain unfolded, indicating that protein dynamics are important. Failure to fold into a native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances, misfolded proteins have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allostery
In the fields of biochemistry and pharmacology an allosteric regulator (or allosteric modulator) is a substance that binds to a site on an enzyme or Receptor (biochemistry), receptor distinct from the active site, resulting in a conformational change that alters the protein's activity, either enhancing or inhibiting its function. In contrast, substances that bind directly to an enzyme's active site or the binding site of the endogenous ligand of a receptor are called orthosteric regulators or modulators. The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site'' or ''regulatory site''. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein, often resulting in a conformational change and/or a change in protein dynamics. Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as ''allosteric activators'', whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called ''allosteric inhibitors''. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformational Change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors. A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or other factors; each possible shape is called a conformation, and a transition between them is called a ''conformational change''. Factors that may induce such changes include temperature, pH, voltage, light in chromophores, concentration of ions, phosphorylation, or the binding of a ligand. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. Laboratory analysis Many biophysical techniques such as crystallography, NMR, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) using spin label techniques, circular dichroism (CD), hydrogen exchange, and FRET can be used to study macromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Domains
Multiple may refer to: Economics *Multiple finance, a method used to analyze stock prices *Multiples of the price-to-earnings ratio *Chain stores, are also referred to as 'Multiples' *Box office multiple, the ratio of a film's total gross to that of its opening weekend Sociology *Multiples (sociology), a theory in sociology of science by Robert K. Merton, see Science *Multiple (mathematics), multiples of numbers *List of multiple discoveries, instances of scientists, working independently of each other, reaching similar findings *Multiple birth, because having twins is sometimes called having "multiples" *Multiple sclerosis, an inflammatory disease *Parlance for people with multiple identities, sometimes called "multiples"; often theorized as having dissociative identity disorder *Multiple myeloma (MM), a cancer that forms in a type of white blood cell (WBC) called plasma cells. Printing *Printmaking, where ''multiple'' is often used as a term for a print, especially in the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups (Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- (γ-) amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, Chemical polarity, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid ''Residue (chemistry)#Biochemistry, residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissue (biology), tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's Peptide, polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that Protein folding, folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or Disulfide bond, disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF-hand, EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimera (protein), chimeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexible Linker
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other proteins or RNA. IDPs range from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coil, molten globule-like aggregates, or flexible linkers in large multi- domain proteins. They are sometimes considered as a separate class of proteins along with globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. They are most numerous in eukaryotes, with an estimated 30-40% of residues in the eukaryotic proteome located in disordered regions. Disorder is present in around 70% of proteins, either in the form of disordered tails or flexible linkers. Proteins can also be entirely disordered and lack a defined secondary and/or tertiary structure. Their discovery has disproved the idea that three-dimensional struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Hairpins
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced bilabial fricative while in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter and the Cyrillic letters and . Name Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word ('house', compare and ). In Greek, the name was , pronounced in Ancient Greek. It is spelled in modern monotonic orthography and pronounced . History The letter beta was derived from the Phoenician letter beth . The letter Β had the largest number of highly divergent local forms. Besides the standard form (either rounded or pointed, ), there were forms as varied as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
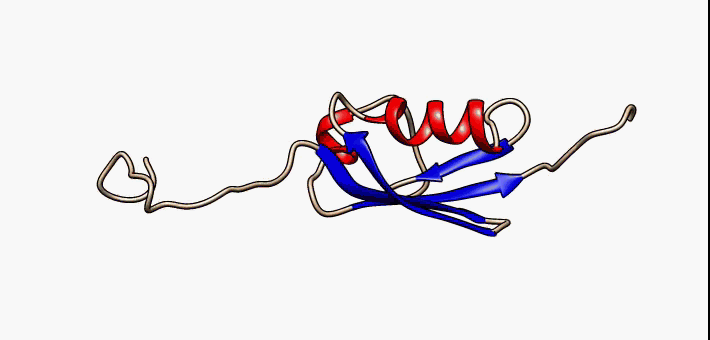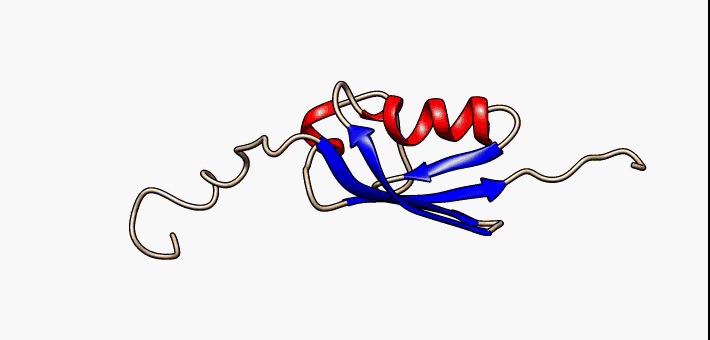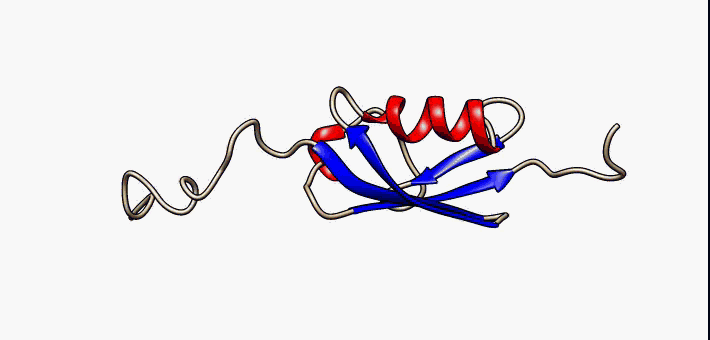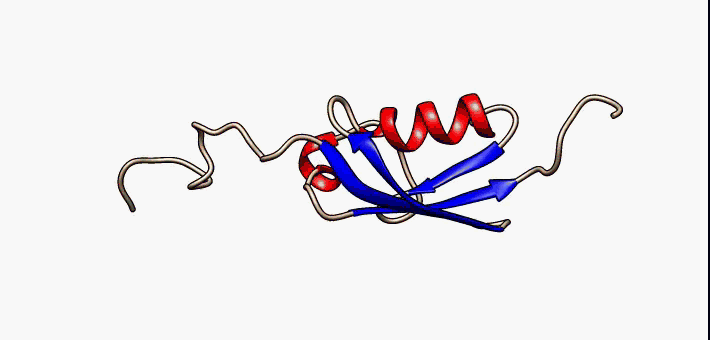
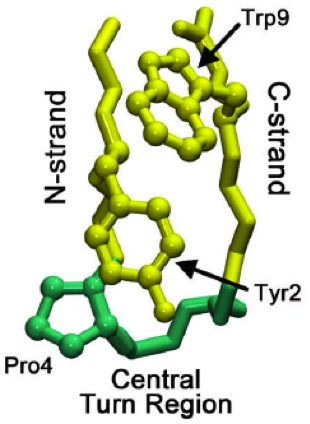
Beta Hairpin
The beta hairpin (sometimes also called beta-ribbon or beta-beta unit) is a simple protein structural motif involving two beta strands that look like a Hairpin (fashion), hairpin. The motif consists of two strands that are adjacent in primary structure, oriented in an Antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel direction (the N-terminus of one sheet is adjacent to the C-terminus of the next), and linked by a short loop of two to five amino acids. Beta hairpins can occur in isolation or as part of a series of hydrogen bonded strands that collectively comprise a beta sheet. Researchers such as Francisco J. Blanco, Francisco Blanco ''et al.'' have used protein NMR to show that beta-hairpins can be formed from isolated short peptides in aqueous solution, suggesting that hairpins could form nucleation sites for protein folding. Classification Beta hairpins were originally categorized solely by the number of amino acid residues in their loop sequences, such that they were named one-resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |