|
Liudewit
Ljudevit () or Liudewit ( la, Liudewitus), often also , was the Duke of the Slavs in Lower Pannonia from 810 to 823. The capital of his realm was in Sisak (today in Croatia). As the ruler of the Pannonian Slavs, he led a resistance to Frankish domination. Having lost the war against Franks, he fled to the south, presumably to Dalmatia, first to an unknown Serb župa (a topic of historical debates), and then to the Croat ruler Ljudemisl, who treacherously killed him. Rebellions against the Franks In 818 Ljudevit sent his emissaries to Emperor Louis in Heristal. They described the horrors conducted by Margrave Cadolah of Friuli (800-819) and his men in Pannonia, but the King of Franks refused to make peace. Ljudevit raised a rebellion against his Frankish rulers in 819 after he was seriously accused by the Frankish court. The Emperor Louis the Pious (814-840) sent Cadolah to quell the rebellion. The Frankish Frontier forces led by Cadolah have raided the land and tortured the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croat
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Slovenia. Due to political, social and economic reasons, many Croats migrated to North and South America as well as New Zealand and later Australia, establishing a diaspora in the aftermath of World War II, with grassroots assistance from earlier communities and the Roman Catholic Church. In Croatia (the nation state), 3.9 million people identify themselves as Croats, and constitute about 90.4% of the population. Another 553,000 live in Bosnia and Herzegovina, where they are one of the three constituent ethnic groups, predominantly living in Western Herzegovina, Central Bosnia and Bosnian Posavina. The minority in Serbia number about 70,000, mostly in Vojvodina. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
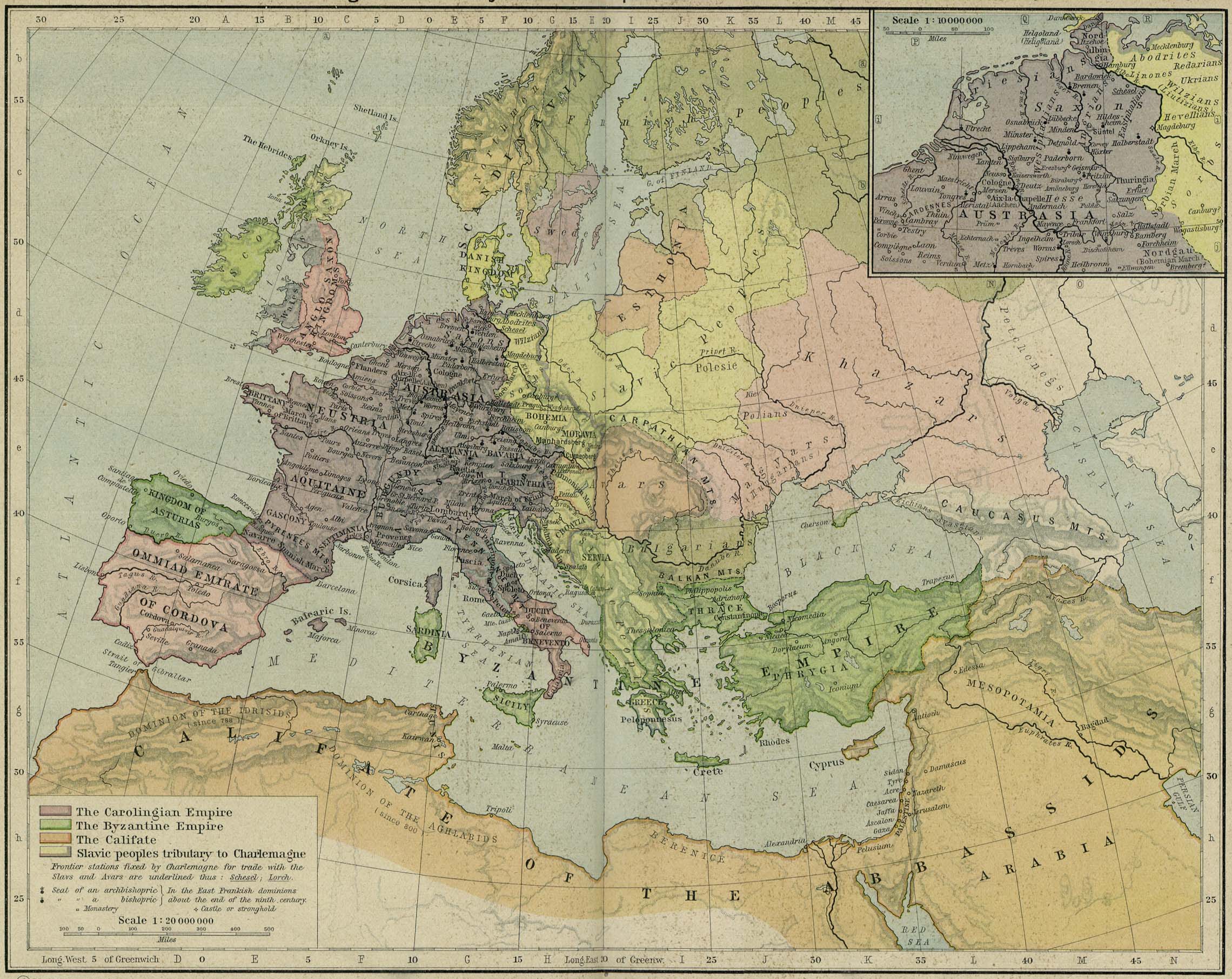
Slavs In Lower Pannonia
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spodnja Panonija) was used to designate those areas of the Pannonian plain that lie to the east and south of the river Rába, with the division into ''Upper'' and ''Lower'' inherited from the Roman terminology. From the middle of the 6th to the end of the 8th century, the region was under the domination of the Avars, while the Slavic inhabitants lived under Avar rule. By the beginning of the 9th century, that state was destroyed and replaced by the supreme rule of the Frankish Empire, which lasted until the Magyar conquest (c. 900). During the Frankish period, the region of Lower Pannonia was governed by local Slavic rulers, who were under the suzerainty of Frankish kings. Within the Frankish administrative system, the March of Pannonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position which he held until his death, save for the period 833–34, during which he was deposed. During his reign in Aquitaine, Louis was charged with the defence of the empire's southwestern frontier. He conquered Barcelona from the Emirate of Córdoba in 801 and asserted Frankish authority over Pamplona and the Basques south of the Pyrenees in 812. As emperor he included his adult sons, Lothair, Pepin and Louis, in the government and sought to establish a suitable division of the realm among them. The first decade of his reign was characterised by several tragedies and embarrassments, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timočani
