|
Liubar
Liubar ( uk, Любар, russian: Лю́бар, pl, Lubar) is an urban-type settlement in Zhytomyr Raion, Zhytomyr Oblast, Ukraine. Population: History According to historical and archaeological data, Liubar is the possible location of the ancient Ruthenian city of Bolokhov. In the 13th century, the Bolokhov land was devastated by the military campaigns of Daniel of Galicia as well as Mongol raids. In the 14th century, Lithuanian prince Lubart built a fortress on the Sluch River, which was named in his honour. Since 1387, the location belonged to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. After 1569, the settlement, known in Polish as Lubartów, was divided between the Kyiv and Volhynian Voivodeship of the Crown of Poland. At the time, it was controlled by prince Constantine Ostrozky and received Magdeburg rights. Since 1623, Liubar belonged to the Polish Lubomirski family. A Jewish community lived in Liubar for centuries. A wooden synagogue was erected in 1491. It was destroyed du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubart
Demetrius of Liubar or Liubartas (also ''Lubart'', ''Lubko'', ''Lubardus'', baptized ''Dmitry''; died ) was Prince of Lutsk and Liubar (Volhynia) (1323–1383), Prince of Zhytomyr (1363–1374), Grand Prince of Volhynia (1340–1383), Grand Prince of Halych–Volhynia (1340–1349). Biography Liubartas was the youngest son of Gediminas, Grand Duke of Lithuania. In the early 1320s he married a daughter of Andrew of Galicia and ruled Lutsk with Liubar (today town in Zhytomyr Oblast) in eastern Volhynia. After Andrew and his brother Leo II died around 1322, Galicia–Volhynia did not have a male successor. Instead of promoting Liubartas and causing a war with Poland, Gediminas compromised with Ladislaus the Short. Both parties agreed to install Yuri II Boleslav, nephew of Leo and Andrew. Boleslaw-Yuri was a son of Trojden I, Duke of Masovia from the Piast dynasty, a cousin of Władysław I, and nephew of Gediminas' son-in-law Wenceslaus of Płock. At the time Boleslaw was fourte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation born from several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. The Grand Duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Lithuania, Belarus and parts of Ukraine, Latvia, Poland, Russia and Moldova. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. The consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 13th century. Mindaugas, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in a religious crusade by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volhynian Voivodeship (1569–1795)
pl, Województwo wołyńskie uk, Волинське воєводство , subdivision = Voivodeship , nation = Lithuania (1566–1569) and then Poland (1569–1795) , year_start = 1566 , event1 = To Polish Crown , date_event1 = 1569 , event_end = Annexed by Russia , year_end = 1795 , date_end = 24 October , p1 = Grand Duchy of Lithuania , image_p1 = , s1 = Volhynian Governorate , image_s1 = , image_coat = Herbarz Kaspra Niesieckiego Волынское.svg , image_map = RON województwo wołyńskie map.svg , image_map_caption = The Volhynian Voivodeship (red) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1635 , capital = Lutsk ( pl, Łuck) , stat_area1 = 38324 , stat_year1 = , stat_pop1 = , political_subdiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban-type Settlement
Urban-type settlementrussian: посёлок городско́го ти́па, translit=posyolok gorodskogo tipa, abbreviated: russian: п.г.т., translit=p.g.t.; ua, селище міського типу, translit=selyshche mis'koho typu, abbreviated: uk, с.м.т., translit=s.m.t.; be, пасёлак гарадскога тыпу, translit=pasiolak haradskoha typu; pl, osiedle typu miejskiego; bg, селище от градски тип, translit=selishte ot gradski tip; ro, așezare de tip orășenesc. is an official designation for a semi-urban settlement (previously called a "town A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an ori ..."), used in several Eastern European countries. The term was historically used in Bulgaria, Poland, and the Soviet Union, and remains in use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Boruszkowce
The Battle of Boruszkowce was a battle in the Polish–Russian War of 1792. The battle took place on 14 June 1792, between a detachment of a Polish army of Michał Wielhorski and a Russian army group under the command of Michail Kachovski. Main Polish forces under command of Poniatowski withdrew to Połonne across Czantoria; they were secured from the south by a division under command of Kościuszko. A Polish army train, secured by a division of Wielhorski, moved the shortest way across Boruszkowice. Wielhorski had under his command 6500 soldiers and 12 cannons. The route which he moved was sodden and an area in which were forests allowing Russian formations cover making it difficult for Polish defence. After getting information about Polish withdrawal, Mikhail Kakhovsky rallied two Cossacks regiments under command of Alexey Orlov and a part of cavalry under command of Alexander Tormasov Count Alexander Petrovich Tormasov (; 22 August 1752 – 25 November 1819) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna; or ''Cossack state''), officially the Zaporizhian Host or Army of Zaporizhia ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viisko Zaporozke, links=no; la, Exercitus Zaporoviensis), was a Ukrainian Cossack state in the region of what is today Central Ukraine between 1648 and 1764 (although its administrative-judicial system persisted until 1782). The Hetmanate was founded by the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host Bohdan Khmelnytsky during the Uprising of 1648–57 in the eastern territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Establishment of vassal relations with the Tsardom of Russia in the Treaty of Pereyaslav of 1654 is considered a benchmark of the Cossack Hetmanate in Soviet, Ukrainian, and Russian historiography. The second Pereyaslav Council in 1659 further restricted the independence of the Hetmanate, and from the Russian side there were attempts to declare agreements reached with Yurii Khmelnytsky in 1659 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsardom Of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I in 1721. From 1551 to 1700, Russia grew by 35,000 km2 per year. The period includes the upheavals of the transition from the Rurik to the Romanov dynasties, wars with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sweden and the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian conquest of Siberia, to the reign of Peter the Great, who took power in 1689 and transformed the Tsardom into the Russian Empire. During the Great Northern War, he implemented substantial reforms and proclaimed the Russian Empire after victory over Sweden in 1721. Name While the oldest endonyms of the Grand Duchy of Moscow used in its documents were "Rus'" () and the "Russian land" (), a new form of its name, ''Rusia'' or ''Russia'', appeared and became common in the 15th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
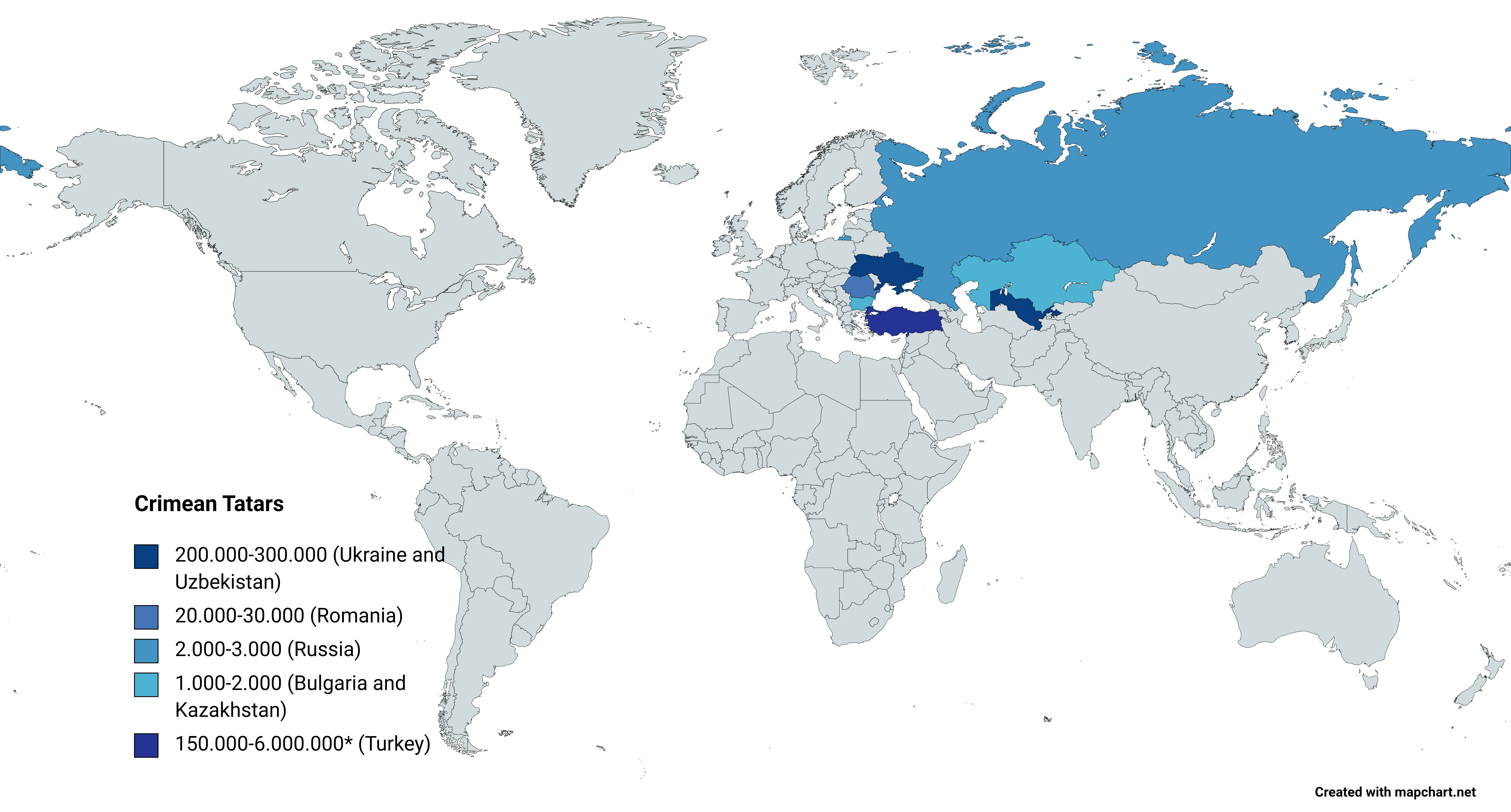
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lyubar
The Battle of Lyubar or battle of Lubar took place on 14–27 September 1660 near Lyubar, during the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667), between the forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (allied with the Tatars) and Tsardom of Russia (allied with the Cossacks). It was the first battle of the 1660 campaign in the south. It ended with a Polish victory. The Russian army retreated and was subsequently destroyed during the battle of Chudniv. Background In July 1660, Tsar Alexis I of Russia ordered Vasily Sheremetev to resume the sporadic Russo-Polish War (1654–1667) and push the Poles west, taking Lviv and securing disputed Ukrainian territories for Russia. In September 1660, the commander of the Russian army, Sheremetev, acting on misleading information that greatly underestimated the numerical strength of the Polish army decided to seek out and destroy the Polish forces with what he believed would be overwhelming strength (15,000 Russian soldiers and 15,000–35,000 of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or , sk, kozáci , uk, козаки́ are a predominantly East Slavic Orthodox Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic-speaking Orthodox Christians. The Cossacks were particularly noted for holding democratic traditions. The rulers of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |