|
List Of Monitors Of The Second World War
A monitor is a class of relatively small warship that is lightly armoured, often provided with disproportionately large guns, and originally designed for coastal warfare. The term "monitor" grew to include breastwork monitors, the largest class of riverine warcraft known as river monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term "monitor" included shallow-draft armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns that fired the heaviest shells ever used at sea and saw action against German targets during World War I. Two small Royal Navy monitors from the First World War, and survived to fight in the Second World War. When the requirement for shore support and strong shallow-water coastal defence returned, new monitors and variants such as coastal defence ships were built (e.g. the British s). Allied monitors saw service in the Mediterranean in support of the British Eighth Army' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship which is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine warcraft, known as river monitors. During the Vietnam War these much sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
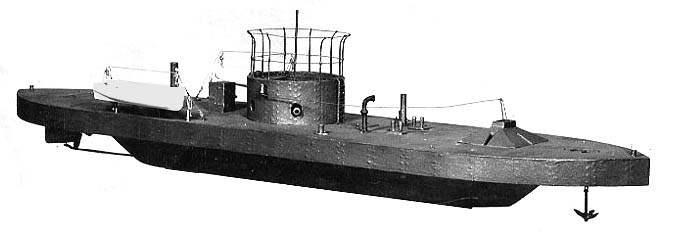
Brătianu-class River Monitor
The ''Brătianu''-class river monitors were a class of four river monitors used by the Romanian Navy. They were named ''Ion C. Brătianu'', ''Lascăr Catargiu'', ''Mihail Kogălniceanu'' and ''Alexandru Lahovari''. Design and construction The class was based on similar Austro-Hungarian river monitors, such as the ''Körös'' and '' Temes'' classes. The Romanian warships were larger and had a main armament of three 120 mm naval guns in individual turrets, two 120 mm howitzers, four QF guns of 47 mm and two 6.5 mm machine guns. Armor thickness reached 70–75 mm around the belt, turrets and conning tower, 60 mm at the bulkheads and down to only 20 mm over some portions of the deck. The four warships were built by STT in Austria-Hungary in sections, transported to Romania by rail then assembled and launched at the Galați shipyard in Romania between 1907 and 1908. Operational service World War I During the Romanian Campaign of the First World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Monitor Faà Di Bruno
''Faà di Bruno'' was an Italian monitor built during World War I. Completed in 1917, the ship played a small role in the 11th Battle of the Isonzo later that year. She was decommissioned in 1924, but returned to service as the floating battery ''GM 194'' at the beginning of World War II and was towed to Genoa and where she spent the rest of the war. The ship had her guns disabled when the Royal Navy bombarded Genoa in 1941. ''GM 194'' was captured by the Germans after the Italian Armistice in 1943 and was turned over to the puppet (Italian Social Republic) that they installed afterward. She was scuttled at the end of the war and subsequently scrapped. Development and description ''Faà di Bruno'' was built when 40-caliber Cannone navale da 381/40 guns from the s became available after their construction was suspended in 1916. Her guns were built by Ansaldo-Schneider and originally destined for the ''Cristoforo Colombo''. She displaced , with a length between perpendiculars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Monitor Flyagin
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including: *Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and people of Russia, regardless of ethnicity *Russophone, Russian-speaking person (, ''russkogovoryashchy'', ''russkoyazychny'') *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *Russian alphabet *Russian cuisine *Russian culture *Russian studies Russian may also refer to: *Russian dressing *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith *Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series *Russian (solitaire), a card game * "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album '' '' by Caravan Palace *Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 *The South African name for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erebus Class Monitor
The ''Erebus'' class of warships was a class of 20th century Royal Navy monitors armed with a main battery of two 15-inch /42 Mk 1 guns in a single turret. It consisted of two vessels, '' ''Erebus'''' and '' ''Terror'''', named after the two ships lost in the Franklin Expedition. Both were launched in 1916 and saw active service in World War I off the Belgian coast. After being placed in reserve between the wars, they served in World War II, with ''Terror'' being lost in 1941 and ''Erebus'' surviving to be scrapped in 1946. Ships * ''Erebus'' was built by Harland and Wolff, Govan. She was laid down on 12 October 1915, launched on 19 June 1916 and commissioned in September 1916. After seeing service in both World Wars, ''Erebus'' was scrapped in 1946. * ''Terror'' was built by Harland and Wolff, Belfast. She was laid down on 26 October 1915, launched on 18 May 1916 and commissioned in August 1916. She saw extensive service in both World Wars. In the Second World War ''Terro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Erebus (I02)
HMS ''Erebus'' was a First World War Monitor warship type, monitor launched on 19 June 1916 and which served in both world wars. She and her sister ship are known as the . They were named after the two bomb vessels sent to investigate the Northwest Passage as part of Franklin's lost expedition (1845–1848), in which all 129 members eventually perished. Monitors were designed as stable gun platforms with a shallow Draft (hull), draught to allow operations close inshore in support of land operations, and were not intended to contest naval battles. ''Erebus'' was equipped with two 15 inch /42 (38.1 cm) Mark I naval gun, /42 guns (removed from ) in a single forward turret mounted on a tall barbette to extend the range of fire to . The ''Erebus'' class were designed to outrange German heavy shore batteries and they were also fitted with highly effective anti-torpedo bulges on each side of the Hull (watercraft), hull. Background During the First World War, the Royal Navy developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
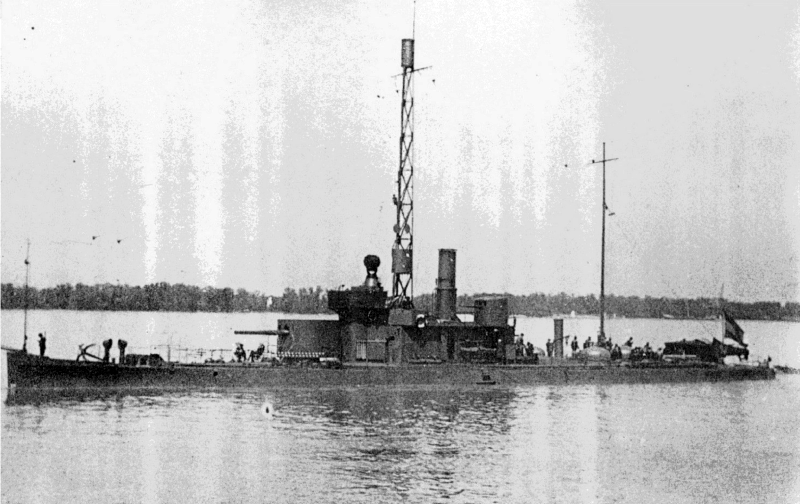
Enns-class River Monitor
The ''Enns''-class river monitors were built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy during the mid-1910s. The two ships of the class were assigned to the Danube Flotilla and participated in World War I. The ships survived the war and were transferred to Romania and the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later Yugoslavia) as reparations. Description and construction The ships had an overall length of , a beam of , and a normal draught of . They displaced , and their crew consisted of 95 officers and enlisted men. The ''Enns''-class ships were powered by two triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one shaft, using steam generated by two Yarrow boilers. The engines were rated at and were designed to reach a top speed of . They carried of fuel oil. The main armament of the ''Enns''-class river monitors was a pair of /L45 guns in a single turret forward of the conning tower and three /L10 howitzers to the rear, in individual armored cupolas. They also mounted two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav Monitor Drava
The Yugoslav monitor ''Drava'' was a river monitor operated by the Royal Yugoslav Navy between 1921 and 1941. She was originally built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy as the name ship of the ''Enns''-class river monitors. As SMS ''Enns'', she was part of the Danube Flotilla during World War I, and fought against the Serbian and Romanian armies from Belgrade to the lower Danube. In October 1915, she was covering an amphibious assault on Belgrade when she was holed below the waterline by a direct hit, and had to be towed to Budapest for repairs. After brief service with the Hungarian People's Republic at the end of the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later Yugoslavia), and renamed ''Drava''. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, but was not always in full commission due to budget restrictions. During the German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia in April 1941, ''Drava'' spent six days shelling airfields near Mohá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Training Ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classrooms. The hands-on aspect provided by sail training has also been used as a platform for everything from semesters at sea for undergraduate oceanography and biology students, marine science and physical science for high school students, to character building for at-risk youths. Notable training ships Royal Navy * * * * * * * ''Cornwall'' * * * * * * '' Indefatigable'' * , including adjacent * * * * ''Mount Edgcumbe'' * * * '' Warspite'' (1877) * '' Warspite'' (1922) * * '' Wellesley'' * Other navies * Algerian Navy ** '' El-Mellah'' * Argentine Navy ** ** * Bangladesh Navy ** BNS ''Shaheed Ruhul Amin'' * Brazilian Navy ** ''Cisne Branco'' * Bulgarian Navy ** * Royal Canadian Navy ** (sail training) ** HMCS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M15-class Monitor
The ''M15'' class comprised fourteen monitors of the Royal Navy, all built and launched during 1915. Design The ships of this class were ordered in March, 1915, as part of the Emergency War Programme of ship construction. They were designed to use the 9.2 inch Mk VI gun turrets removed from the and the Mk X turrets held in stock for the and s. This resulted in the first four of the class, which were built by William Gray & Company of Hartlepool, receiving the Mk X mounting. The remaining ten ships, all built by Sir Raylton Dixon & Co., Middlesbrough, all received the Mk VI mounting. During September 1915, the 9.2 inch guns of HMS ''M24'', ''M25'', ''M26'' and ''M27'' were removed for use as artillery. These were replaced by 7.5-inch guns. ''M24'' and ''M25'' received the spare guns reserved for the recently sunk pre-dreadnought battleship , ''M26'' received one of ''Swiftsure''s spare guns. ''M27'' received 6-inch (M27) guns. ''M21'' and ''M23'' also had their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M23
HMS ''M23'' was a First World War Royal Navy ''M15''-class monitor. After service in the Mediterranean and the Dover Patrol, she was also served in the British intervention in Russia in 1919. Converted to the RNVR drillship ''Claverhouse'' in 1922, she served in that capacity at "Leith" until 1958. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M23''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk VI gun removed from the HMS ''Grafton''. In addition to her 9.2-inch gun, she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with a four-shaft Bolinder four-cylinder semi-diesel engine with 640 horsepower that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty-nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M23'' ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the Sir Raylton Dixon & Co. Ltd shipyard at Govan in March 1915, launched on 17 June 1915, and completed in July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czechoslovakia , life_span = 1918–19391945–1992 , p1 = Austria-Hungary , image_p1 = , s1 = Czech Republic , flag_s1 = Flag of the Czech Republic.svg , s2 = Slovakia , flag_s2 = Flag of Slovakia.svg , image_flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia.svg , flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia , flag_type = Flag(1920–1992) , flag_border = Flag of Czechoslovakia , image_coat = Middle coat of arms of Czechoslovakia.svg , symbol_type = Middle coat of arms(1918–1938 and 1945–1961) , image_map = Czechoslovakia location map.svg , image_map_caption = Czechoslovakia during the interwar period and the Cold War , national_motto = , anthems = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)