The Timočani (also Timochani, or Timochans; Serbian and Bulgarian: Тимочани) were a medieval South Slavic tribe that lived in the territory of present-day eastern Serbia, west of the Timok River, as well as in the regions of Banat, Syrmia and Moesia Superior. Timočani settled in the Balkans in the 6-7th century in the former Dacia Ripensis province and became later subjects of the Avar Khaganate. It is considered that with the arrival of the Bulgars in the 7th century came under Bulgarian suzerainty, but for a good period of time between the mid-8th and early 9th century local Slavs lived in anarchy until around 805 when the area was reconquered and reimposed control of the Bulgar Khanate under Khan Krum. In the beginning of the 9th century they were also attacked from the West by the Serbs. In 818 during the rule of Omurtag of Bulgaria (814-836) they, together with other border tribes of the First Bulgarian Empire, revolted because of an administrative reform of ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Of Croatia
Borna was the Duke of Croatia from to 821 and vassal of the Frankish Empire. He resided in Nin and was the ruler of most of the Croats in northern Dalmatia.John Van Antwerp Fine: The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, 1991, p. 255 Borna's predecessor was Višeslav of Croatia, probably his father. After his death in 821, he was succeeded by his nephew Vladislav. He is mentioned in the Royal Frankish Annals (''Annales regni Francorum'') in entries regarding 818–821. His titles were "Duke of the Guduscani" (a Croatian tribe from Lika and northern Dalmatia) in 818; "Duke of Dalmatia" in 819; "Duke of Dalmatia and Liburnia" in 821. Historiography treats him as a ruler of ''Dalmatian Croatia''. History Borna is documented in the "Royal Frankish Annals" (''Annales regni Francorum''). He is first mentioned regarding an 818 meeting at Herstal of Frankish Emperor Louis the Pious with envoys of the Obotrites, Borna (duke of the Gudus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guduscani
The Guduscani or Goduscani ( hr, Guduščani, Gačani) were a tribe whose location and origin on the territory of early medieval Croatia remains a matter of dispute. According to one hypothesis they were located around present-day Gacka (Lika), between upper Kupa (river), Kupa river and the Dalmatia, Dalmatian coast, or that were inhabitants around the river Guduča near the Bribir, Šibenik-Knin County, Bribir region. Etymology They are mentioned three times in the ''Frankish Annals'' (''Guduscani'', ''Guduscanorum'', ''Guduscanis'') and twice in ''Vita Hludovici'' (''Goduscanorum''). Petar Skok and Radoslav Katičić derived their ethnonym from Proto-Slavic ''*gъd-'', similar to Proto-Prussian ''gude'' in the meaning of "forest". Skok, and Petar Šimunović, also derived it from Proto-Slavic ''*gadъ'' ('' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carantanians
Carantanians ( la, Quarantani, sl, Karantanci) were a Slavic people of the Early Middle Ages (Latin: , or "Slavs called Caranthanians"), living in the principality of Carantania, later known as Carinthia, which covered present-day southern Austria and parts of Slovenia. They are considered ancestors of modern Slovenes, particularly Carinthian Slovenes. In the high Middle Ages, the term Carantanians and Carinthians were used interchangibly and denoted both the inhabitants of the bilingual Slavic-German Duchy of Carinthia, as well as South Slavs living within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire (that is, the ancestors of present-day Slovenes and Istrian Croats). Historical background After the disintegration of Samo's realm, Alpine Slavs established the Principality of Carantania in the Eastern Alps, which was independent from around 660 to around 745, when it fell under the Bavarian zone of influence and was later incorporated in the Frankish Empire. The formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of Carniola
The March (or Margraviate) of Carniola ( sl, Kranjska krajina; german: Mark Krain) was a southeastern state of the Holy Roman Empire in the High Middle Ages, the predecessor of the Duchy of Carniola. It corresponded roughly to the central Carniolan region of present-day Slovenia. At the time of its creation, the march served as a frontier defense against the Kingdoms of Hungary and Croatia. History Before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC), the Taurisci dwelt in the north of Carniola, the Pannonians in the south-east, the Iapodes or Carni, a Celtic tribe, in the south-west. Carniola formed part of the Roman province of Pannonia; the northern part was joined to Noricum, the south-western and south-eastern parts and the city of Aemona to Venice and Istria. In the time of Augustus all the region from Aemona to Kolpa river belonged to the province of Savia. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire (476), Carniola was incorporated into the Kingdom of Italy, and (493) unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratimir, Duke Of Pannonian Croatia
Ratimir ( la, Ratimarus) was a duke or prince (''knez (title), knez'') of the Slavs in Lower Pannonia between ca. 829 to 838. It is believed that Ratimir descends from a royal dynasty that provided rulers for Moravia and Croatia. In 827, the Bulgars under Great Khan Omurtag of Bulgaria, Omurtag invaded and conquered Lower Pannonia and parts of Frankish territories to the north. In 829 the Bulgars imposed a local prince, Ratimir, as the new ruler of the territory. His province is believed to have been the territory of the former Roman Pannonia Savia, which is located in modern-day Croatia. Earlier, Sigismund Calles (1750) called him "Slavic duke of the Drava". In 838, nine years later, following the Bulgarian conquest of Macedonia (region), Macedonia, the Danubian count Radbod (prefect), Radbod, prefect of the March of Pannonia, East March, deposed Ratimir and restored Frankish rule. Ratimir fled the land, and the Franks instated dukes Pribina and Kocelj to rule Pannonian area in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timok (river)
The Timok (Serbian and Bulgarian: Тимок; ro, Timoc), sometimes also known as Great Timok ( sr, Велики Тимок, Veliki Timok; ro, Timocul Mare), is a river in eastern Serbia, a right tributary of the Danube. For the last 15 km of its run it forms a border between eastern Serbia and western Bulgaria. It is a branchy system of many shorter rivers, many of them having the same name (Timok), only clarified with adjectives. From the farthest source in the system, that of the Svrljiški Timok, until its confluence (as ''Veliki Timok''), the Timok is 202 km long. The area of the river basin is .Velika Morava River Basin [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giulia, i.e. the administrative provinces of Udine, Pordenone, and Gorizia, excluding Trieste. Names The multiethnic and subsequent multilingual tradition of Friuli means that the name of the region varies according to locality. Besides from Italian (), other local Romance forms include Friulan () and Venetian ; in German and in Slovene. The name ''Friuli'' originates from the ancient Roman town of (now ). Geography Friuli is bordered on the west by the Veneto region with the border running along the Livenza river, on the north by the crest of the Carnic Alps between Carnia and Austrian Carinthia, on the east by the Julian Alps, the border with Slovenia and the Timavo river, and on the south by the Adriatic Sea. The ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.png)