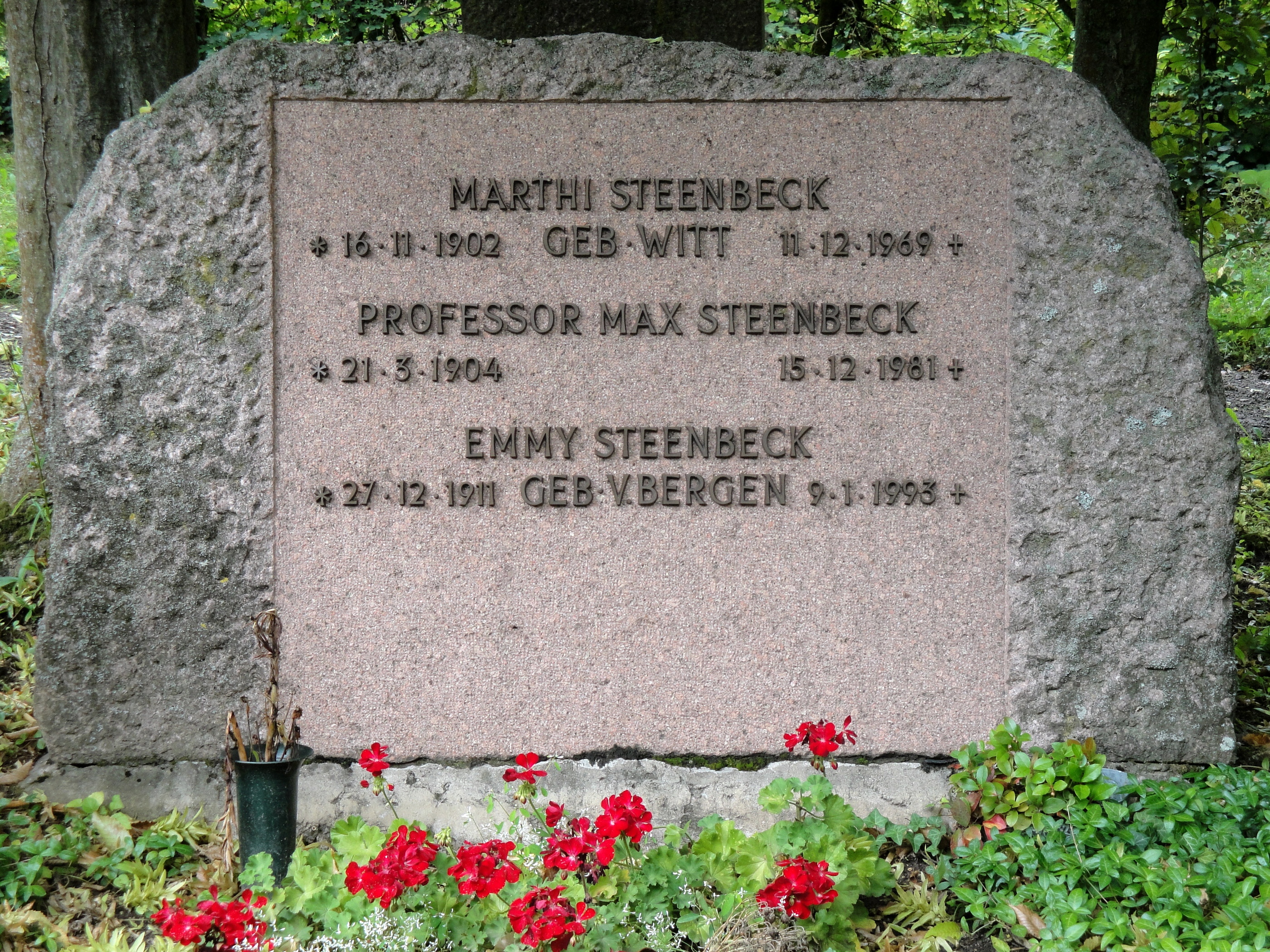|
Lomonosov Medal
The Lomonosov Gold Medal (russian: Большая золотая медаль имени М. В. Ломоносова ''Bol'shaya zolotaya medal' imeni M. V. Lomonosova''), named after Russian scientist and polymath Mikhail Lomonosov, is awarded each year since 1959 for outstanding achievements in the natural sciences and the humanities by the Soviet Union, USSR Academy of Sciences and later the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS). Since 1967, two medals are awarded annually: one to a Russian and one to a foreign scientist. It is the Academy's highest accolade. Recipients of Lomonosov Gold Medal __NOTOC__ 1959 * Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa: cumulatively, for works in physics of low temperatures. 1961 * Aleksandr Nikolaevich Nesmeyanov: accumulatively for works in chemistry. 1963 * Sin-Itiro Tomonaga (member of the Japanese academy of Sciences, president of the Scientific Council of Japan): for substantial scientific contributions to the development of physics. * Hideki Yukawa (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov (; russian: Михаил (Михайло) Васильевич Ломоносов, p=mʲɪxɐˈil vɐˈsʲilʲjɪvʲɪtɕ , a=Ru-Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov.ogg; – ) was a Russian Empire, Russian polymath, scientist and writer, who made important contributions to literature, education, and science. Among his discoveries were the atmosphere of Venus and the law of conservation of mass in chemical reactions. His spheres of science were natural science, chemistry, physics, mineralogy, history, art, philology, optical devices and others. The founder of modern geology,Vernadsky, V. (1911) Pamyati M.V. Lomonosova. Zaprosy zhizni, 5: 257-262 (in Russian) [In memory of M.V. Lomonosov] Lomonosov was also a poet and influenced the formation of the modern Russian language, Russian literary language. Early life and family Lomonosov was born in the village of Kholmogorsky District, Mishaninskaya (later renamed Lomonosovo, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Lomonosovo in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giulio Natta
Giulio Natta (26 February 1903 – 2 May 1979) was an Italian chemical engineer and Nobel laureate. He won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1963 with Karl Ziegler for work on high polymers. He also received a Lomonosov Gold Medal in 1969. Biography Early years Natta was born in Imperia, Italy. He earned his degree in chemical engineering from the Politecnico di Milano university in Milan in 1924. In 1927 he passed the exams for becoming a professor there. From 1929 to 1933, he was also in charge of physical chemistry at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Milan. In 1933 he became a full professor and the director of the Institute of General Chemistry of Pavia University, where he stayed until 1935. During this time he began using crystallography to elucidate the structures of a wide variety of molecules including phosphine, arsine and others. In that year he was appointed full professor in physical chemistry at the University of Rome. Career From 1936 to 1938 he moved as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Klare
Hermann Klare (12 May 1909 – 22 August 2003) was a chemistry academic who played a prominent role in scientific administration and research in the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Klare held professorships at the Technical University Leuna-Merseburg Technical University Leuna-Merseburg (German: Technische Hochschule „Carl Schorlemmer“ Leuna-Merseburg, abbreviated: THLM) was an institution of tertiary education in the city of Merseburg in today's Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It was founded on 1 S ... and at Humboldt University (Berlin). From 1968 to 1979 he was president of the German Academy of Sciences (renamed the Academy of Sciences of the GDR in 1972). Publications *Technology and chemistry of synthetic polyamide fibers. Berlin 1954 *Synthetic polyamide fibers: technology and chemistry. Berlin 1963 (as co-author) *The Academy of Sciences of the GDR: the 275th anniversary of the founding of the Academy. Berlin 1975 *History of chemical fiber research to the present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semyon Isaakovich Volfkovich
Semyon Isaakovich Volfkovich (russian: Семён Исаакович Вольфкович) (October 23, 1896 – November 12, 1980) was a Soviet chemist, technologist and member of the Soviet Academy of Sciences (1946). In 1941 he was awarded the Stalin Prize and in 1976 he received the Lomonosov Gold Medal The Lomonosov Gold Medal (russian: Большая золотая медаль имени М. В. Ломоносова ''Bol'shaya zolotaya medal' imeni M. V. Lomonosova''), named after Russian scientist and polymath Mikhail Lomonosov, is awarde .... (accessed 20 October 2022) References 1896 births 1980 deaths[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mstislav Vsevolodovich Keldysh
Mstislav Vsevolodovich Keldysh (russian: Мстисла́в Все́володович Ке́лдыш; – 24 June 1978) was a Soviet mathematician who worked as an engineer in the Soviet space program. He was the academician of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union (1946), President of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union (1961–1975), three-time Hero of Socialist Labour (1956, 1961, 1971), and fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1968). He was one of the key figures behind the Soviet space program. Among scientific circles of the USSR Keldysh was known by the epithet "the Chief Theoretician" in analogy with epithet "the Chief Designer" used for Sergei Korolev. Family Keldysh was born to a professional family of Russian nobility. His grandfather, Mikhail Fomich Keldysh (1839–1920), was a military physician, who retired with the military rank of General. Keldysh's grandmother, Natalia Keldysh (née Brusilova), was a cousin of general Aleksei Brusilov. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angel Balevski
Angel Balevski ( bg, Ангел Балевски) (4 March 1910 – 15 September 1997) was a Bulgarian inventor and engineer. Academician Balevski was president of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (1968-1988), Co-president of the International Academy of Science, Munich (1988-1997) and chairman of the Bulgarian Pugwash Group. Life He graduated from a technical school in Brno in the Czech Republic in 1934 and started his professional career as a metallurgical engineer. Later he was a professor at numerous universities across Europe. Balevski was the founder of the Bulgarian academic school in the field of metal sciences and technologies. He was successful in designing a hot pressing machine for non-ferrous metals. He developed an original method for cast iron production from Bulgarian raw materials in a rotating drum furnace. Together with Ivan Dimov, he developed a counter-pressure casting method which was a novelty in world foundry technology and was protected by over 100 patent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Ivanovich Tselikov
Alexander Ivanovich Tselikov (russian: Александр Иванович Це́ликов; 20 April 1904, in Moscow – 28 October 1984, in Moscow) was a Soviet metallurgist, industrial machines designer, and Hero of Socialist Labor (1964, 1984). He was elected a corresponding member of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR in 1953 and full member (academician An academician is a full member of an artistic, literary, engineering, or scientific academy. In many countries, it is an honorific title used to denote a full member of an academy that has a strong influence on national scientific life. In syst ...) in 1964. 1904 births 1984 deaths Heroes of Socialist Labour Full Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Engineers from Moscow Soviet metallurgists {{USSR-scientist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimír Zoubek
Vladimír Zoubek (21 September 1903 in Heřmanův Městec – 24 May 1995 in Prague) was a Czech geologist. He won the Lomonosov Prize The Lomonosov Gold Medal (russian: Большая золотая медаль имени М. В. Ломоносова ''Bol'shaya zolotaya medal' imeni M. V. Lomonosova''), named after Russian scientist and polymath Mikhail Lomonosov, is awarded ... for his contributions to geology. In turn, from ''The Great Soviet Encyclopedia'', 3rd Edition (1970-1979). Retrieved May 22, 2016. The mineral Zoubekite is named after him. Notes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Pavlovich Vinogradov
Alexander Pavlovich Vinogradov (russian: Алекса́ндр Па́влович Виногра́дов) (August 21, 1895 in Petretsovo, Yaroslavl Oblast – November 16, 1975 in Moscow) was a Soviet geochemist, academician (1953), and Hero of Socialist Labour (1949, 1975). In 1928, he took up a position as assistant professor in the laboratory for biogeochemical problems of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. He was director of Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. Mons Vinogradov, a mountain on the near side of the moon, is named after him. So is a large crater on Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Steenbeck
Max Christian Theodor Steenbeck (21 March 1904 – 15 December 1981) was a German physicist who worked at the '' Siemens-Schuckertwerke'' in his early career, during which time he invented the betatron in 1934. He was taken to the Soviet Union after World War II, and he contributed to the Soviet atomic bomb project. In 1955, he returned to East Germany to continue a career in nuclear physics. Early life Steenbeck was born in Kiel. He studied physics and chemistry at the University of Kiel from 1922 to 1927. He completed his thesis on x-rays under Walther Kossel; he submitted the thesis in 1927/1928 and his doctorate was awarded in January 1929. While a student at Kiel, he formulated the concept of the cyclotron. Career Early years From 1927 to 1945, Steenbeck was a physicist at the '' Siemens-Schuckertwerke'' in Berlin. From 1934, he was a laboratory director, and it was in that year that he submitted a patent for the betatron. In 1943, he was appointed technical dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikoloz Muskhelishvili
Nikoloz (Niko) Muskhelishvili ( ka, ნიკოლოზ (ნიკო) მუსხელიშვილი ; – 15 July 1976) was a renowned Soviet Georgian mathematician, physicist and engineer who was one of the founders and first President (1941–1972) of the Georgian SSR Academy of Sciences (now Georgian Academy of Sciences). He is often referred by the Russian version of his name, Nikolai Ivanovich Muskhelisvili (Николай Иванович Мусхелишвили). Life and career Muskhelishvili was born on in Tbilisi, then part of the Russian Empire into a family of engineers. He graduated from local grammar school in 1909 and afterwards from the Physics and Mathematics Faculty of Saint Petersburg in 1914. Immediately after his graduation he became head of Applied Mathematics of the same faculty and in 1918 passed the exam for the master's degree. His first scientific magazine was published already earlier in 1915 containing a number of issues on elasticity theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannes Alfvén
Hannes Olof Gösta Alfvén (; 30 May 1908 – 2 April 1995) was a Swedish electrical engineer, plasma physicist and winner of the 1970 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). He described the class of MHD waves now known as Alfvén waves. He was originally trained as an electrical power engineer and later moved to research and teaching in the fields of plasma physics and electrical engineering. Alfvén made many contributions to plasma physics, including theories describing the behavior of aurorae, the Van Allen radiation belts, the effect of magnetic storms on the Earth's magnetic field, the terrestrial magnetosphere, and the dynamics of plasmas in the Milky Way galaxy. Education Alfvén received his PhD from the University of Uppsala in 1934. His thesis was titled "Investigations of High-frequency Electromagnetic Waves." Early years In 1934, Alfvén taught physics at both the University of Uppsala and the Nobel Institute for Physics (late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |