|
Llandochau
Llandough ( /l├”n╦łd╔Æk/; cy, Llandochau Fach ¼an'do╦ÉŽća╔© vaŽć is a village, community and electoral ward in the Vale of Glamorgan ( cy, Bro Morgannwg, links=no), Wales, approximately 2.3 miles (3.7 km) south west of Cardiff city centre, and approximately 1.3 miles (2 km) north west of Penarth. Toponymy ''Llandough'' is an anglicisation of the Welsh placename , which as a combination of the words (meaning 'church') and (Saint /), followed by (meaning 'small', however, consonant mutation in Welsh means this is changed to ). History Excavations have shown that the village's history goes back as far as the Roman occupation of Wales. Until the mid-1960s, Llandough was a small farming and quarrying village but experienced an expansion involving the building of a large number of houses, a primary school, and a block of six shopping units. However, these shops have now been demolished. There were around six thatched cottages in the village around 1960, but only on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vale Of Glamorgan
The Vale of Glamorgan ( cy, Bro Morgannwg ), often referred to as The Vale, is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. It borders Bridgend County Borough to the west, Cardiff to the east, Rhondda Cynon Taf to the north, and the Bristol Channel to the south. With an economy based largely on agriculture and chemicals, it is the southernmost unitary authority in Wales. Attractions include Barry Island Pleasure Park, the Barry Tourist Railway, Medieval wall paintings in St Cadoc's Church, Llancarfan, Porthkerry Park, St Donat's Castle, Cosmeston Lakes Country Park and Cosmeston Medieval Village. The largest town is Barry. Other towns include Penarth, Llantwit Major, and Cowbridge. There are many villages in the county borough. History The area is the southernmost part of the county of Glamorgan. Between the 11th century and 1536 the area was part of the Lordship of Glamorgan. In medieval times, the village of Cosmeston, near what is today Penarth in the south east of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary, and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi (; 25 April 187420 July 1937) was an Italians, Italian inventor and electrical engineering, electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based Wireless telegraphy, wireless telegraph system. This led to Marconi being credited as the inventor of radio, and he shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".Guglielmo Marconi: The Nobel Prize in Physics 1909 . nobelprize.org Marconi was also an entrepreneur, businessman, and founder of Marconi Company, The Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom in 1897 (which became the Marconi Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amgueddfa Cymru ŌĆō National Museum Wales
Amgueddfa Cymru ŌĆō Museum Wales, branded as simply Amgueddfa Cymru (formerly the National Museums and Galleries of Wales and legally National Museum of Wales), is a Welsh Government sponsored body that comprises seven museums in Wales: * National Museum Cardiff ŌĆō formerly the National Museum of Wales * St Fagans National Museum of History, Cardiff * Big Pit National Coal Museum, Blaenavon * National Wool Museum, Dre-fach Felindre near Llandysul * National Slate Museum, Llanberis * National Roman Legion Museum, Caerleon * National Waterfront Museum, Swansea In addition to these sites, the organisation runs Oriel y Parc, a gallery of Welsh landscape art in St David's, in partnership with the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park Authority. The National Collections Centre in Nantgarw is AC-NMW's storage facility. Directors of the National Museum of Wales * William Evans Hoyle (1908ŌĆō1924) * Sir Mortimer Wheeler (1925ŌĆō1926) * Sir Cyril Fox (1926ŌĆō1948) * D. Dilwyn John (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutton Stone
Sutton stone is a geologic formation located only in South Wales. Sutton stone consists of white, conglomeratic limestones with pebbles of black chert (silica) and carboniferous limestones, laid down in early Jurassic times. It was named by geologist Henry De la Beche Sir Henry Thomas De la Beche KCB, FRS (10 February 179613 April 1855) was an English geologist and palaeontologist, the first director of the Geological Survey of Great Britain, who helped pioneer early geological survey methods. He was the ... in 1846. Notes {{reflist Jurassic Wales Limestone formations Shale formations Geologic formations of the United Kingdom Stratigraphy of the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchyard
In Christian countries a churchyard is a patch of land adjoining or surrounding a church, which is usually owned by the relevant church or local parish itself. In the Scots language and in both Scottish English and Ulster-Scots, this can also be known as a kirkyard. While churchyards can be any patch of land on church grounds, historically, they were often used as graveyards (burial places). Use of churchyards as a place of burial After the establishment of the parish as the centre of the Christian spiritual life, the possession of a cemetery, as well as the baptismal font, was a mark of parochial status. During the Middle Ages, religious orders also constructed cemeteries around their churches. Thus, the most common use of churchyards was as a consecrated burial ground known as a graveyard. Graveyards were usually established at the same time as the building of the relevant place of worship (which can date back to the 6th to 14th centuries) and were often used by those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Cross
Stone crosses (german: Steinkreuze) in Central Europe are usually bulky Christian monuments, some high and wide, that were almost always hewn from a single block of stone, usually granite, sandstone, limestone or basalt. They are amongst the oldest open-air monuments. A larger variant of the stone cross, with elements of a wayside shrine is called a shaft cross (''Schaftkreuz''). Distribution These small monuments are found along old routes and crossroads, by trees and forest edges, on hilltops or on old municipal and territorial boundaries. They are especially common in the Upper Palatinate region of Bavaria and in Central Germany, whereas basalt crosses occur almost exclusively in the Eifel region. Unfortunately, many of these stone witnesses to a bygone era have disappeared due to carelessness, ignorance or deliberate destruction. As Rainer H. Schmeissner writes in his 1977 monograph, ''Stone Crosses in the Upper Palatinate'', there are still about 300 such monumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritan─½'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291ŌĆō292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians in the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
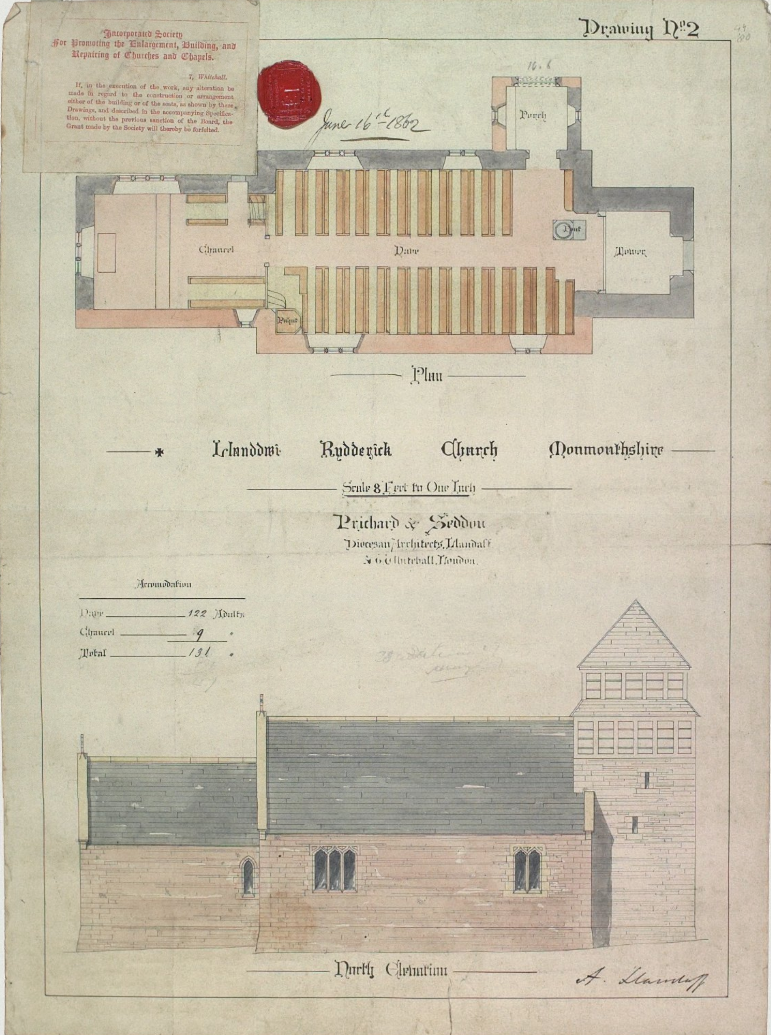
St Dochdwy's Church, Llandough
St Dochdwy's Church is a historic listed church in the village of Llandough, near Penarth in the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales. History Llandough was an important site for Christian worship from the early years of Celtic Christianity. The word 'Llan' refers to an enclosure which often surrounded an early building of worship, and many other Welsh locations drew their names from early churches in this way, such as Llanishen, Llanedeyrn and Llandewi (the original name for Nottage). The saint for whom the church is named is known by numerous other renderings, such as Cyngar, Dochau, Dochow, Dochwy, Dogwyn and Docco, amongst others. St Dochau established a monastic community known as Bangor Dochau in the 5th century, one of many in Glamorgan (then known as Morganwg). An archaeological excavation took place at the church in 1994, at which a large cemetery was uncovered. Subsequent radiocarbon dating showed that the burials commenced there in the period ŌĆō . The latest radiocarbon date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leckwith
Leckwith ( cy, Lecwydd) is a small village in the Vale of Glamorgan, just west of Cardiff. Historically, the parish of Leckwith also included land on the east side of the river Ely that is now part of Cardiff itself. This area is also commonly known as Leckwith. Etymology The name ''Leckwith'' is an anglicisation of the Welsh ''Lecwydd'', with the common replacement of Welsh by English (as in ''Gruffudd''>''Griffith''). ''Lecwydd'' probably derives from the personal name ''Helygwydd'' (possibly the name of a local holy man or Welsh saint). The change from to may be compared to that in the personal name ''Tecwyn'' (<''Tegwyn''). Since at least the nineteenth century ''Lecwydd'' sometimes appears in Welsh as ''Llechwydd'' or ''Llechwedd''. These forms have been linked to the common Welsh noun ''llechwedd'' (hillside, slope), which has been taken to refer to Leckwith Woods, which rise up steeply from the river Ely. Linguistically, however, there is no relationship between ''Lecw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pollard Seddon
John Pollard Seddon FRIBA (19 September 1827 ŌĆō 1 February 1906) was a British architect, working largely on churches. His father was a cabinetmaker, and his brother Thomas Seddon (1821ŌĆō1856) a landscape painter. Born in London, he was educated at Bedford School. He was later a pupil of Thomas Leverton Donaldson, though Donaldson was a classical architect and Seddon preferred the Gothic Revivalism of John Ruskin. Between 1852 and 1863, Seddon formed a partnership with John Prichard. Many of their major commissions were church restoration works, most famously for Llandaff Cathedral. In 1871 he submitted a design in a competition for Holloway Sanatorium. C. F. A. Voysey was articled as a pupil of Seddon in 1873. From 1884 to 1904 he was in partnership with John Coates Carter. In 1904 he was Diocesan Architect for London and designed a gigantic Imperial Monumental Halls, with a tall tower, to be added to Westminster Abbey; it was intended to restore the dominance of the ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Prichard
John Prichard (6 May 1817 ŌĆō 13 October 1886) was a Welsh architect in the neo-Gothic style. As diocesan architect of Llandaff, he was involved in the building or restoration of many churches in south Wales. Personal history John Prichard was born in Llangan, near Cowbridge, Wales on 6 May 1817, the twelfth son of the rector Richard Prichard, who served as vicar-choral of Llandaff for 35 years. He was descended from the Prichard family of Collenna. John Prichard trained as an architect under Thomas Larkins Walker, and as a result was deeply influenced by the ideas of Augustus Pugin; much of his work was in a neo-Gothic style. He established a practice in Llandaff, Cardiff, becoming 'Resident Diocesan Architect' in December 1844. Between 1852 and 1863 he was in partnership with John Pollard Seddon. Many of his major commissions were restoration works, most famously for Llandaff Cathedral (1843ŌĆō69); Prichard and Seddon worked on the cathedral from the 1840s until 1869, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |