|
Llangadwaladr
Llangadwaladr () is a small village in south-west Anglesey, Wales, located around 2 miles east of Aberffraw and 3 miles south of Gwalchmai, Anglesey, Gwalchmai. It is part of the community (Wales), community of Bodorgan. The village is a short distance from the ancient ''llys'' ( en, royal court) of the kings of Gwynedd, and is reputed to have been their royal burial ground. The inscription on one monumental stone in the church (pictured) reads "Catamanus rex sapientisimus opinatisimus omnium regum" ( en, King Cadfan, most wise and renowned of all kings), suggesting that Cadfan ap Iago (c. 569 – c. 625) Kingdom of Gwynedd, King of Gwynedd, is buried there. One of the windows of St Cadwaladr's church dates from the 12th century. Unusually, the advowson (right of presentation) of the benefice lay with the monarch rather than the bishop, until Disestablishment (1920). The inscription is the subject of a "detective story" that interprets it as containing a series of coded messages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadfan Ap Iago
Cadfan ap Iago (c. 569 – c. 625) was King of Gwynedd (reigned c. 616 – c. 625). Little is known of the history of Gwynedd from this period, and information about Cadfan and his reign is minimal. The historical person is known only from his appearance in royal genealogies, from his grant to Saint Beuno for the monastery at Clynnog Fawr, and from his inscribed gravestone in Llangadwaladr church. Cadfan was the son and successor of King Iago ap Beli, and is listed in the royal genealogies of the Harleian genealogies and in Jesus College MS. 20. Cadfan came to the throne near the time of the Battle of Chester ( cy, Gwaith Caerlleon) in 616, in which the Northumbrians under Æthelfrith decisively defeated the neighboring Welsh Kingdom of Powys and then massacred the monks of Bangor Is Coed. However, there is no evidence that Gwynedd had any part in the battle, so Cadfan's accession at that time appears to be no more than coincidence. Cadfan was succeeded as king by his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owen Ap Hugh
Owen ap Hugh (1518–1613), of Bodeon, near Llangadwaladr, Anglesey was a Welsh politician. He was a Member (MP) of the Parliament of England The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised t ... for Newborough in 1545. He was High Sheriff of Anglesey from 1563 to 1580. He was the eldest son and heir of Hugh ap Owen and Gwenllian ferch Maurice. He married Sibill Griffith, daughter of Sir William Griffith and Jane Puleston. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ap Hugh, Owen 1518 births 1613 deaths 16th-century Welsh politicians People from Anglesey High Sheriffs of Anglesey English MPs 1545–1547 Members of the Parliament of England (pre-1707) for constituencies in Wales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodorgan
Bodorgan is a village and community (Wales), community on the Isle of Anglesey, Wales, United Kingdom. According to the United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001 Census, there were 1,503 residents in the now former Wards of the United Kingdom, electoral ward, 72.7% of them being able to speak Welsh language, Welsh. This increased to 1,704 at the 2011 Census but only 67.72% of this increased population were Welsh speakers. The village is served by Bodorgan railway station, which is located near the hamlets of Bethel, Anglesey, Bethel and Llangadwaladr to the north-west, which are in the community, as is Malltraeth. It lies on an unclassified road to the southwest of the village of Hermon, Anglesey, Hermon, through which the A4080 road passes. To the east and south of Bodorgan lies the estuary of the Afon Cefni and the extensive Malltraeth Sands. Bodorgan Hall is the largest country estate in Anglesey. The house, dovecote and a barn are Listed building, Grade II listed buildings. The reaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
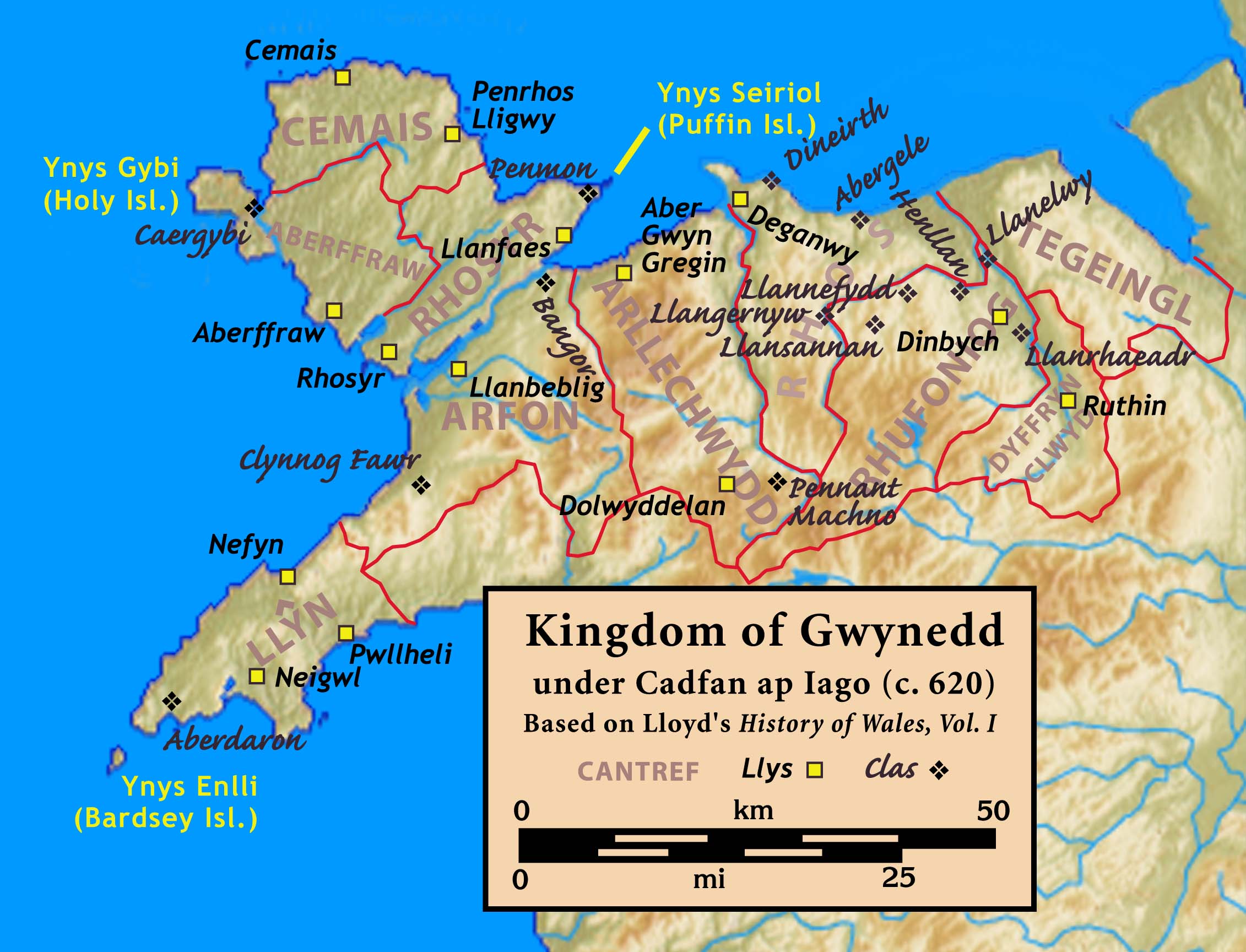
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as " King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadwaladr
Cadwaladr ap Cadwallon (also spelled Cadwalader or Cadwallader in English) was king of Gwynedd in Wales from around 655 to 682 AD. Two devastating plagues happened during his reign, one in 664 and the other in 682; he himself was a victim of the second. Little else is known of his reign. The red dragon ( cy, Y Ddraig Goch), long known as a Welsh symbol, appearing in the ''Mabinogion'', the ''Historia Brittonum'', and the stories of Geoffrey of Monmouth. Since the accession of Henry VII to the English throne, it has often been referred to as "The Red Dragon of Cadwaladr". The association with Cadwaladr is a traditional one, without a firm historical provenance. Though little is known about the historical Cadwaladr, he became a mythical redeemer figure in Welsh culture. He is a prominent character in the romantic stories of Geoffrey of Monmouth, where he is portrayed as the last in an ancient line to hold the title King of Britain. In Geoffrey's account, he does not die of plag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eryl Thomas
Eryl Stephen Thomas (20 October 1910 – 6 December 2001) was a Welsh Anglicanism, Anglican clergyman who served as Bishop of Monmouth and Bishop of Llandaff. An Anglesey man, after education at St John's College, Oxford, St John's College, Oxford, Eryl Thomas served curacies in the Diocese of St Asaph before being appointed to a parish (Risca) in South Wales then as Warden of St Michael's College, Llandaff. He was appointed Dean of Llandaff in 1954, and in this post completed the restoration of the war-damaged cathedral begun under his predecessor Glyn Simon. Stephen Thomas was in many ways a charismatic figure, he was renowned for his pastoral and preaching gifts, but he could also divide opinion. He vigorously exposed an important case of misuse of funds in the Church in Wales, incurring thereby some ill-will, and his opposition to the Sunday Closing (Wales) Act 1881, Sunday closing legislation applicable to Welsh public houses irritated Nonconformist temperance movement, abs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadfan
{{disambig ...
Cadfan or St Cadfan might refer to: * The Battle of Cadfan, fought between English and Welsh armies in 1257 * Cadfan ap Iago, King of Gwynedd (7th century floruit) * John Cadvan Davies (1846–1923), Archdruid of Wales, used the bardic name ''Cadfan'' * Saint Cadfan, founder of a monastery on Bardsey Island (6th century or 7th century floruit) ** St Cadfan's Church, Tywyn in Mid Wales ** The Cadfan Stone in the above church * ''St. Cadfan'', a diesel locomotive on the Talyllyn Railway The Talyllyn Railway ( cy, Rheilffordd Talyllyn) is a narrow gauge preserved railway in Wales running for from Tywyn on the Mid-Wales coast to Nant Gwernol near the village of Abergynolwyn. The line was opened in 1865Drummond 2015, page 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disestablishment
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular state (with or without legally explicit church-state separation) and to disestablishment, the changing of an existing, formal relationship between the church and the state. Although the concept is older, the exact phrase "separation of church and state" is derived from "wall of separation between church and state", a term coined by Thomas Jefferson. The concept was promoted by Enlightenment philosophers such as John Locke. In a society, the degree of political separation between the church and the civil state is determined by the legal structures and prevalent legal views that define the proper relationship between organized religion and the state. The arm's length principle proposes a relationship wherein the two political entities interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benefice
A benefice () or living is a reward received in exchange for services rendered and as a retainer for future services. The Roman Empire used the Latin term as a benefit to an individual from the Empire for services rendered. Its use was adopted by the Western Church in the Carolingian, Carolingian Era as a benefit bestowed by the crown or church officials. A benefice specifically from a church is called a precaria (pl. ''precariae)'', such as a stipend, and one from a monarch or nobleman is usually called a fief. A benefice is distinct from an allodial title, allod, in that an allod is property owned outright, not bestowed by a higher authority. Roman Catholic Church Roman imperial origins In ancient Rome a ''benefice'' was a gift of land (precaria) for life as a reward for services rendered, originally, to the state. The word comes from the Latin language, Latin noun ''beneficium'', meaning "benefit". Carolingian Era In the 8th century, using their position as Mayor of the Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advowson
Advowson () or patronage is the right in English law of a patron (avowee) to present to the diocesan bishop (or in some cases the ordinary if not the same person) a nominee for appointment to a vacant ecclesiastical benefice or church living, a process known as ''presentation'' (''jus praesentandi'', Latin: "the right of presenting"). The word derives, via French, from the Latin ''advocare'', from ''vocare'' "to call" plus ''ad'', "to, towards", thus a "summoning". It is the right to nominate a person to be parish priest (subject to episcopal – that is, one bishop's – approval), and each such right in each parish was mainly first held by the lord of the principal manor. Many small parishes only had one manor of the same name. Origin The creation of an advowson was a secondary development arising from the process of creating parishes across England in the 11th and 12th centuries, with their associated parish churches. A major impetus to this development was the legal exac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island, at , is the largest in Wales, the seventh largest in Britain, largest in the Irish Sea and second most populous there after the Isle of Man. Isle of Anglesey County Council administers , with a 2011 census population of 69,751, including 13,659 on Holy Island. The Menai Strait to the mainland is spanned by the Menai Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford in 1826, and the Britannia Bridge, built in 1850 and replaced in 1980. The largest town is Holyhead on Holy Island, whose ferry service with Ireland handles over two million passengers a year. The next largest is Llangefni, the county council seat. From 1974 to 1996 Anglesey was part of Gwynedd. Most full-time residents are habitual Welsh speakers. The Welsh name Ynys M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |