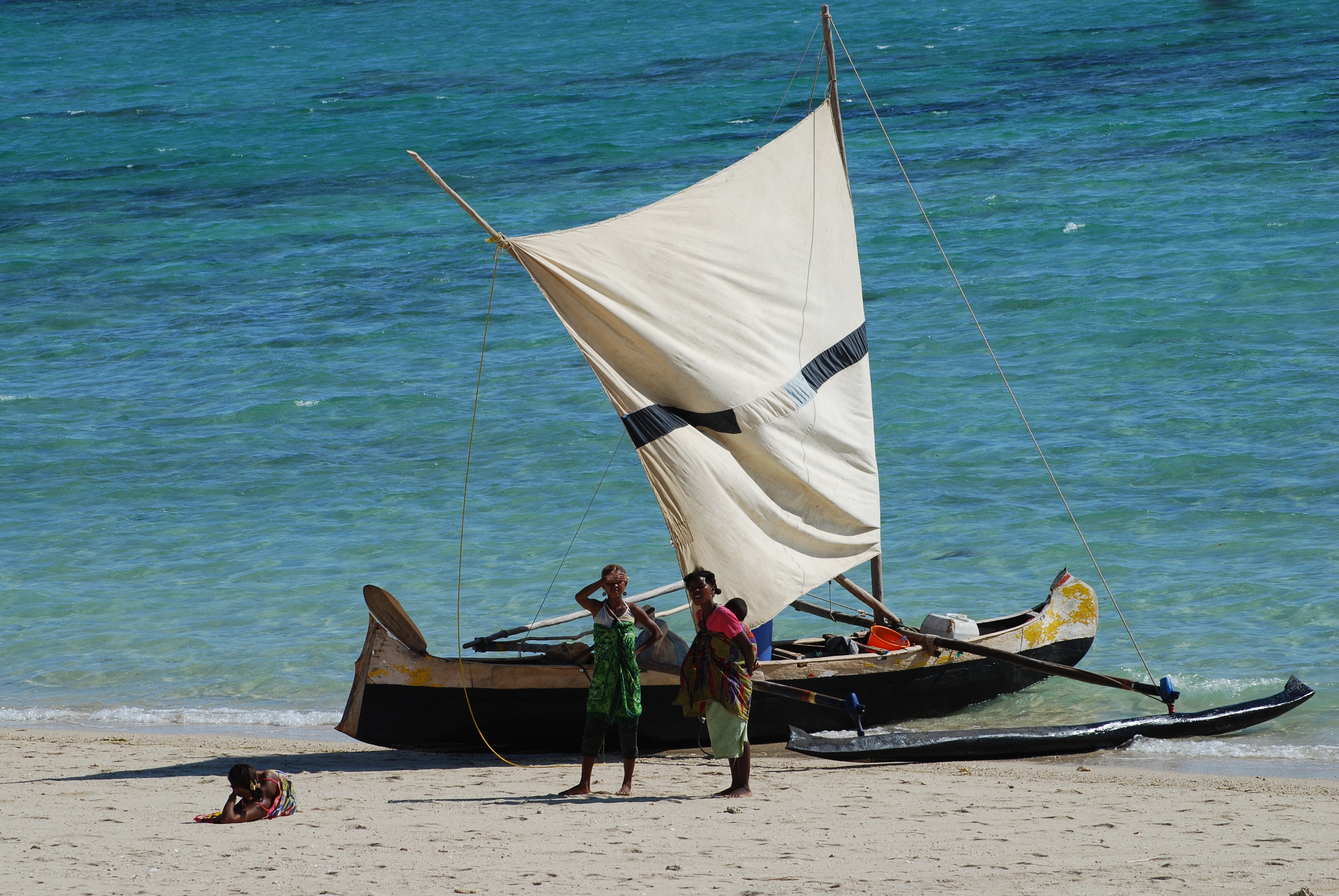|
List Of Multihulls
Types * catamaran = two symmetric hulls * proa = two asymmetric hulls, reverse-shunting (interchangeable bow/stern) * trimaran = three hulls * quadrimaran = four hulls * pentamaran = five hulls Pre-modern Austronesian * ʻalia * Amatasi * Balangay * Basnigan * Baurua * Camakau * Catamaran * Drua * Jukung * Kaep * Kalia * Karakoa * Kora kora * Lakana * Lakatoi * Ngalawa * Oruwa * Outrigger canoe * Pahi * Paraw * Paruwa * Proa * Sandeq * Takia * Tepukei * Tipairua * Tongiaki * Va'a-tele * Vaka katea * Vinta * Wa * Yathra doni Pre-modern Western * ''Tessarakonteres'' and ''Thalamegos'' (3rd century BC) * '' Simon & Jude'' or ''Invention I'' (1662) * ''Invention II'' (1662) * ''Experiment'' (1664) * '' St. Michael the Archangel'' (1684) * ''Experiment'' (1786) * '' Taurus'' (1790s) 19th century *''Jersey'' (1812) *''York'' (1813) *'' Nassau'' (1814) *'' Steam Battery'' (1815) *'' Double Trouble'' (1820) *'' Castaliâ'' (1874) *'' Amaryllis'' (1876) *'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-stabilized craft, deriving its stability from its wide beam, rather than from a ballasted keel as with a monohull boat. Catamarans typically have less hull volume, smaller displacement, and shallower draft (draught) than monohulls of comparable length. The two hulls combined also often have a smaller hydrodynamic resistance than comparable monohulls, requiring less propulsive power from either sails or motors. The catamaran's wider stance on the water can reduce both heeling and wave-induced motion, as compared with a monohull, and can give reduced wakes. Catamarans were invented by the Austronesian peoples which enabled their expansion to the islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Catamarans range in size from small sailing or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaep
Kaep is a traditional type of double-ended Proa sailboat native to Palau. Some of the essential design elements have also been adopted as a modern smaller multihull prototype variant. Larger context The Pacific Ocean and particularly Micronesia gave birth to many different forms of simple sailing craft. Sail plan and hull form differ. Sail plans may include lateen, also known as crab-claw or half-crab-claw, Latin, or triangular. Hull formats include catamarans, doubles, proa, and singles. Presence of a beam spanning a double hull is optional. Likewise, hull end forms and shapes vary greatly. Masts for these type of sailboats can be made with one or two poles. The vessels may be made by hollowing out tree trunks, or may be assembled from planking. Other design considerations include the intended use of the vessel, for fishing, sea voyages or war, and whether they are to be used in sheltered lagoons or in the open sea. Additionally, there is an important and fundamental div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandeq
A Sandeq is a type of outrigger sailboat or trimaran used by the Mandarese people for fishing and as a means of transportation between islands. The size of Sandeq varies, with hulls ranging from long and wide. Its carrying capacity ranges from a few hundred kilograms to over 2 tons. The sleek shape of the Sandeq makes it more agile and faster than other sailboats. The name of the vessel comes from a word in the Mandar language that means pointy, referring to the bow's shape. This boat is a well-known piece of maritime cultural heritage to the Mandarese people in West Sulawesi, Indonesia. Before the use of outboard motors, the Sandeq was one of the dominant means travelling between islands of the archipelago, not only because of its smoothness and speed, but also thanks to its ability to sail close-hauled almost directly against the direction of the wind. The zig-zag technique called beating in English is called ''Makkarakkayi'' in the Mandar language. Although Mandarese seaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proa
Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the double-ended single-outrigger boats of Oceania, the double-outrigger boats of Island Southeast Asia, and sometimes ships with no outriggers or sails at all. In its most common usage, the term ''proa'' refers to the Pacific proas which consist of two (usually) unequal-length parallel hulls. It is sailed so that one hull is kept to windward, and the other to leeward. It is double-ended, since it needs to " shunt" to reverse direction when tacking. It is most famously used for the '' sakman'' ships of the Chamorro people of the Northern Marianas, which were known as the "flying proas" for their remarkable speed. In Island Southeast Asia, the term ''proa'' may also sometimes be used, but the terms perahu, prau, prahu, paraw and prow are mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double Outrigger canoe, outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term ''bangka (boat), bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing canoes to large merchant lashed-lug plank boats (''balangay'' or ''baloto'') with two outriggers (''katig'') propelled by sails (usually a large crab-claw sail opposite a smaller triangular foresail) Etymology The word ''paraw'' (also spelled ''parao'') is a cognate of the terms ''proa'' of the Pacific Islands, and ''perahu'' or ''prau'' of Malay Indonesians, Malay-Indonesia. It refers to outrigger boats propelled by sails (''layag''). It is a type of ''bangka (boat), bangka'', the wider term used for boats (with or without outriggers) in the Philippines. Characteristics The paraw has three major elements that make it a paraw: the ''bangka'' (canoe or main hull), the ''katig'' (outriggers), and the ''layag'' (sails). Motorized versions of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pahi (ship)
Pahi were the traditional double-hulled sailing watercraft of Tahiti. They were large, two masted, and rigged with crab claw sail The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isl ...s. References Multihulls Sailing ships Tahiti {{ship-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outrigger Canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger boats can also vary in their configuration, from the ancestral double-hull configuration ( catamarans), to single-outrigger vessels prevalent in the Pacific Islands and Madagascar, to the double-outrigger vessels ( trimarans) prevalent in Island Southeast Asia. They are traditionally fitted with Austronesian sails, like the crab claw sails and tanja sails, but in modern times are often fitted with petrol engines. Unlike a single-hulled vessel, an outrigger or double-hull vessel generates stability as a result of the distance between its hulls rather than due to the shape of each individual hull. As such, the hulls of outrigger or double-hull boats are typically longer, narrower and more hydrodynamically efficient than those of single-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngalawa
The ngalawa or ungalawa is a traditional, double-outrigger canoe of the Swahili people living in Zanzibar and the Tanzanian coast. It is usually 5–6 m long and has two outriggers, a centrally-placed mast (often inclining slightly towards the prow) and a single triangular sail. It is used for short-distance transport of goods or people, as well as a coastal fishing boat. It can be classified as a variation of another common type of Swahili canoe known as '. The name and the outrigger technology was adapted from the outrigger ''lakana'' of the Austronesian Malagasy people of Madagascar. See also *Outrigger canoe *Trimaran A trimaran (or double-outrigger) is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or "floats") which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recrea ... References Sailboat types Outrigger canoes Indigenous boats Swahili culture {{swahili-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakatoi
Lakatoi (also Lagatoi) are double-hulled sailing watercraft of Papua New Guinea. They are named in the Motu language and traditionally used in the Hiri trade cycle. Gallery File:Picturesque New Guinea Plate V (a) - Loading Lakatoi, Port Moresby.jpg, Loading a ''lakatoi'' at Port Moresby, prior to 1885. File:Picturesque New Guinea Plate VII (a) - Lakatoi, Near Elevala Island.jpg, ''Lakatoi'' near Elevala Island, prior to 1885. File:PSM V52 D045 Papuan lake dwellings with a lakatoi under sail.jpg, Papuan lake dwellings with a ''lakatoi'' under sail, 1898 or before. File:Papua Lakatoi 2s 6d stamp with POSTAGIE variety.jpg, 1901 stamp by the British Government depicting a ''lakatoi''. See also *Crab claw sail The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isl ... References M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakana (boat)
''Lakana'', also known as ''la'kana'' or ''laka'', are traditional outrigger canoes of the Malagasy people of Madagascar. It is a single-outrigger canoe with a dugout main hull. It was traditionally rigged with the Austronesian crab claw sail, but most modern ''lakana'' are equipped with motor engines. The boat is often referred to by the general French term "pirogue", which can include boats with no outriggers. The technology was adapted in neighboring East Africa, like the Tanzanian '' ngalawa'' and the Fulani '' laana''. These are made from ''Farafatsy wood'' ('' Givotia madagascariensis'' (Euphorbiaceae)). Its outrigger is of ''Mafaiboha'' wood ('' Commiphora mafaidoha'' (Burseraceae)) though locals prefer the ''Hazomalany wood'' ('' Hazomalania voyronii'' of the family of Hernandiaceae). See also * Jukung *Proa *Va'a Vaʻa is a word in Samoan, Hawaiian and Tahitian which means 'boat', 'canoe' or 'ship'. A larger traditional seagoing vessel for long-distance voyages i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)