|
Local Inertial Frame
In theoretical physics, a local reference frame (local frame) refers to a coordinate system or frame of reference that is only expected to function over a small region or a restricted region of space or spacetime. The term is most often used in the context of the application of local inertial frames to small regions of a gravitational field. Although gravitational tidal forces will cause the background geometry to become noticeably non-Euclidean over larger regions, if we restrict ourselves to a sufficiently small region containing a cluster of objects falling together in an ''effectively'' uniform gravitational field, their physics can be described as the physics of that cluster in a space free from explicit background gravitational effects. Equivalence principle When constructing his general theory of relativity, Einstein made the following observation: a freely falling object in a gravitational field will not be able to detect the existence of the field by making local measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
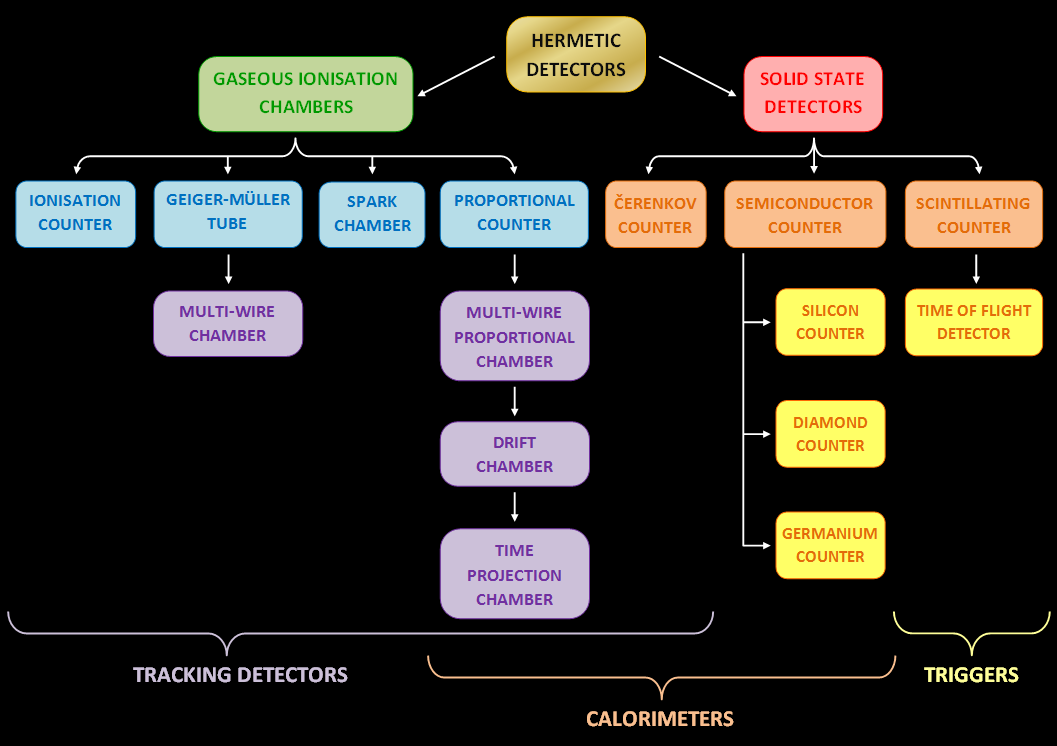
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minkowski Space
In physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is the main mathematical description of spacetime in the absence of gravitation. It combines inertial space and time manifolds into a four-dimensional model. The model helps show how a spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded. Mathematician Hermann Minkowski developed it from the work of Hendrik Lorentz, Henri Poincaré, and others said it "was grown on experimental physical grounds". Minkowski space is closely associated with Einstein's theories of special relativity and general relativity and is the most common mathematical structure by which special relativity is formalized. While the individual components in Euclidean space and time might differ due to length contraction and time dilation, in Minkowski spacetime, all frames of reference will agree on the total interval in spacetime between events.This makes spacetime distance an inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Covariance
In relativistic physics, Lorentz symmetry or Lorentz invariance, named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz, is an equivalence of observation or observational symmetry due to special relativity implying that the laws of physics stay the same for all observers that are moving with respect to one another within an inertial frame. It has also been described as "the feature of nature that says experimental results are independent of the orientation or the boost velocity of the laboratory through space". Lorentz covariance, a related concept, is a property of the underlying spacetime manifold. Lorentz covariance has two distinct, but closely related meanings: # A physical quantity is said to be Lorentz covariant if it transforms under a given representation of the Lorentz group. According to the representation theory of the Lorentz group, these quantities are built out of scalars, four-vectors, four-tensors, and spinors. In particular, a Lorentz covariant scalar (e.g., the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Spacetime Structure
In theoretical physics, a local reference frame (local frame) refers to a coordinate system or frame of reference that is only expected to function over a small region or a restricted region of space or spacetime. The term is most often used in the context of the application of local inertial frames to small regions of a gravitational field. Although gravitational tidal forces will cause the background geometry to become noticeably non-Euclidean over larger regions, if we restrict ourselves to a sufficiently small region containing a cluster of objects falling together in an ''effectively'' uniform gravitational field, their physics can be described as the physics of that cluster in a space free from explicit background gravitational effects. Equivalence principle When constructing his general theory of relativity, Albert Einstein, Einstein made the following observation: a freely falling object in a gravitational field will not be able to detect the existence of the field by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Coordinates
Local coordinates are the ones used in a ''local coordinate system'' or a ''local coordinate space''. Simple examples: * Houses. In order to work in a house construction, the measurements are referred to a control arbitrary point that will allow to check it: stick/sticks on the ground, steel bar, nails... * Addresses. Using house numbers to locate a house on a street; the street is a local coordinate system within a larger system composed of city townships, states, countries, postal codes, etc. Local systems exist for convenience. On ancient times, every work was made on relative bases as there was no conception of global systems. Practically, it is better to use local systems for small works as houses, buildings... For most of the applications, it is desired the position of one element relative to one building or location, and in a more local way, relative to one furniture or person. In a regular way, you will not give your position by geographical coordinates rather than "I am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Frame Of Reference
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called an inertial space or a Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference in which objects exhibit inertia: they remain at rest or in uniform motion relative to the frame until acted upon by external forces. In such a frame, the laws of nature can be observed without the need to correct for acceleration. All frames of reference with zero acceleration are in a state of constant rectilinear motion (straight-line motion) with respect to one another. In such a frame, an object with zero net force acting on it, is perceived to move with a constant velocity, or, equivalently, Newton's laws of motion#Newton's first law, Newton's first law of motion holds. Such frames are known as inertial. Some physicists, like Isaac Newton, originally thought that one of these frames was absolute — the one approximated by the fixed stars. However, this is not required for the definition, and it is now known that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Bundle
In mathematics, a frame bundle is a principal fiber bundle F(E) associated with any vector bundle ''E''. The fiber of F(E) over a point ''x'' is the set of all ordered bases, or ''frames'', for ''E_x''. The general linear group acts naturally on F(E) via a change of basis, giving the frame bundle the structure of a principal ''\mathrm(k,\mathbb)''-bundle (where ''k'' is the rank of ''E''). The frame bundle of a smooth manifold is the one associated with its tangent bundle. For this reason it is sometimes called the tangent frame bundle. Definition and construction Let ''E \to X'' be a real vector bundle of rank ''k'' over a topological space ''X''. A frame at a point ''x \in X'' is an ordered basis for the vector space ''E_x''. Equivalently, a frame can be viewed as a linear isomorphism :p : \mathbf^k \to E_x. The set of all frames at ''x'', denoted ''F_x'', has a natural right action by the general linear group ''\mathrm(k,\mathbb)'' of invertible ''k \times k'' matrices: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center-of-mass Frame
In physics, the center-of-momentum frame (COM frame) of a system, also known as zero-momentum frame, is the inertial frame in which the total momentum of the system vanishes. It is unique up to velocity, but not origin. The ''center of momentum'' of a system is not a location, but a collection of relative momenta/velocities: a reference frame. Thus "center of momentum" is a short for "center-of-momentum ".Dynamics and Relativity, J.R. Forshaw, A.G. Smith, Wiley, 2009, A special case of the center-of-momentum frame is the center-of-mass frame: an inertial frame in which the center of mass (which is a single point) remains at the origin. In all center-of-momentum frames, the center of mass is at rest, but it is not necessarily at the origin of the coordinate system. In special relativity, only when the system is isolated is the COM frame necessarily unique. Properties General The center of momentum frame is defined as the inertial frame in which the sum of the linear moment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breit Frame
In particle physics, the Breit frame (also known as infinite-momentum frame or IMF) is a frame of reference used to describe scattering experiments of the form , that is experiments in which particle scatters off particle , possibly producing particles C_i in the process. The frame is defined so that the particle A has its momentum reversed in the scattering process. Another way of understanding the Breit frame is to look at the elastic scattering . The Breit frame is defined as the frame in which . There are different occasions when Breit frame can be useful, e.g., in measuring the electromagnetic form factor of a hadron, is the scattered hadron; while for deep inelastic scattering process, the elastically scattered parton should be considered as . It is only in the latter case the Breit frame gets related to infinite-momentum frame. It is named after the American physicist Gregory Breit. See also * Center-of-momentum frame In physics, the center-of-momentum frame (COM fram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncology, oncological purposes, Isotopes in medicine, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, Ion implantation, ion implanters for the manufacturing of Semiconductor, semiconductors, and Accelerator mass spectrometry, accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon. Large accelerators include the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, and the largest accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, Switzerland, operated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events. In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind. The scope and application of measurement are dependent on the context and discipline. In natural sciences and engineering, measurements do not apply to nominal properties of objects or events, which is consistent with the guidelines of the International Vocabulary of Metrology (VIM) published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). However, in other fields such as statistics as well as the social and behavioural sciences, measurements can have multiple levels, which would include nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio scales. Measurement is a cornerstone of trade, science, technology and quantitative research in many disciplines. Historically, many measurement syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |