|
List Of Clinically Important Bacteria
This is a list of bacteria that are significant in medicine. It is not intended as an exhaustive list of all bacterial species: that should be at List of bacteria. For viruses, see list of viruses. ____ {{compact ToC, side=yes, top=yes, num=yes A *'' Acetobacter aurantius'' *'' Acinetobacter baumannii'' *'' Actinomyces israelii'' *'' Agrobacterium radiobacter'' *''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' *'' Anaplasma'' **'' Anaplasma phagocytophilum'' *''Azorhizobium caulinodans'' *''Azotobacter vinelandii'' *'' viridans streptococci'' B *'' Bacillus'' **''Bacillus anthracis'' **'' Bacillus brevis'' **'' Bacillus cereus'' **'' Bacillus fusiformis'' **'' Bacillus licheniformis'' **'' Bacillus megaterium'' **'' Bacillus mycoides'' **''Bacillus stearothermophilus'' **'' Bacillus subtilis'' **''Bacillus thuringiensis'' *'' Bacteroides'' **'' Bacteroides fragilis'' **'' Bacteroides gingivalis'' **''Bacteroides melaninogenicus'' (now known as '' Prevotella melaninogenica'') *'' Bartonella'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
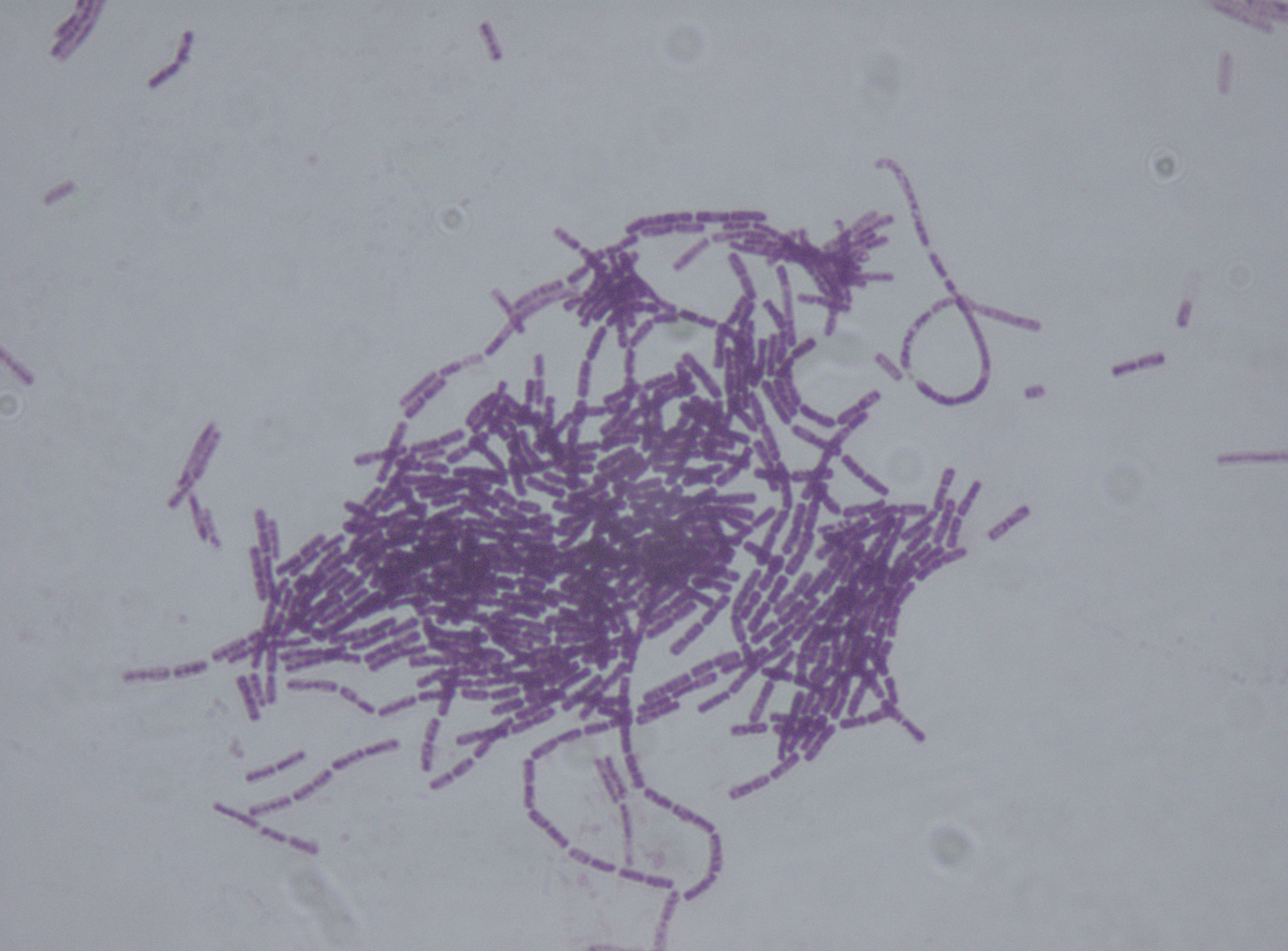
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be anaerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella Henselae
''Bartonella henselae'', formerly ''Rochalimæa henselae'', is a bacterium that is the causative agent of cat-scratch disease ( bartonellosis). ''Bartonella henselae'' is a member of the genus ''Bartonella'', one of the most common types of bacteria in the world. It is a facultative intracellular microbe that targets red blood cells. One study showed it invaded the mature blood cells of humans. It infects the host cell by sticking to it using trimeric autotransporter adhesins. In the United States, about 22,000 people(per year?)are diagnosed, most under the age of 20. Most often, it is transmitted from kittens. Diagnosis ''Bartonella henselae'' is a Gram-negative rod. It can be cultured in a lysis-centrifugation blood culture. The presence of bacteria can be detected by Warthin-Starry stain, or by a similar silver stain technique performed on infected tissue. The specific name ''henselae'' honors Diane Marie Hensel (b. 1953), a clinical microbiology technologist at University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella
''Bartonella'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, ''Bartonella'' species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. ''Bartonella'' species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight ''Bartonella'' species or subspecies are known to infect humans. ''Bartonella henselae'' is the organism responsible for cat scratch disease. History ''Bartonella'' species have been infecting humans for thousands of years, as demonstrated by ''Bartonella quintana'' DNA in a 4000-year-old tooth. The genus is named for Alberto Leonardo Barton Thompson (1871–October 26, 1950), a Peruvian scientist. Infection cycle The currently accepted model explaining the infection cycle holds that the transmitting vectors are blood-sucking arthropods and the reservoir hosts are mammals. Immediately after infection, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevotella Melaninogenica
''Prevotella melaninogenica'' is a species of bacterium in the normal microbiota of the upper respiratory tract. It is an important human pathogen in various anaerobic infections, often mixed with other aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. ''P. melaninogenica'' is an anaerobic, Gram-negative rod, named for its black colonies, and black pigment. ''P. melaninogenica'' is associated with hypertension together with ''Campylobacter rectus'' and ''Veillonella parvula''. Description ''P. melaninogenica'' are Gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria. They cannot survive in the presence of oxygen. They are not motile, and do not form spores. ''P. melaninogenica'' grow well on blood agar, where they form circular dark-colored colonies that darken over one to two weeks. History ''P. melaninogenica'' was originally described as ''Bacteroides melaninogenicus'' in 1921 by Wade Oliver and William Wherry at the University of Cincinnati as a new bacterium isolated from various sites of several different hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides Gingivalis
''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' belongs to the phylum ''Bacteroidota'' and is a nonmotile, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, anaerobic, pathogenic bacterium. It forms black colonies on blood agar. It is found in the oral cavity, where it is implicated in periodontal disease, as well as in the upper gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory tract and the colon. It has been isolated from women with bacterial vaginosis. Collagen degradation observed in chronic periodontal disease results in part from the collagenase enzymes of this species. It has been shown in an '' in vitro'' study that ''P. gingivalis'' can invade human gingival fibroblasts and can survive in the presence of antibiotics. ''P. gingivalis'' invades gingival epithelial cells in high numbers, in which case both bacteria and epithelial cells survive for extended periods of time. High levels of specific antibodies can be detected in patients harboring ''P. gingivalis''. ''P. gingivalis'' infection has been linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides Fragilis
''Bacteroides fragilis'' is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, pleomorphic to rod-shaped bacterium. It is part of the normal microbiota of the human colon and is generally commensal, but can cause infection if displaced into the bloodstream or surrounding tissue following surgery, disease, or trauma. Habitat ''Bacteroides fragilis'' resides in the human gastrointestinal tract and is essential to healthy gastrointestinal function such as mucosal immunity and host nutrition. As a mesophile, optimal growth occurs at 37 °C and a pH around 7. Morphology Cells of ''B. fragilis'' are rod-shaped to pleomorphic with a cell size range of 0.5-1.5 x 1.0-6.0 μm.''B. fragilis'' is a Gram-negative bacterium and does not possess flagella or cilia making it immotile. However, it does utilize peritrichous fimbriae for adhesion to other molecular structures. ''B. fragilis'' also utilizes a complex series of surface proteins, lipopolysaccharide chains, and outer membrane vesicles to help su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides
''Bacteroides'' is a genus of Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacteria. ''Bacteroides'' species are non endospore-forming bacilli, and may be either motile or nonmotile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40–48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, ''Bacteroides'' membranes contain sphingolipids. They also contain meso-diaminopimelic acid in their peptidoglycan layer. ''Bacteroides'' species are normally mutualistic, making up the most substantial portion of the mammalian gastrointestinal microbiota, where they play a fundamental role in processing of complex molecules to simpler ones in the host intestine. As many as 1010–1011 cells per gram of human feces have been reported. They can use simple sugars when available; however, the main sources of energy for ''Bacteroides'' species in the gut are complex host-derived and plant glycans. Studies indicate that long-term diet is strongly associated with the gut microbiome composition—those who eat plenty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, and renamed ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Stearothermophilus
''Geobacillus stearothermophilus'' (previously ''Bacillus stearothermophilus'') is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive bacterium and a member of the phylum Bacillota. The bacterium is a thermophile and is widely distributed in soil, hot springs, ocean sediment, and is a cause of spoilage in food products. It will grow within a temperature range of 30 to 75 °C. Some strains are capable of oxidizing carbon monoxide aerobically. It is commonly used as a challenge organism for sterilization validation studies and periodic check of sterilization cycles. The biological indicator contains spores of the organism on filter paper inside a vial. After sterilizing, the cap is closed, an ampule of growth medium inside of the vial is crushed and the whole vial is incubated. A color and/or turbidity change indicates the results of the sterilization process; no change indicates that the sterilization conditions were achieved, otherwise the growth of the spores indicates that the sterilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Mycoides
''Bacillus mycoides'' is a bacterium of the genus ''Bacillus''. Like other ''Bacillus'' species, ''B. mycoides'' is Gram positive, rod-shaped, and forms spores. ''B. mycoides'' is distinguished from other ''Bacillus'' species by its unusual growth on agar plates, where it forms expansive hairy colonies with characteristic swirls. Description ''B. mycoides'' are rod-shaped cells about 1 micron across and 3 to 5 microns long. When growing, they either grow as single cells or form loosely connected chains of cells. They are not motile. ''B. mycoides'' can survive with or without oxygen and grows at temperatures ranging from 10 to 15 °C to 35–40 °C. ''B. mycoides'' is distinguished from a number of other ''Bacillus'' species in the unusual morphology of the colonies it forms when grown on agar plates. ''B. mycoides'' forms white opaque colonies that are characteristically hairy in appearance (often referred to as "rhizoid"). These colonies rapidly spread to fill the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |