|
List Of Equations
This is a list of equations, by Wikipedia page under appropriate bands of maths, science and engineering. Eponymous equations Mathematics * Cauchy–Riemann equations * Chapman–Kolmogorov equation * Maurer–Cartan equation * Pell's equation * Poisson's equation * Riccati equation * sine-Gordon equation * Verhulst equation Physics * Ampère's circuital law * Bernoulli's equation * Bogoliubov–Born–Green–Kirkwood–Yvon hierarchy of equations * Bessel's differential equation * Boltzmann equation * Borda–Carnot equation * Burgers' equation * Darcy–Weisbach equation * Dirac equation ** Dirac equation in the algebra of physical space * Dirac–Kähler equation * Doppler equations * Drake equation (aka Green Bank equation) * Einstein's field equations * Euler equations (fluid dynamics) * Euler's equations (rigid body dynamics) * Relativistic Euler equations * Euler–Lagrange equation * Faraday's law of induction * Fokker–Planck equation * Fresnel equatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Equation
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin- massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. It was validated by accounting for the fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum in a completely rigorous way. The equation also implied the existence of a new form of matter, ''antimatter'', previously unsuspected and unobserved and which was experimentally confirmed several years later. It also provided a ''theoretical'' justification for the introduction of several component wave functions in Pauli's phenomenological theory of spin. The wave functions in the Dirac theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Equations
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, even though no one realized that the "vibrations" of the wave were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index ''n''1 and a second medium with refractive index ''n''2, both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
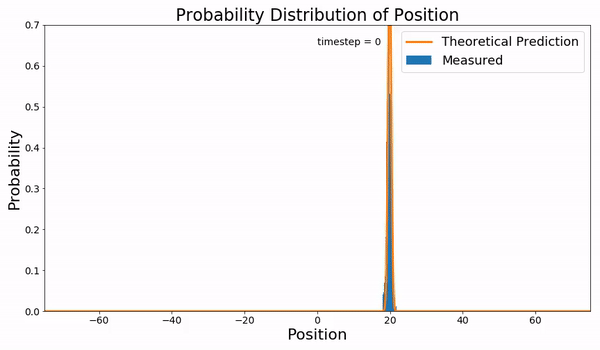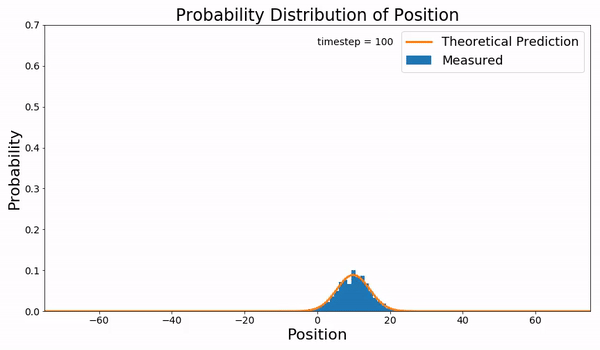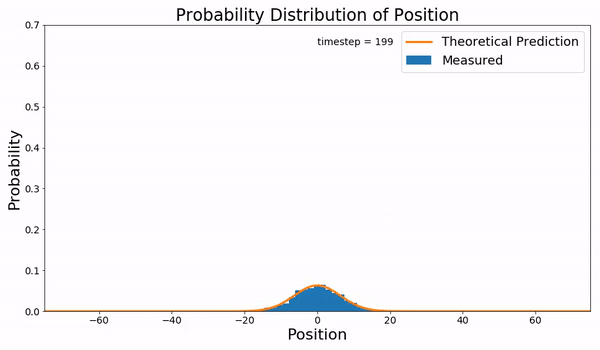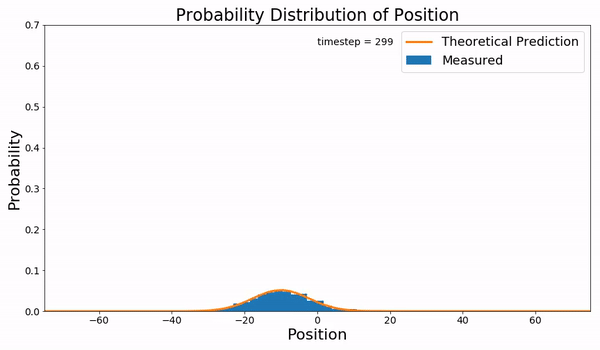
Fokker–Planck Equation
In statistical mechanics, the Fokker–Planck equation is a partial differential equation that describes the time evolution of the probability density function of the velocity of a particle under the influence of drag forces and random forces, as in Brownian motion. The equation can be generalized to other observables as well. It is named after Adriaan Fokker and Max Planck, who described it in 1914 and 1917. It is also known as the Kolmogorov forward equation, after Andrey Kolmogorov, who independently discovered it in 1931. When applied to particle position distributions, it is better known as the Smoluchowski equation (after Marian Smoluchowski), and in this context it is equivalent to the convection–diffusion equation. The case with zero diffusion is the continuity equation. The Fokker–Planck equation is obtained from the master equation through Kramers–Moyal expansion. The first consistent microscopic derivation of the Fokker–Planck equation in the single schem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday's Law Of Induction
Faraday's law of induction (briefly, Faraday's law) is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf)—a phenomenon known as electromagnetic induction. It is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors, generators and solenoids. The Maxwell–Faraday equation (listed as one of Maxwell's equations) describes the fact that a spatially varying (and also possibly time-varying, depending on how a magnetic field varies in time) electric field always accompanies a time-varying magnetic field, while Faraday's law states that there is emf (electromotive force, defined as electromagnetic work done on a unit charge when it has traveled one round of a conductive loop) on the conductive loop when the magnetic flux through the surface enclosed by the loop varies in time. Faraday's law had been discovered and one aspect of it (transformer emf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Lagrange Equation
In the calculus of variations and classical mechanics, the Euler–Lagrange equations are a system of second-order ordinary differential equations whose solutions are stationary points of the given action functional. The equations were discovered in the 1750s by Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler and Italian mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange. Because a differentiable functional is stationary at its local extrema, the Euler–Lagrange equation is useful for solving optimization problems in which, given some functional, one seeks the function minimizing or maximizing it. This is analogous to Fermat's theorem in calculus, stating that at any point where a differentiable function attains a local extremum its derivative is zero. In Lagrangian mechanics, according to Hamilton's principle of stationary action, the evolution of a physical system is described by the solutions to the Euler equation for the action of the system. In this context Euler equations are usually called Lagrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relativistic Euler Equations
In fluid mechanics and astrophysics, the relativistic Euler equations are a generalization of the Euler equations that account for the effects of general relativity. They have applications in high-energy astrophysics and numerical relativity, where they are commonly used for describing phenomena such as gamma-ray bursts, accretion phenomena, and neutron stars, often with the addition of a magnetic field. ''Note: for consistency with the literature, this article makes use of natural units, namely the speed of light'' c=1 ''and the Einstein summation convention.'' Motivation For most fluids observable on Earth, traditional fluid mechanics based on Newtonian mechanics is sufficient. However, as the fluid velocity approaches the speed of light or moves through strong gravitational fields, or the pressure approaches the energy density (P\sim\rho), these equations are no longer valid. Such situations occur frequently in astrophysical applications. For example, gamma-ray bursts often fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler's Equations (rigid Body Dynamics)
In classical mechanics, Euler's rotation equations are a vectorial quasilinear first-order ordinary differential equation describing the rotation of a rigid body, using a rotating reference frame with angular velocity ω whose axes are fixed to the body. Their general vector form is : \mathbf \dot + \boldsymbol\omega \times \left( \mathbf \boldsymbol\omega \right) = \mathbf. where ''M'' is the applied torques and ''I'' is the inertia matrix. The vector \boldsymbol\alpha=\dot is the angular acceleration. In orthogonal principal axes of inertia coordinates the equations become : \begin I_1\,\dot_ + (I_3-I_2)\,\omega_2\,\omega_3 &= M_\\ I_2\,\dot_ + (I_1-I_3)\,\omega_3\,\omega_1 &= M_\\ I_3\,\dot_ + (I_2-I_1)\,\omega_1\,\omega_2 &= M_ \end where ''Mk'' are the components of the applied torques, ''Ik'' are the principal moments of inertia and ω''k'' are the components of the angular velocity. Derivation In an inertial frame of reference (subscripted "in"), Euler's second law s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler Equations (fluid Dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, the Euler equations are a set of quasilinear partial differential equations governing adiabatic and inviscid flow. They are named after Leonhard Euler. In particular, they correspond to the Navier–Stokes equations with zero viscosity and zero thermal conductivity. The Euler equations can be applied to incompressible or compressible flow. The incompressible Euler equations consist of Cauchy equations for conservation of mass and balance of momentum, together with the incompressibility condition that the flow velocity is a solenoidal field. The compressible Euler equations consist of equations for conservation of mass, balance of momentum, and balance of energy, together with a suitable constitutive equation for the specific energy density of the fluid. Historically, only the equations of conservation of mass and balance of momentum were derived by Euler. However, fluid dynamics literature often refers to the full set of the compressible Euler equations – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein Field Equations
In the general theory of relativity, the Einstein field equations (EFE; also known as Einstein's equations) relate the geometry of spacetime to the distribution of matter within it. The equations were published by Einstein in 1915 in the form of a tensor equation which related the local ' (expressed by the Einstein tensor) with the local energy, momentum and stress within that spacetime (expressed by the stress–energy tensor). Analogously to the way that electromagnetic fields are related to the distribution of charges and currents via Maxwell's equations, the EFE relate the spacetime geometry to the distribution of mass–energy, momentum and stress, that is, they determine the metric tensor of spacetime for a given arrangement of stress–energy–momentum in the spacetime. The relationship between the metric tensor and the Einstein tensor allows the EFE to be written as a set of nonlinear partial differential equations when used in this way. The solutions of the EFE are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Bank Equation
The Drake equation is a probabilistic argument used to estimate the number of active, communicative extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way Galaxy. The equation was formulated in 1961 by Frank Drake, not for purposes of quantifying the number of civilizations, but as a way to stimulate scientific dialogue at the first scientific meeting on the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). The equation summarizes the main concepts which scientists must contemplate when considering the question of other radio-communicative life. It is more properly thought of as an approximation than as a serious attempt to determine a precise number. Criticism related to the Drake equation focuses not on the equation itself, but on the fact that the estimated values for several of its factors are highly conjectural, the combined multiplicative effect being that the uncertainty associated with any derived value is so large that the equation cannot be used to draw firm conclusions. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
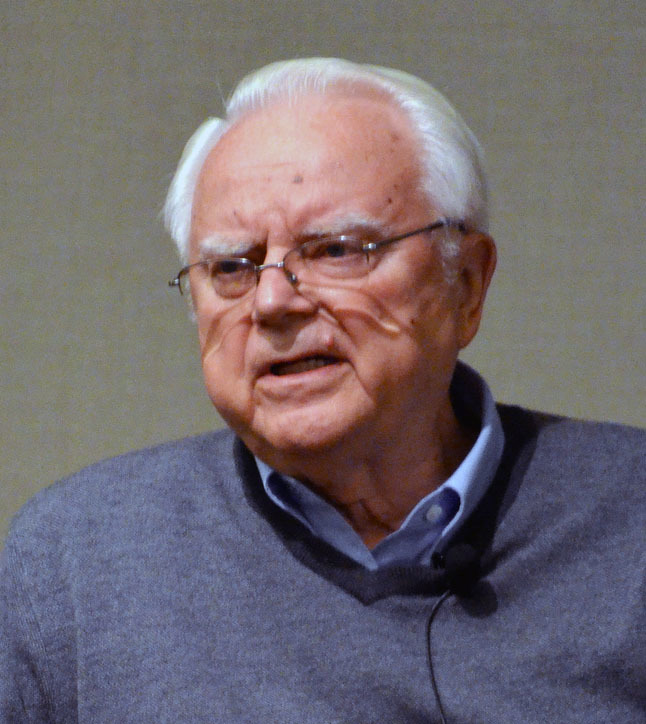
Drake Equation
The Drake equation is a probabilistic argument used to estimate the number of active, communicative extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way Galaxy. The equation was formulated in 1961 by Frank Drake, not for purposes of quantifying the number of civilizations, but as a way to stimulate scientific dialogue at the first scientific meeting on the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). The equation summarizes the main concepts which scientists must contemplate when considering the question of other radio-communicative life. It is more properly thought of as an approximation than as a serious attempt to determine a precise number. Criticism related to the Drake equation focuses not on the equation itself, but on the fact that the estimated values for several of its factors are highly conjectural, the combined multiplicative effect being that the uncertainty associated with any derived value is so large that the equation cannot be used to draw firm conclusions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |