|
Liu Wenjing
Liu Wenjing (568–619), courtesy name Zhaoren, formally the Duke of Lu, was a Chinese politician during the Tang dynasty. He initially served as an official of the Sui dynasty and was one of the driving forces in persuading the general Li Yuan to rebel against Emperor Yang of Sui. He assisted Li Yuan in establishing the Tang dynasty and becoming its first ruler. After Li Yuan became the emperor, he did not award the same honours to Liu Wenjing as he did to Pei Ji, thus Liu became very resentful. He engaged sorcerers to help him seek divine favours, but was executed after Li Yuan found out about it. Background According to Liu Wenjing himself, his ancestors were from Pengcheng (彭城, in modern Xuzhou, Jiangsu), but later moved to the Chang'an region. His grandfather Liu Yi (劉懿) was a provincial governor during Northern Zhou. His father Liu Shao (劉韶) served in the army of the succeeding Sui Dynasty and died in battle. As a result of this and the posthumous honors th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wugong County
Wugong County is a county under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Xianyang, in the central part of Shaanxi province, China. Tai was also one of the ancestral homes of the royal Ji clan of the Zhou dynasty The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th .... Administrative divisions As 2016, this County is divided to 8 towns. ;Towns Climate References External links * Official website of Wugong County Government County-level divisions of Shaanxi {{Shaanxi-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
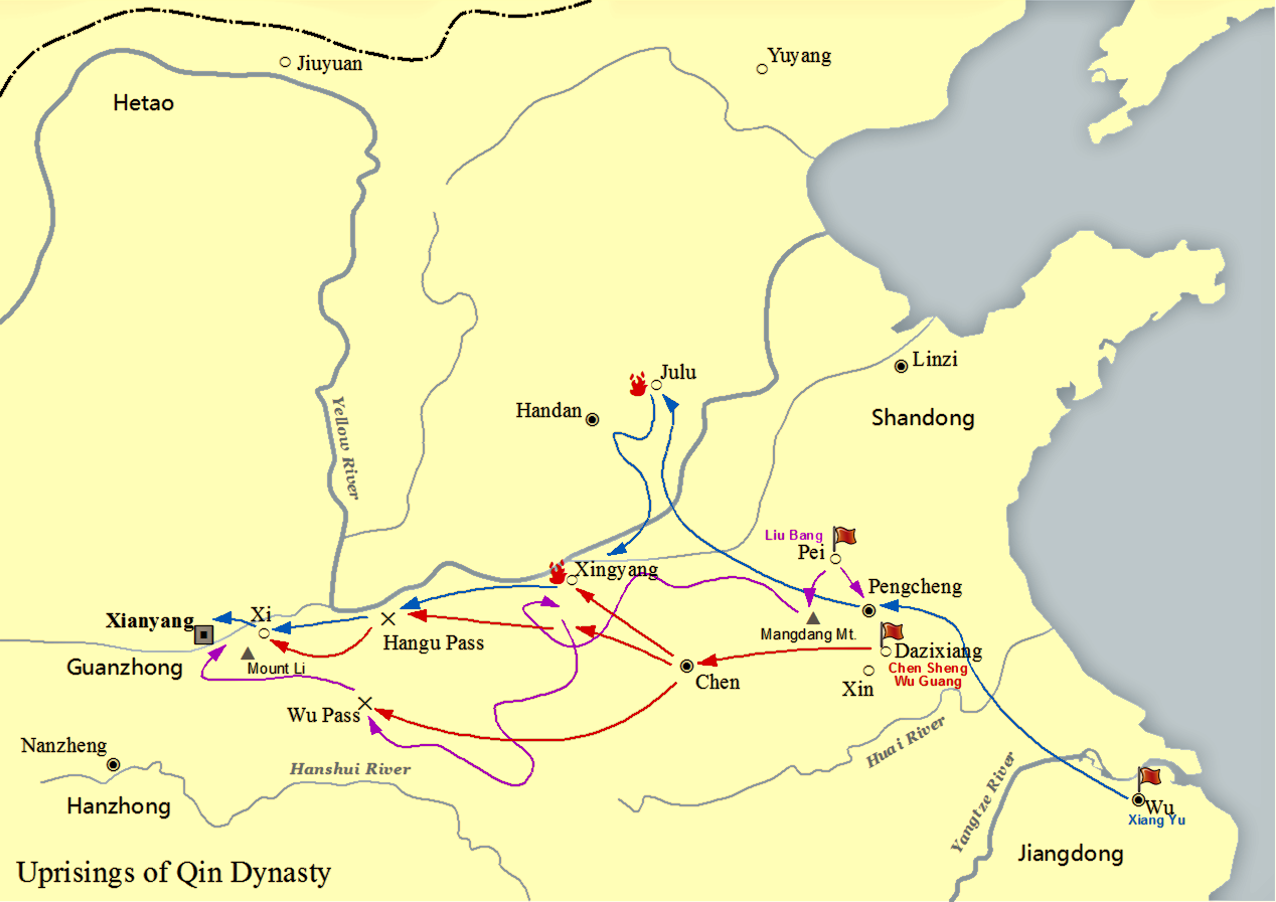
Emperor Gao Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Jiancheng
Li Jiancheng (; 589 – July 2, 626, formally Crown Prince Yin (, literally, "the hidden crown prince"), nickname Vaishravana (; Sanskrit: Vaiśravaṇa), was the first crown prince of the Chinese Tang Dynasty. He was the oldest son of the founding emperor Emperor Gaozu (Li Yuan) and the crown prince after the founding of the dynasty in 618 CE. Li Jiancheng was murdered by his younger brother, Tang general Li Shimin, the Prince of Qin, in the Xuanwu Gate incident in 626, in which Li Shimin seized control of the imperial government and forced their father Emperor Gaozu to abdicate. Li Jiancheng's sons were subsequently executed or excluded from the imperial clan. After Li Shimin took the throne, Li Jiancheng was posthumously stripped of his crown prince status and granted the title "Prince Yin of Xi" (息隐王). Later, he was buried with the ceremonies due to an imperial prince. In 642, Li Jiancheng's title of Crown Prince Yin (隐太子) was restored. Background Li Jian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fields. Etymology Early Chinese literature including the '' Yu Gong'' or ''Tribute of Yu'' dating to the Warrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuncheng, Shanxi
Yuncheng is the southernmost prefecture-level city in Shanxi province, People's Republic of China. It borders Linfen and Jincheng municipalities to the north and east, and Henan (Luoyang and Jiyuan to the east, Sanmenxia to the south) and Shaanxi (Weinan) provinces to the east, south and west, respectively. As of the 2020 census, its population was 4,774,508 inhabitants (5,134,779 in 2010), of whom 928,334 (680,036 in 2010) lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of Yanhu District. One can note than Pinglu County, 205,080 inhabitants in the south, is now part of Sanmenxia built-up (or metro) area. History In early China, it was the location of the state of Kunwu (). Yuncheng was the site of the Yuncheng Campaign (三打运城), battle between the Kuomintang army and the People's Liberation Army during Chinese civil war. The famous general Guan Yu from the late Han Dynasty was also born in this region. Archaeology In July 2022, archaeologists announced a discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Yong (Sui Dynasty)
Yang Yong (; died August 604), Xianbei name Xiandifa (睍地伐), also known by his posthumous title of Prince of Fangling (房陵王), was a crown prince of Sui dynasty. He was the oldest son of Emperor Wen and Empress Dugu. He drew ire from his parents for wastefulness (which Emperor Wen disliked) and having many concubines (which Empress Dugu disliked), while his younger brother, Yang Guang, whom Emperor Wen and Empress Dugu thought lacked these faults, was favored by them. In 600, Emperor Wen deposed Yang Yong and replaced him with Yang Guang. Subsequently, after Emperor Wen died in 13 August 604 (a death that most historians, while acknowledging a lack of conclusive evidence, believed to be a murder ordered by Yang Guang), Yang Guang had Yang Yong put to death. Family Parents *Father: Emperor Wen of Sui (隋文帝; 21 July 541 – 13 August 604) *Mother: Empress Wenxian, of the Henan Dugu clan (文獻皇后 河南獨孤氏; 544 – 10 September 602) Consort and their re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wen Of Sui
The Emperor Wen of Sui (; 21 July 541 – 13 August 604), personal name Yang Jian (), Xianbei name Puliuru Jian (), alias Narayana () deriving from Buddhist terms, was the founder and the first emperor of the Chinese Sui dynasty. The ''Book of Sui'' records him as having withdrawn his favour from the Confucians, giving it to "the group advocating Xing-Ming and authoritarian government." As a Buddhist, he encouraged the spread of Buddhism through the state. He is regarded as one of the most important emperors in Chinese history, reunifying China proper in 589 after centuries of division since the independence of the Cheng Han and Han Zhao dynasties from the Western Jin dynasty in 304. During his reign, the construction of the Grand Canal began. As a Northern Zhou official, Yang Jian served with apparent distinction during the reigns of the Emperor Wu of Northern Zhou and Emperor Xuan of Northern Zhou. When the erratic Emperor Xuan died in 580, Yang, as his father-in-law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shibi Khan
Shibi Khagan (r. 609 or 611–619 AD) succeeded Yami Qaghan as the second khagan of the Eastern Turkic Khaganate. Reign He succeeded Yami Qaghan in 609 or 611. From 613 to 615 he was actively supporting agrarian rebels inside China. Pei Ju had become apprehensive that khagan was becoming strong and difficult to control and had therefore suggested that Emperor Yang offer to marry a princess to the khan's brother Ashina Chiji (阿史那叱吉). Chiji shad, in fear, declined. This already brought resentment from the khagan, when Pei tricked the Shibi Khan's strategist Shishuhu (史蜀胡) into meeting him at Mayi (present-day Shuozhou, Shanxi) and then killed him, claiming that Shishuhu was planning to rebel against the khagan. Shibi Khahan, knowing that the accusation was false, became resolved to rebel against Sui. In the fall of 615, when Emperor Yang was visiting Yanmen Commandery on the northern frontier, the khagan launched a surprise attack on the area, overrunning most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang You
Emperor Gong of Sui (隋恭帝) (605 – 14 September 619), personal name Yang You (楊侑), was an emperor of the Chinese Sui dynasty. He was installed as a puppet emperor by Li Yuan, and after Emperor Yang of Sui died, Li then became the founding emperor of the Tang dynasty and had Yang You executed. Traditionally, he was considered the last emperor of the Sui dynasty because he was succeeded and executed by Li Yuan (Emperor Gaozu of Tang), the founding emperor of the Tang dynasty. However, after him, his brother Yang Tong claimed the throne and continued to do so until 619. Li had rebelled against the rule of Yang You's grandfather Emperor Yang of Sui in 617 and captured the capital Chang'an later that year, seizing Yang You and installing Yang as a puppet emperor. However, only the commanderies under Li's control recognized Yang You as emperor. The rest of the commanderies continued to recognize Emperor Yang of Sui as emperor. In 618, after news arrived that Emperor Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled most of the Korean peninsula, large parts of Manchuria and parts of eastern Mongolia and Inner Mongolia. Along with Baekje and Silla, Goguryeo was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. It was an active participant in the power struggle for control of the Korean peninsula and was also associated with the foreign affairs of neighboring polities in China and Japan. The '' Samguk sagi'', a 12th-century text from Goryeo, indicates that Goguryeo was founded in 37 BC by Jumong (), a prince from Buyeo, who was enthroned as Dongmyeong. Goguryeo was one of the great powers in East Asia, until its defeat by a Silla–Tang alliance in 668 after prolonged exhaustion and internal strife caused by the death of Yeon Gaesomun (). After its fall, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady In Waiting
A lady-in-waiting or court lady is a female personal assistant at a court, attending on a royal woman or a high-ranking noblewoman. Historically, in Europe, a lady-in-waiting was often a noblewoman but of lower rank than the woman to whom she attended. Although she may either have received a retainer or may not have received compensation for the service she rendered, a lady-in-waiting was considered more of a secretary, courtier, or companion to her mistress than a servant. In other parts of the world, the lady-in-waiting, often referred to as ''palace woman'', was in practice a servant or a slave rather than a high-ranking woman, but still had about the same tasks, functioning as companion and secretary to her mistress. In courts where polygamy was practised, a court lady was formally available to the monarch for sexual services, and she could become his wife, consort, courtesan, or concubine. ''Lady-in-waiting'' or ''court lady'' is often a generic term for women whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


